What is BottomNavigationView?
BottomNavigationView is a part of Android’s Material Components that allows users to quickly switch between top-level views of an app with a bottom menu. It’s especially useful for apps with 3–5 main sections.
Prerequisites
- Android Studio Installed
- Basic knowledge of Java and Android development
Step 1: Add Material Dependency (Optional)
Open your build.gradle (Module: app) and add:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.12.0'
}Step 2: Add BottomNavigationView in activity_main.xml
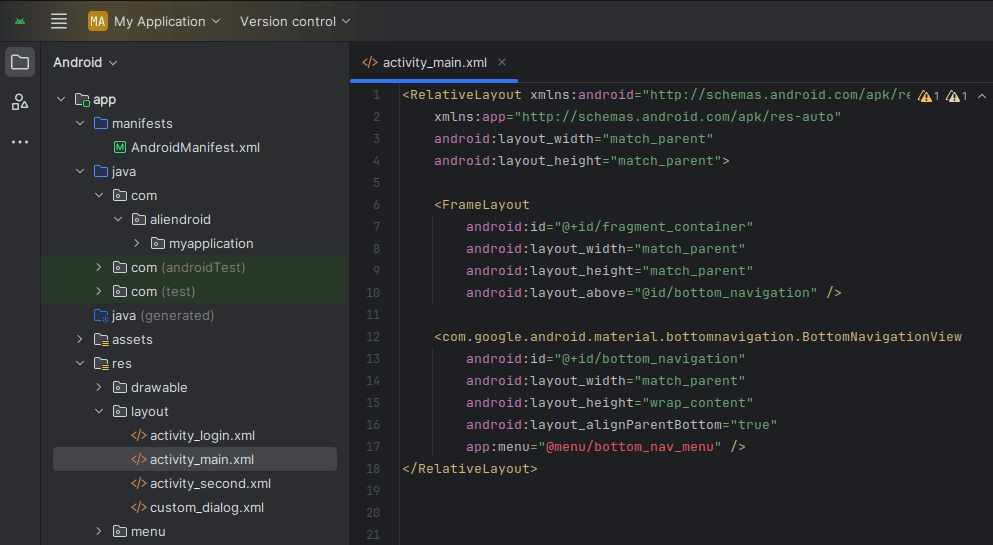
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fragment_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_above="@id/bottom_navigation" />
<com.google.android.material.bottomnavigation.BottomNavigationView
android:id="@+id/bottom_navigation"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
app:menu="@menu/bottom_nav_menu" />
