Dialogs are important components in Android to notify users or collect input. In this guide, you’ll learn how to create two types of dialogs in Java using Android Studio:
- Use Material Components for modern UI
- Don’t block critical UI behind dialogs
- Make dialogs cancelable if needed using
.setCancelable(true)
Conclusion
With AlertDialogs and Custom Dialogs, you can effectively interact with users in your Android app. Whether it’s a simple confirmation or a complex form input, these dialogs help make the user experience smoother and more intuitive.
- AlertDialogs – simple dialogs with buttons.
- Custom Dialogs – fully customizable layouts for complex interactions.
- AlertDialogs – simple dialogs with buttons.
- Custom Dialogs – fully customizable layouts for complex interactions.
1. Creating a Basic AlertDialog
Step-by-Step:
Step 1: Add this code to your Activity (e.g. MainActivity.java)
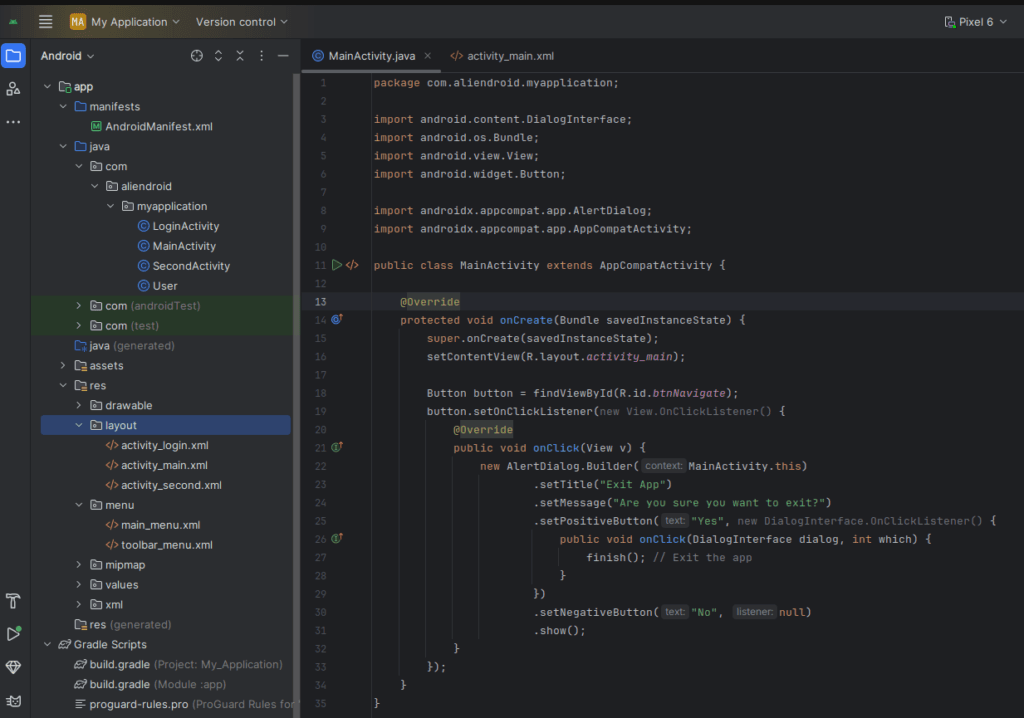
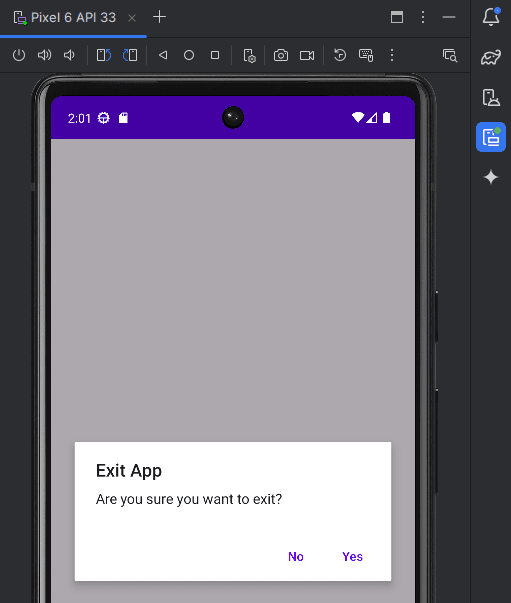
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this)
.setTitle("Exit App")
.setMessage("Are you sure you want to exit?")
