When developing Android apps using Java in Android Studio, managing collections of data is essential. Java offers two powerful ways to store and manipulate groups of data: Arrays and Lists. This guide will help you understand the differences, when to use each, and how to implement them effectively.
1. What is an Array in Java?
An array is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single type. In Java:
String[] fruits = {"Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"};Key Characteristics:
- Fixed size
- Faster access time
- Index-based
Example Usage in Android:
String[] menuItems = {"Home", "Profile", "Settings"};
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, menuItems);
ListView listView = findViewById(R.id.listView);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
2. What is a List in Java?
A List is part of the Java Collections Framework and is more flexible than an array. The most commonly used implementation is ArrayList.
import java.util.ArrayList;
ArrayList<String> cities = new ArrayList<>();
cities.add("New York");
cities.add("Tokyo");
cities.add("London");Key Characteristics:
- Dynamic size
- Easier to modify (add/remove)
- Provides built-in methods
Example Usage in Android:
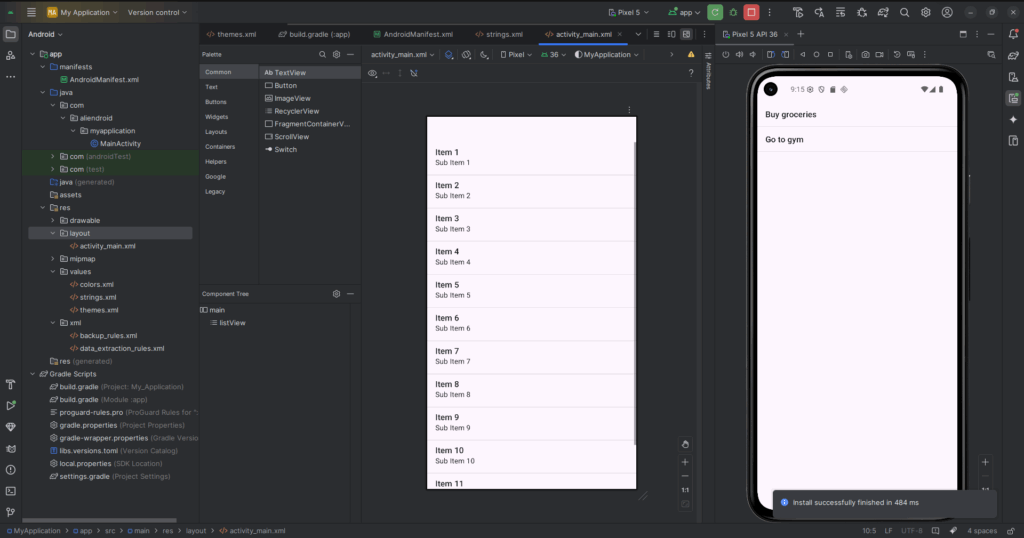
ArrayList<String> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
tasks.add("Buy groceries");
tasks.add("Go to gym");
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, tasks);
ListView listView = findViewById(R.id.listView);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);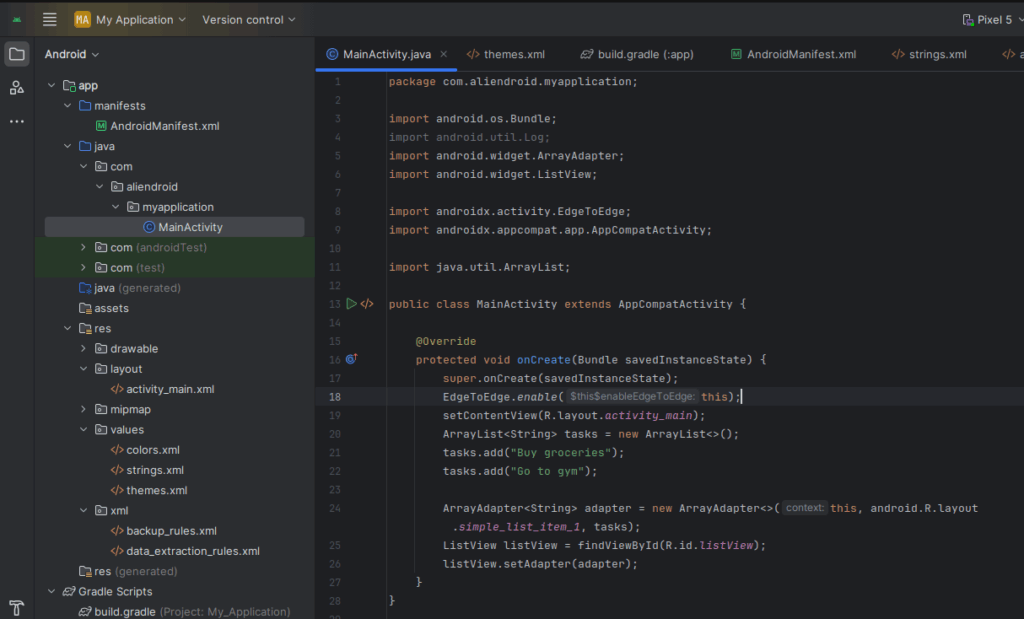
3. Array vs List in Java (Comparison)
| Feature | Array | List (ArrayList) |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Fixed | Dynamic |
| Performance | Fast access | Slightly slower |
| Flexibility | Low | High (add/remove elements) |
| Syntax | Simple | Requires import & methods |
4. When to Use Arrays vs Lists in Android Studio
- Use Arrays when:
- The size of the data is fixed.
- Performance is a priority.
- You’re working with primitive types.
- Use Arrays when:
- Use Lists when:
- The size can change dynamically.
- You need advanced features (e.g., sorting, removing).
- You work with objects in a collection.
- Use Lists when:
5. Bonus: Convert Between Array and List
Convert Array to List:
String[] array = {"One", "Two", "Three"};
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(array);Convert List to Array:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("One");
list.add("Two");
String[] array = list.toArray(new String[0]);Conclusion
Both arrays and lists are essential for managing data in Android app development. While arrays are simple and efficient, lists provide more functionality and flexibility. Understanding when and how to use them can greatly enhance your app’s performance and maintainability.