Displaying and managing images is a common task in Android app development. Whether you’re showing user profile pictures, product thumbnails, or photo galleries, knowing how to work with images efficiently is essential.
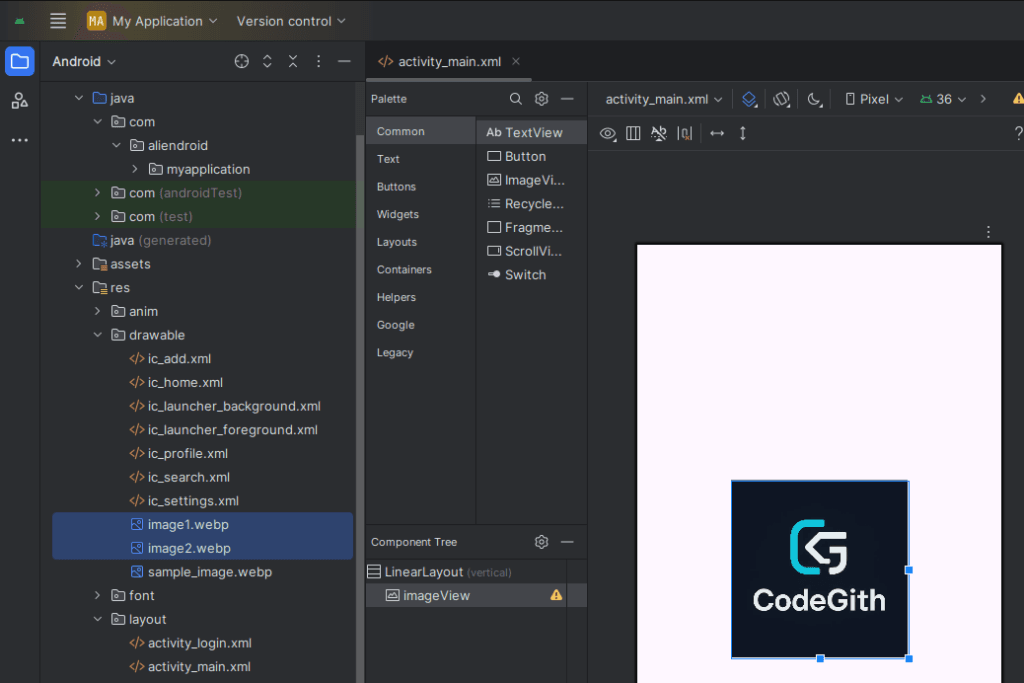
1. Add image to res/drawable
- Right-click on
res > drawable. - Click New > Drawable Resource File or Paste an image (e.g. PNG, JPG).
- Recommended image formats:
.png,.webp,.jpg.
- Right-click on
2. Displaying Images in ImageView
XML Layout
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:src="@drawable/sample_image"
android:scaleType="centerCrop" />Java Code (Activity)
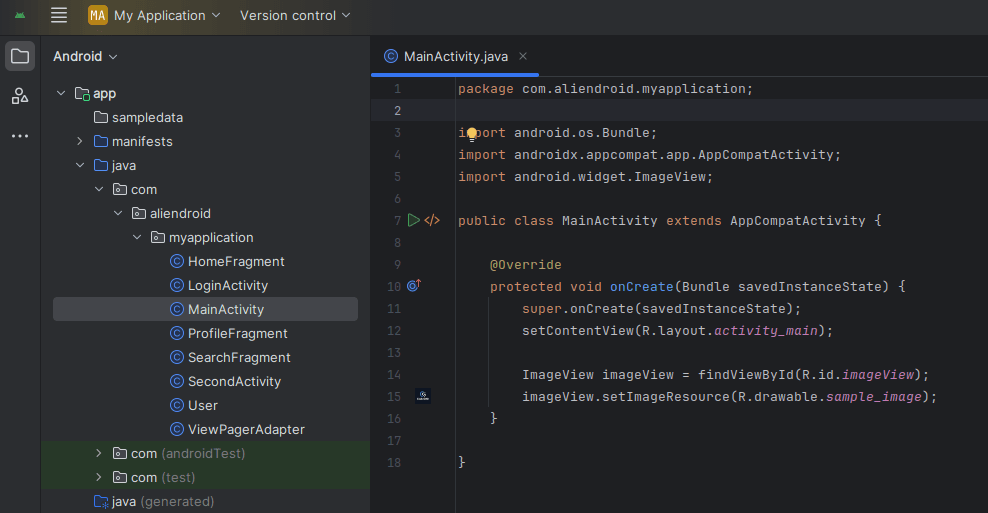
ImageView imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView); imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.sample_image);
