This guide will walk you through the steps to add and play audio files in your Android app using Java in Android Studio.
Prerequisites
- A basic Java Android project created
- An audio file in
.mp3,.ogg, or.wavformat (place it in theres/rawfolder)
Step 1: Add the Audio File
- Create a folder named
rawinside theresdirectory (if it doesn’t exist): - Place your audio file inside the raw folder. For example:
- Create a folder named
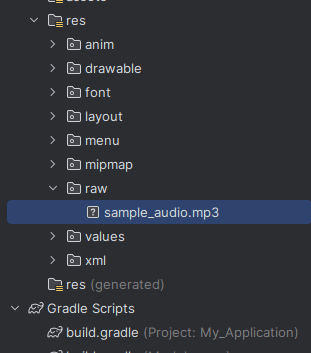
res/raw/sample_audio.mp3
Step 2: Create the UI
Open res/layout/activity_main.xml and add buttons:

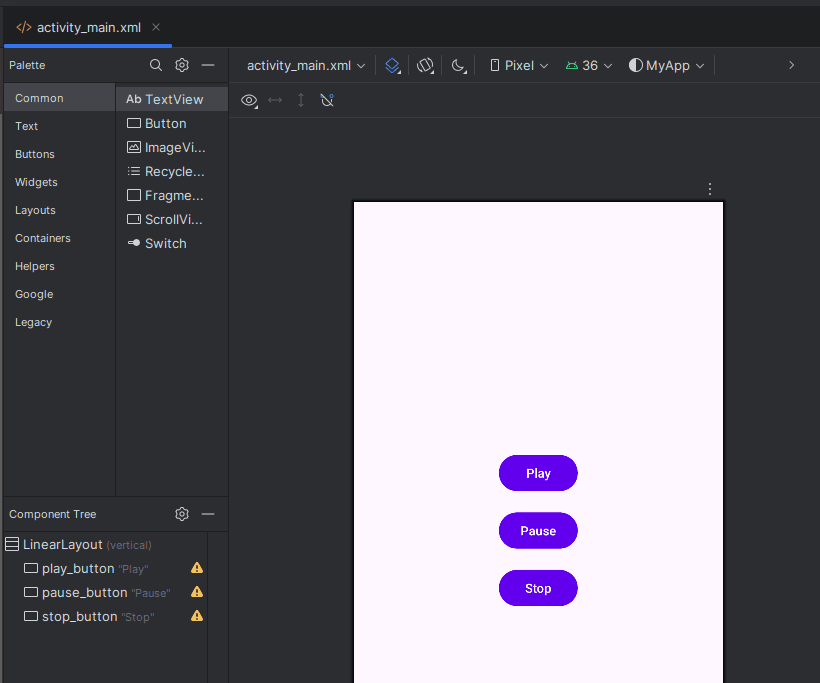
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="24dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/play_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Play" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/pause_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Pause"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/stop_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Stop"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp" />
</LinearLayout>Step 3: Use MediaPlayer in Java
Add this code to your Activity (e.g., MainActivity.java):
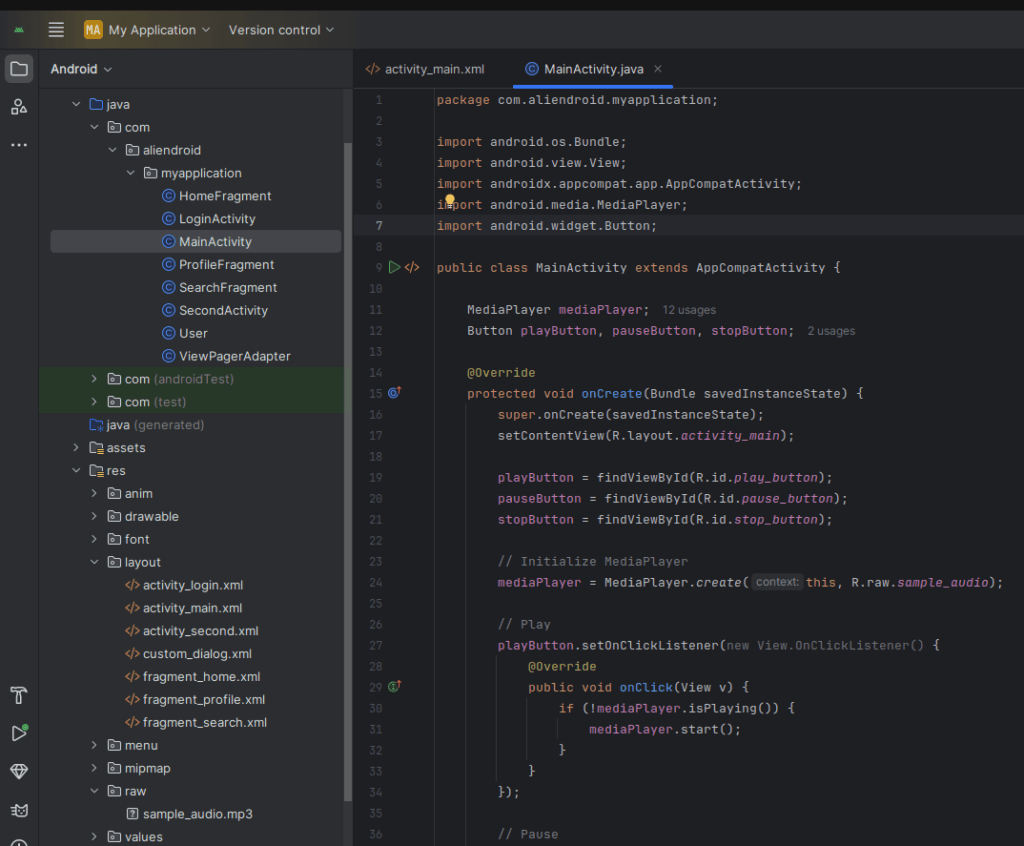
import android.media.MediaPlayer;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
MediaPlayer mediaPlayer;
Button playButton, pauseButton, stopButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
playButton = findViewById(R.id.play_button);
pauseButton = findViewById(R.id.pause_button);
stopButton = findViewById(R.id.stop_button);
// Initialize MediaPlayer
mediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(this, R.raw.sample_audio);
// Play
playButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (!mediaPlayer.isPlaying()) {
mediaPlayer.start();
}
}
});
// Pause
pauseButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (mediaPlayer.isPlaying()) {
mediaPlayer.pause();
}
}
});
// Stop
stopButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (mediaPlayer != null) {
mediaPlayer.stop();
mediaPlayer.release();
mediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(MainActivity.this, R.raw.sample_audio);
}
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
if (mediaPlayer != null) {
mediaPlayer.release();
mediaPlayer = null;
}
super.onDestroy();
}
}Step 4: Test Your App
- Run the app on a real device or emulator.
- Click Play, Pause, or Stop to control the audio playback.
Notes
- Always release
MediaPlayerwhen not needed to avoid memory leaks. - Use audio formats supported by Android (MP3, WAV, OGG).
- You can handle more complex audio features using
ExoPlayer.
- Always release