Interfaces in Java are a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming and are particularly useful in Android development for creating flexible and decoupled architecture.
What is an Interface in Java?
An interface is a reference type in Java, similar to a class, that can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static methods, and nested types. Interfaces are used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance.
public interface OnItemClickListener {
void onItemClick(int position);
}Why Use Interfaces in Android?
- To decouple components (like activities, fragments, or adapters)
- To create custom event listeners
- To make your code reusable and modular
Basic Syntax of Interface in Java
interface SampleInterface {
void doSomething();
}Implementing an Interface in a Class
public class MyClass implements SampleInterface {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
// Implementation here
}
}Android Example: Interface for RecyclerView Click Listener
1. Define the Interface
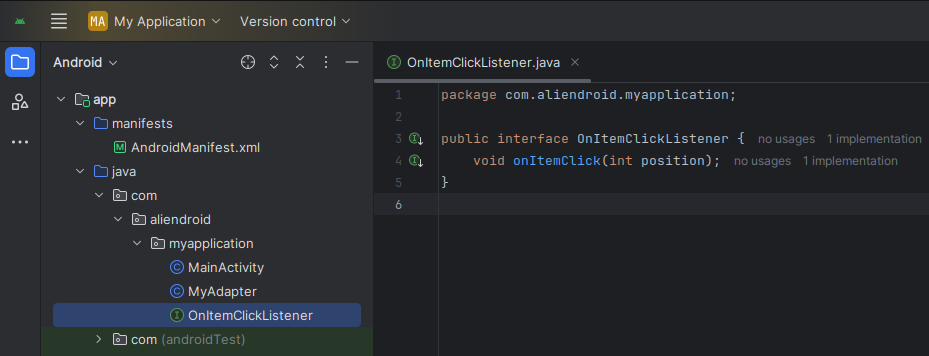
public interface OnItemClickListener {
void onItemClick(int position);
}2. Use in Adapter
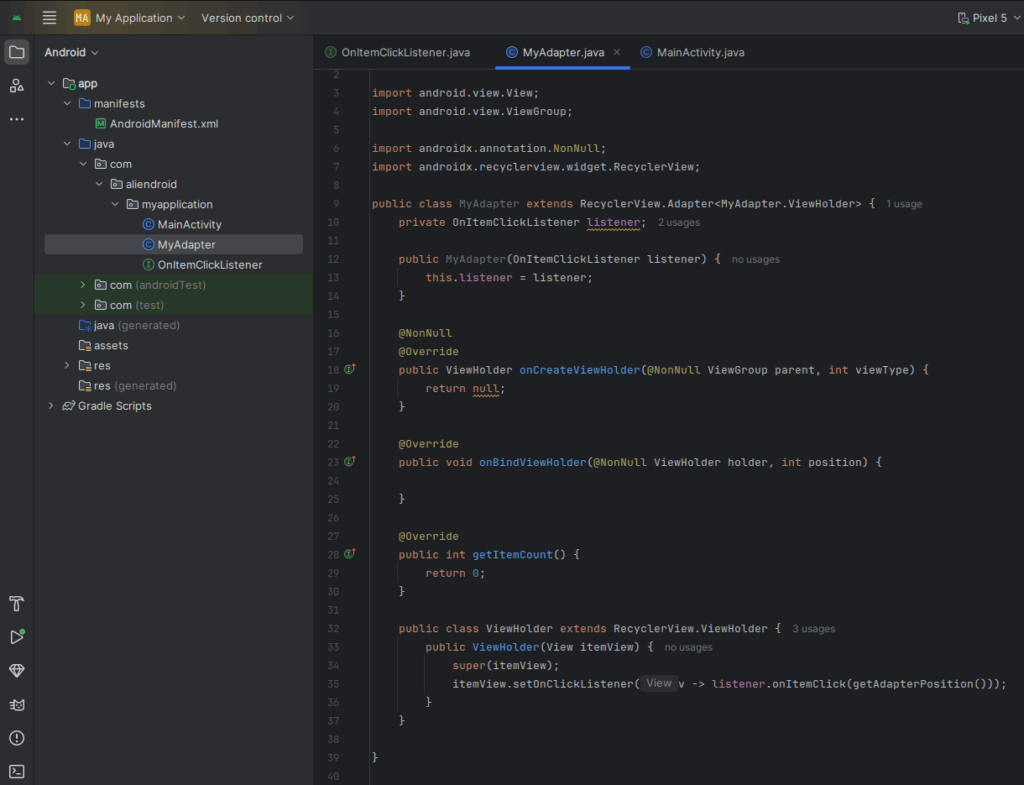
public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.ViewHolder> {
private OnItemClickListener listener;
public MyAdapter(OnItemClickListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) {
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return 0;
}
public class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
public ViewHolder(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
itemView.setOnClickListener(v -> listener.onItemClick(getAdapterPosition()));
}
}
}3. Implement Interface in Activity or Fragment
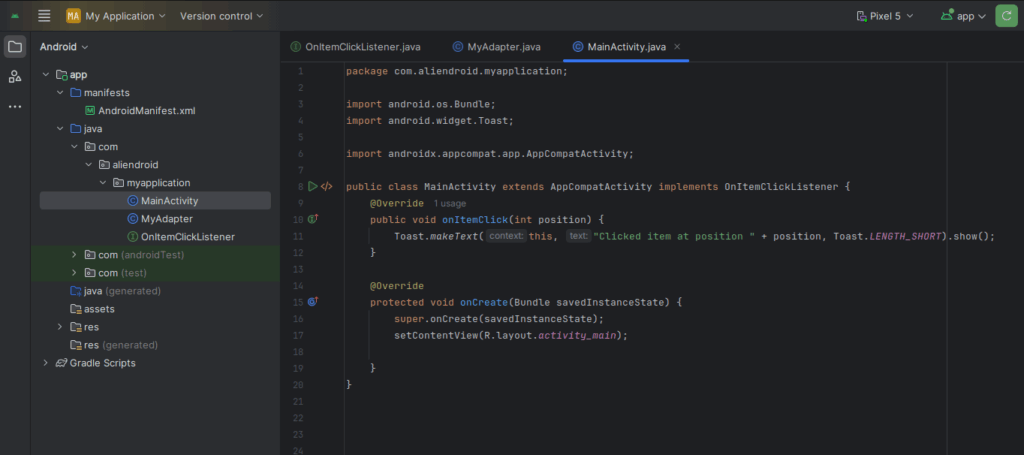
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnItemClickListener {
@Override
public void onItemClick(int position) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Clicked item at position " + position, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}Benefits of Using Interfaces in Android
- Clean and maintainable code
- Easier testing and mocking
- Promotes good architecture (e.g., MVP or MVVM)
Best Practices
- Name interfaces clearly, e.g.,
OnUserClickListener - Keep interface methods short and descriptive
- Avoid defining too many methods in a single interface
- Name interfaces clearly, e.g.,
Conclusion
Using interfaces in Java for Android Studio is a powerful way to write clean, flexible, and maintainable code. By using interfaces, especially for event handling and callbacks, you can create apps that are easy to scale and debug.