4. Loading Images from Storage or URL
From Device Storage
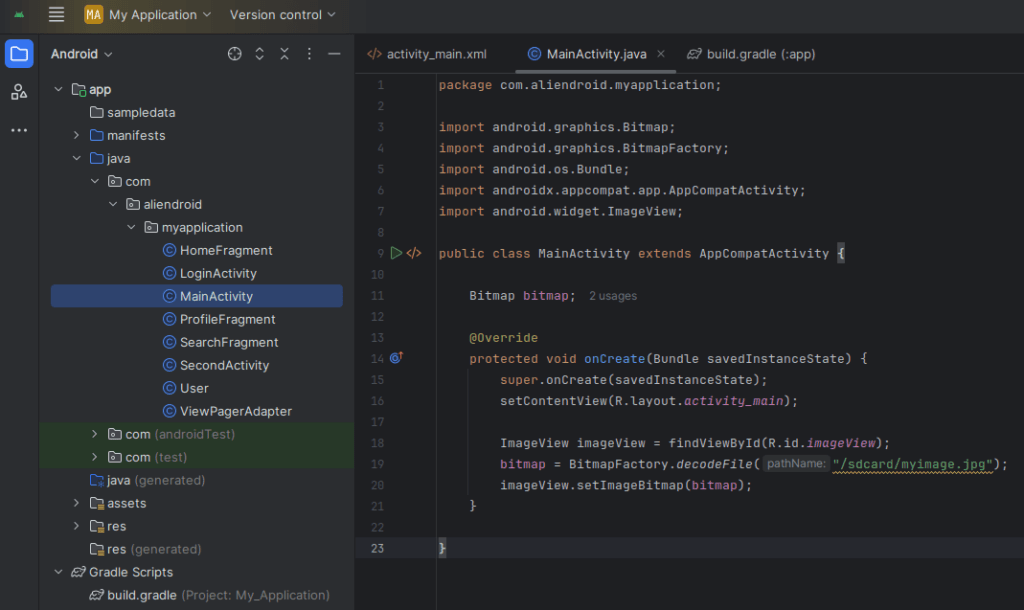
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile("/sdcard/myimage.jpg");
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);From URL (Use Glide or Picasso library)
Add to build.gradle:
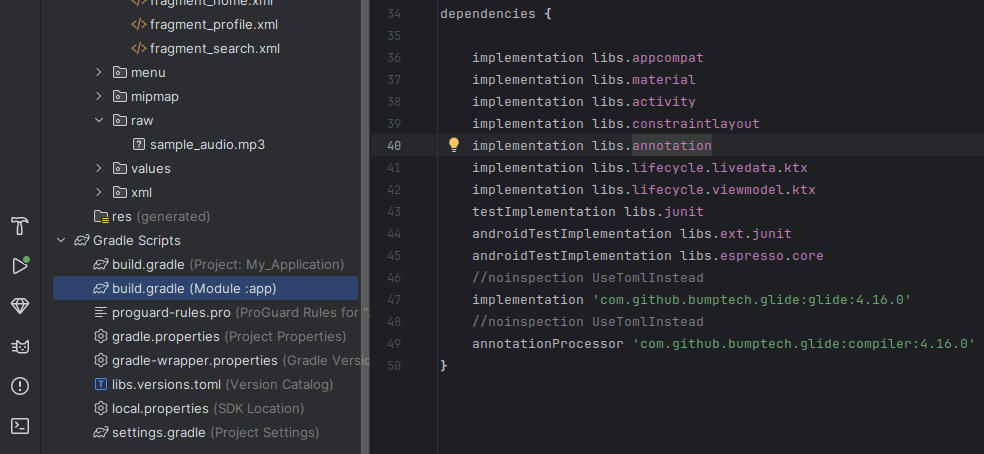
implementation 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.16.0' annotationProcessor 'com.github.bumptech.glide:compiler:4.16.0'
Using Glide:
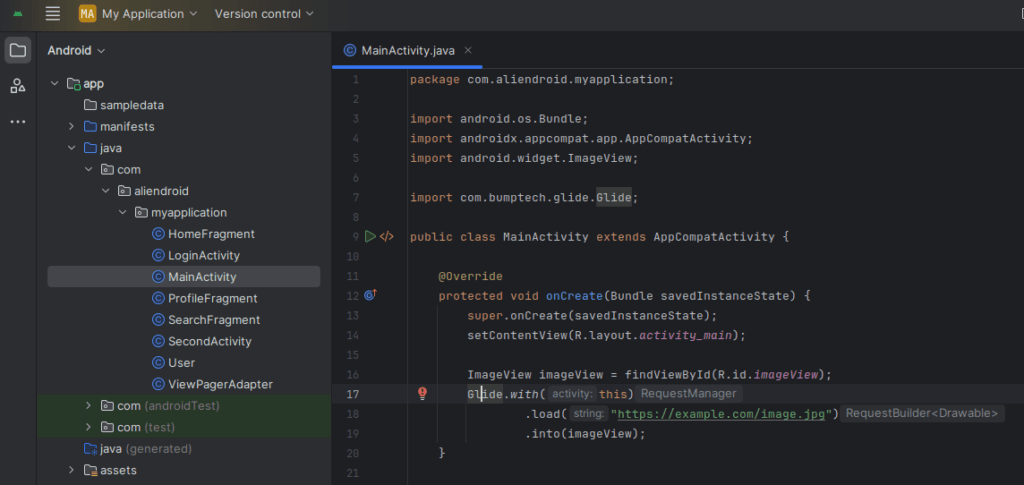
Glide.with(this)
.load("https://example.com/image.jpg")
.into(imageView);5. Managing Image Performance
- Use
WebPformat to reduce image size. - Use
ImageView.setImageBitmap()with care — avoid memory leaks. - Use libraries like Glide or Picasso for efficient caching and memory handling.