</RelativeLayout>Step 3: Create Menu Resource
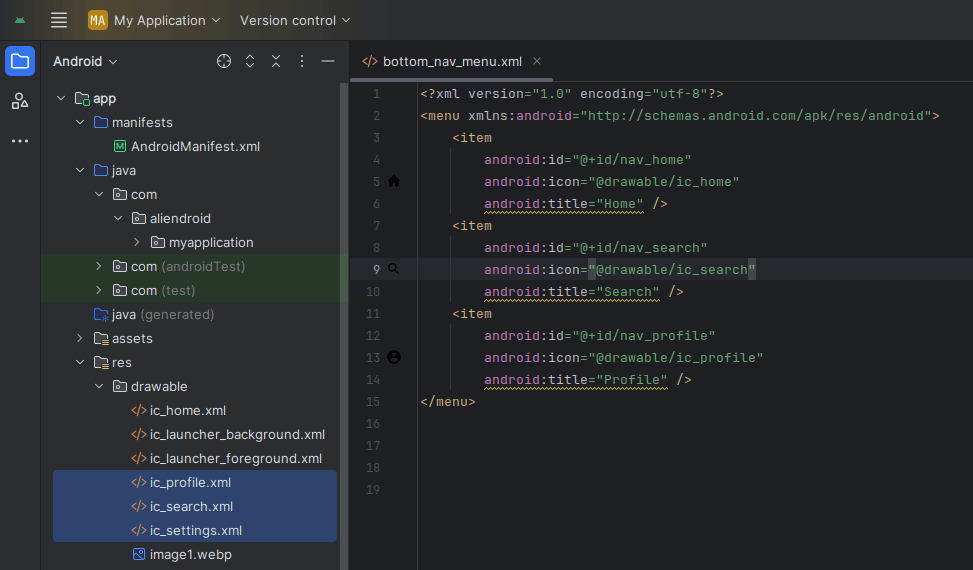
Create a new menu file in res/menu/bottom_nav_menu.xml:
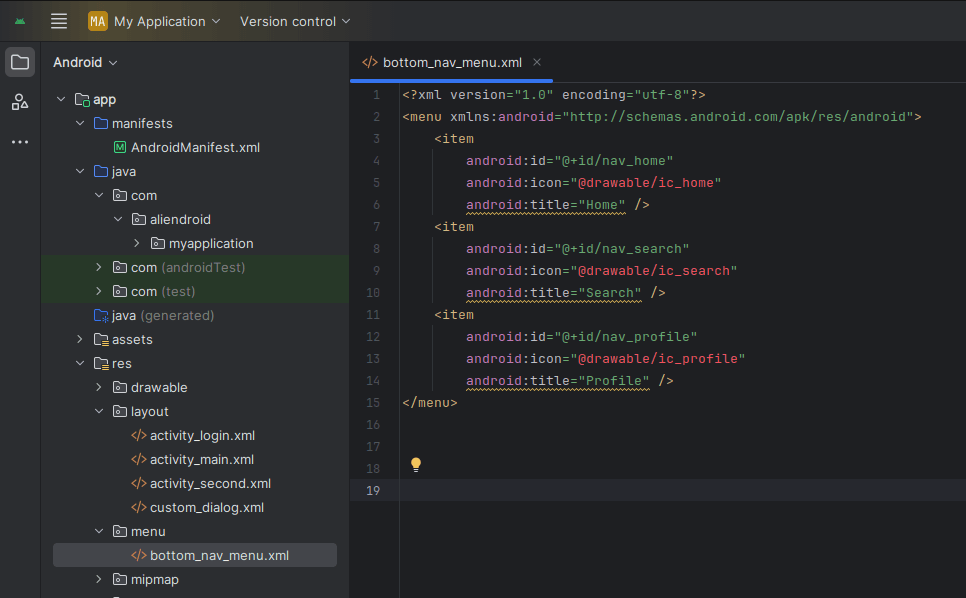
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_home"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_home"
android:title="Home" />
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_search"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_search"
android:title="Search" />
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_profile"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_profile"
android:title="Profile" />
</menu>Add icon from vector asset, Right-click on the drawable > New > Vector Asset.
Click Clip art
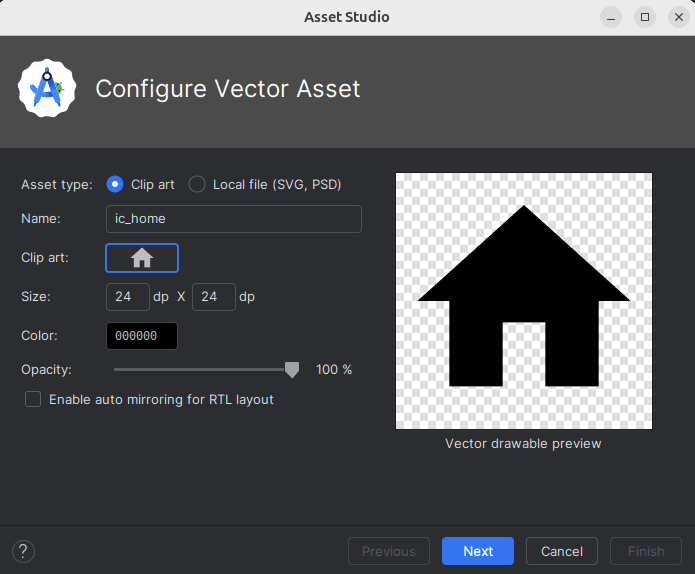
Select icon > OK > Next > Finish
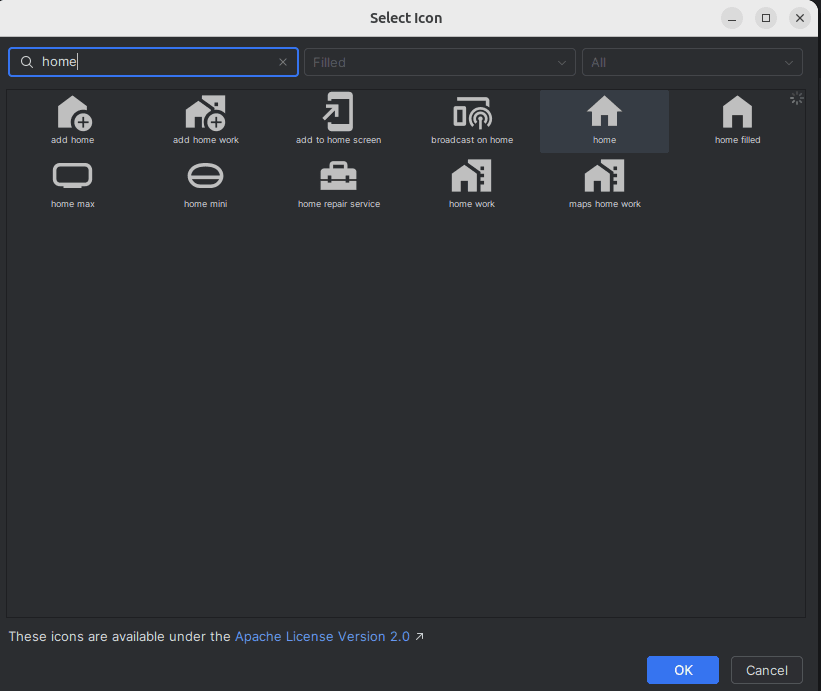
add more icon
Step 4: Create Fragments
