Creating layouts that adapt to different screen sizes is crucial in Android development. When your content exceeds the size of the screen, ScrollView is a powerful tool that lets users scroll vertically or horizontally to access all content.
What is ScrollView?
ScrollView is a view group that allows the view hierarchy placed inside it to be scrollable. It supports vertical scrolling by default.
Basic XML Structure of ScrollView
<ScrollView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!-- Your content goes here -->
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingStart="10dp"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:paddingEnd="10dp"
android:paddingBottom="10dp">
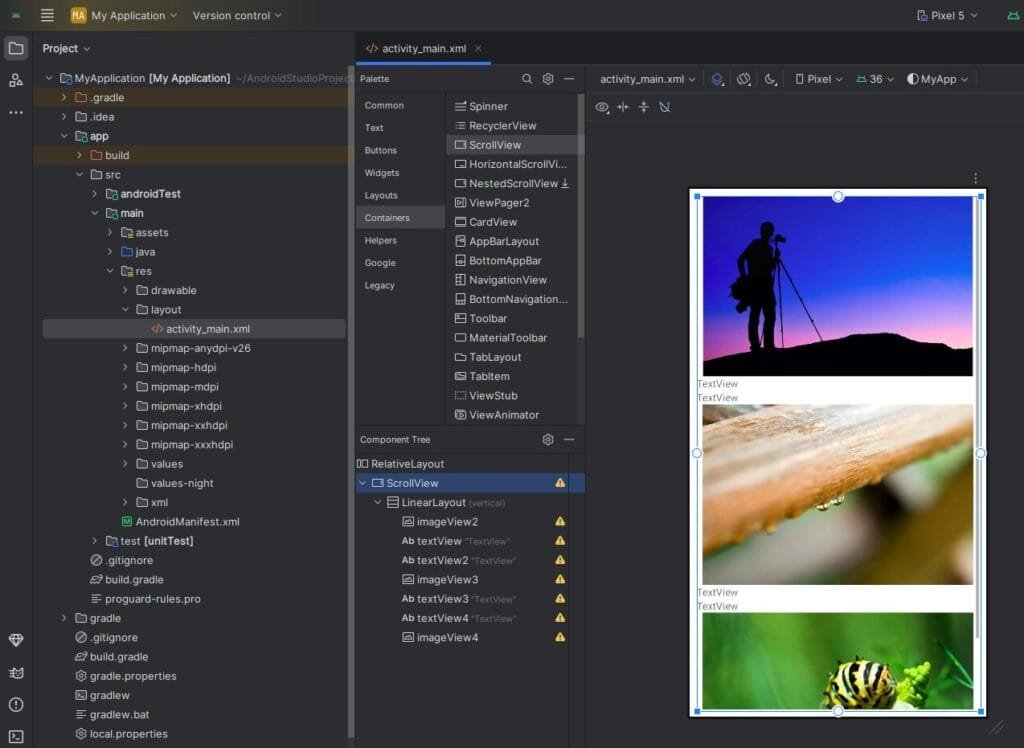
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="250dp"
tools:srcCompat="@tools:sample/backgrounds/scenic" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="250dp"
tools:srcCompat="@tools:sample/backgrounds/scenic" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="250dp"
tools:srcCompat="@tools:sample/backgrounds/scenic" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</RelativeLayout>Note:
ScrollViewcan only host one direct child, which is typically a layout likeLinearLayoutorConstraintLayout.
Vertical vs Horizontal ScrollView
- VerticalScrollView – Default ScrollView behavior (vertical).
- HorizontalScrollView – For horizontal scrolling.
<HorizontalScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!-- Horizontal content -->
</LinearLayout>
</HorizontalScrollView>Common Use Cases
- Forms with many input fields
- Long articles or text content
- Image galleriesProfile or settings pages with multiple sections
Best Practices
- Use
wrap_contentfor the height of child layout insideScrollView. - Avoid nesting multiple
ScrollViewinstances (causes performance issues). - For lists with dynamic items, prefer
RecyclerViewinstead. - Add proper padding and margins to avoid content clipping.
- Always test on multiple screen sizes.
- Use
Troubleshooting Tips
- If ScrollView is not scrolling:
- Make sure inner layout height is
wrap_content. - Check for focusable elements that may prevent scrolling.
- Make sure inner layout height is
- If ScrollView is not scrolling:
- If using
ConstraintLayout, useandroid:fillViewport="true"for better scroll behavior.
- If using