- Use
6. Dynamically Change Images
if (userHasProfilePicture) {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.profile);
} else {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.default_avatar);
}7. Clean Up (Avoid Memory Leaks)
If you use Bitmaps:
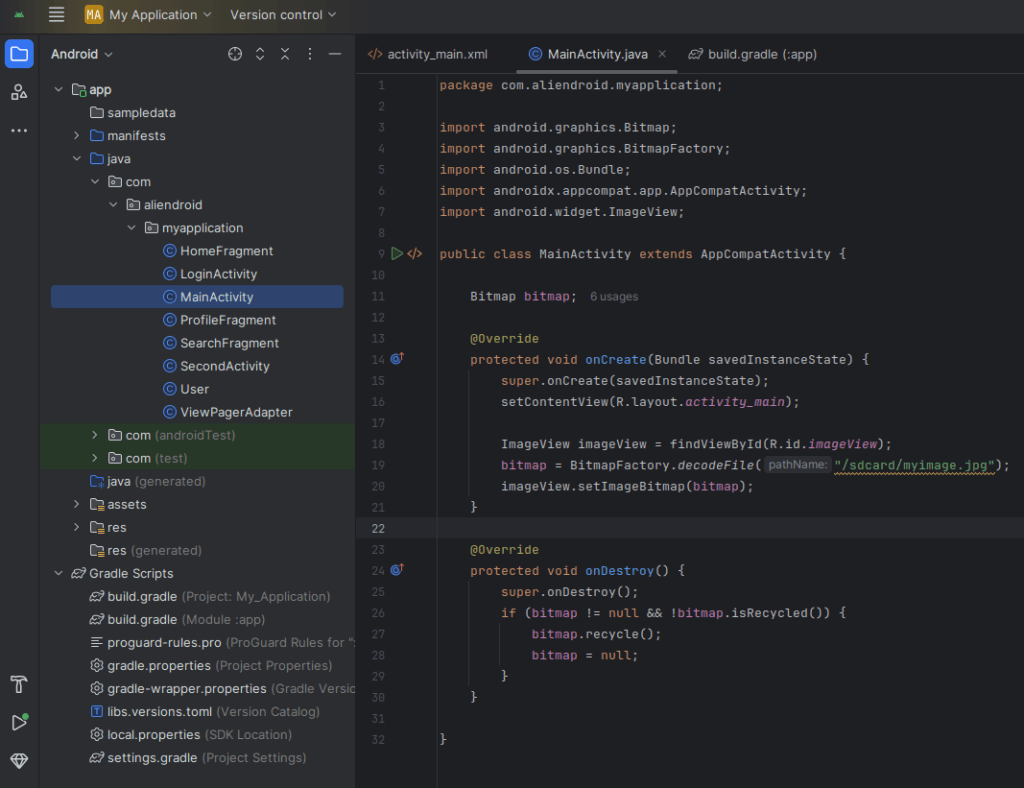
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (bitmap != null && !bitmap.isRecycled()) {
bitmap.recycle();
bitmap = null;
}
}8. Best Practices
- Compress images before adding them.
- Use vector drawables for icons (
.xmlor.svg). - For large image sets, use RecyclerView with ViewHolder.
- Always test image scaling on multiple screen sizes.
Summary
You’ve learned how to:
- Add and display images in XML and Java.
- Load images from storage and URLs.
- Optimize image performance and memory usage.
Tip: Use Glide or Picasso for best results when working with external or large images in real-world apps.