Create three fragments: HomeFragment, SearchFragment, and ProfileFragment.
Example: HomeFragment.java
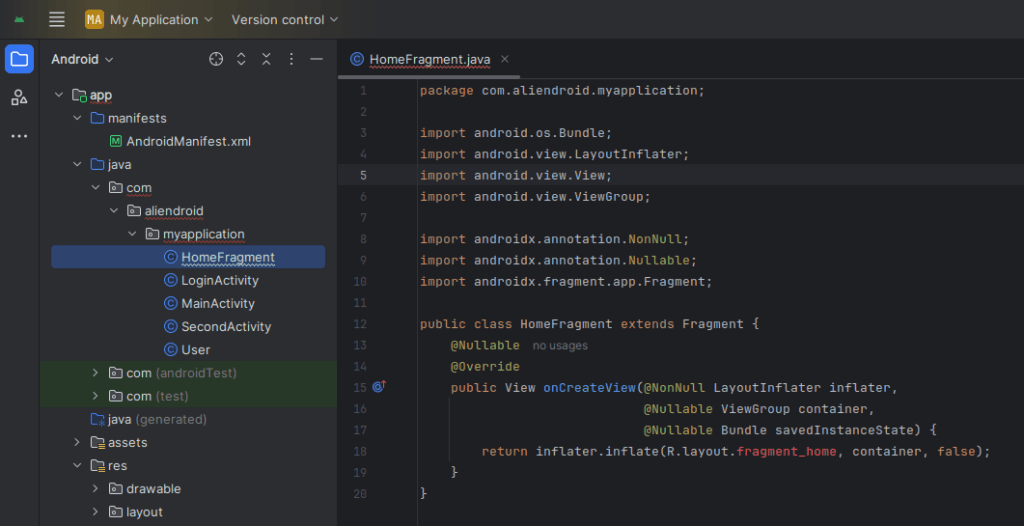
public class HomeFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater,
@Nullable ViewGroup container,
@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_home, container, false);
}
}Step 5: Create Fragment Layouts
Example: res/layout/fragment_home.xml
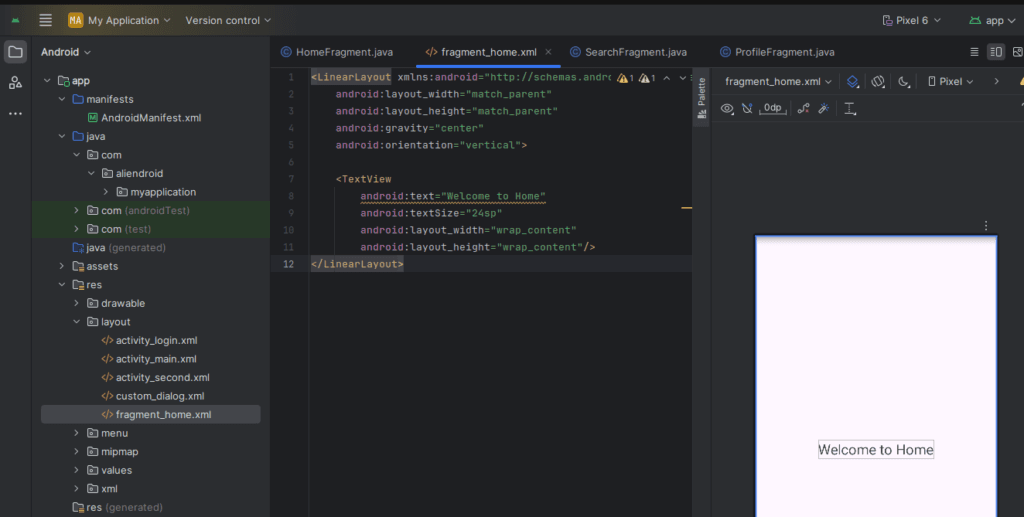
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:text="Welcome to Home"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>Repeat for fragment_search.xml and fragment_profile.xml
Step 6: Add Logic to MainActivity.java
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
import com.google.android.material.bottomnavigation.BottomNavigationView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
BottomNavigationView bottomNavigationView;