.setPositiveButton("Yes", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
finish(); // Exit the app
}
})
.setNegativeButton("No", null)
.show();2. Creating a Custom Dialog
Step-by-Step:
Step 1: Create a layout XML for your custom dialog
res/layout/custom_dialog.xml
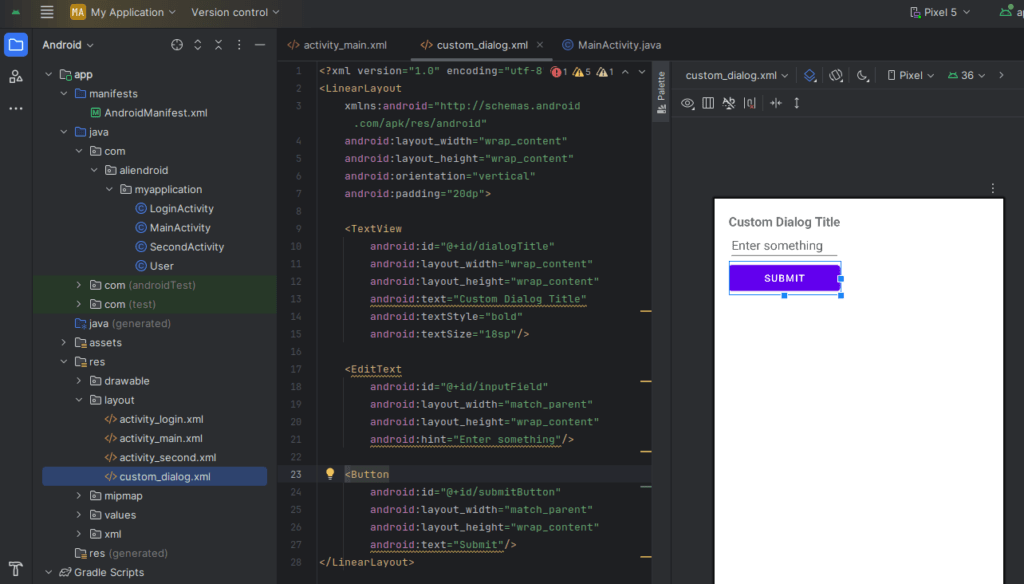
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="20dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/dialogTitle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Custom Dialog Title"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textSize="18sp"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputField"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Enter something"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/submitButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Submit"/>
</LinearLayout>Step 2: Show the dialog in your activity

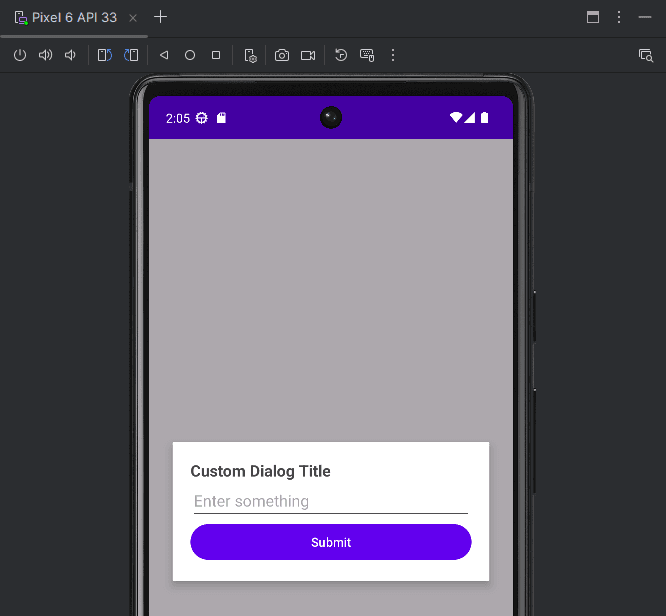
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();
View dialogView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_dialog, null);
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setView(dialogView);
AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
dialog.show();
// Handle button click
Button submitBtn = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.submitButton);
EditText input = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.inputField);
submitBtn.setOnClickListener(v -> {
String text = input.getText().toString();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Input: " + text, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
dialog.dismiss();
});3. Tips for Better Dialog Design
- Use Material Components for modern UI
- Don’t block critical UI behind dialogs
- Make dialogs cancelable if needed using
.setCancelable(true)
Conclusion
With AlertDialogs and Custom Dialogs, you can effectively interact with users in your Android app. Whether it’s a simple confirmation or a complex form input, these dialogs help make the user experience smoother and more intuitive.
- AlertDialogs – simple dialogs with buttons.
- Custom Dialogs – fully customizable layouts for complex interactions.