@SuppressLint("NonConstantResourceId")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bottomNavigationView = findViewById(R.id.bottom_navigation);
// Default Fragment
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, new HomeFragment()).commit();
bottomNavigationView.setOnItemSelectedListener(item -> {
Fragment selectedFragment = null;
if (item.getItemId() == R.id.nav_home) {
selectedFragment = new HomeFragment();
} else if (item.getItemId() == R.id.nav_search) {
selectedFragment = new SearchFragment();
}else if (item.getItemId() == R.id.nav_profile) {
selectedFragment = new ProfileFragment();
} else {
selectedFragment = new HomeFragment();
}
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, selectedFragment).commit();
return true;
});
}
}Done!
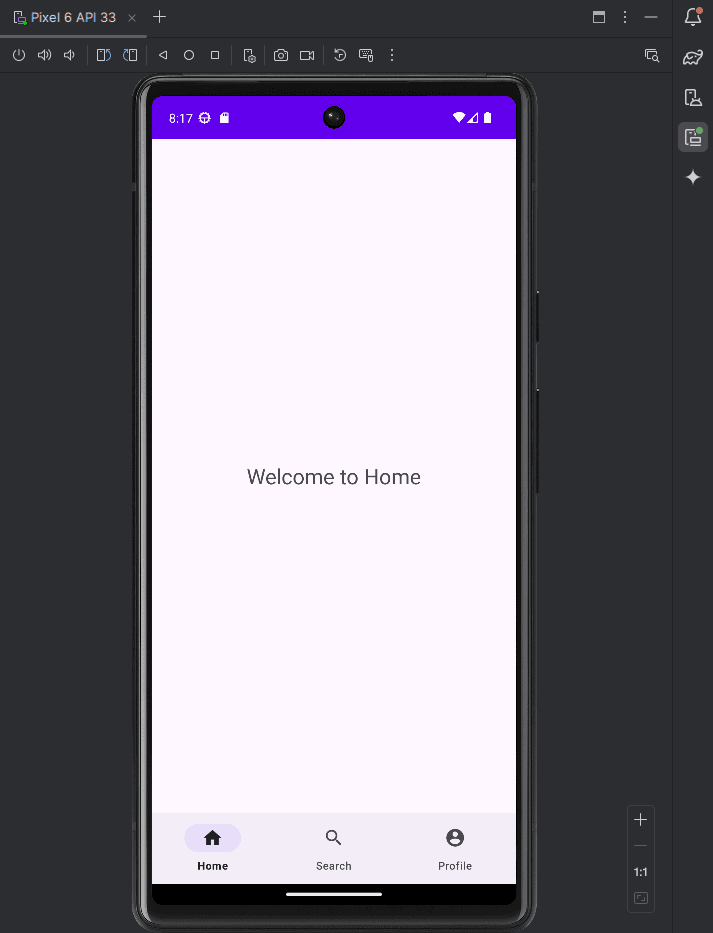
You’ve successfully implemented BottomNavigationView using Java in Android Studio. Now your app has a clean and intuitive navigation interface!