Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a fundamental concept in Java and a core part of Android development. It helps structure code into reusable, modular components using classes and objects. In this tutorial, you will learn how to use OOP principles in Java with Android Studio.
What is a Class?
A class is a blueprint for creating objects. It defines properties (fields) and behaviors (methods).
public class Car {
// Fields
String color;
int speed;
// Constructor
public Car(String color, int speed) {
this.color = color;
this.speed = speed;
}
// Method
public void drive() {
System.out.println("The " + color + " car is driving at " + speed + " km/h.");
}
}What is an Object?
An object is an instance of a class. You can create multiple objects from the same class.
Car myCar = new Car("Red", 120);
myCar.drive(); // Output: The Red car is driving at 120 km/h.Key Concepts in OOP (used in Android Development):
- Encapsulation – Wrapping data (variables) and code (methods) together.
- Inheritance – One class can inherit properties and methods from another.
- Polymorphism – One interface, many implementations.
- Abstraction – Hiding internal details and showing only essential features.
How This Applies in Android Studio
You will often define your Activity, Model, or Adapter as classes and create objects to manage logic or UI:
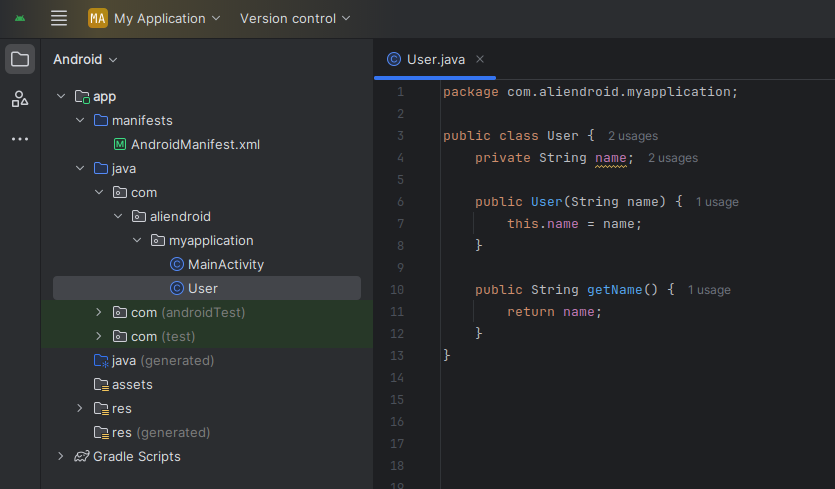
public class User {
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
// Inside MainActivity
User user = new User("Aliendroid");
Log.d("USERNAME", user.getName());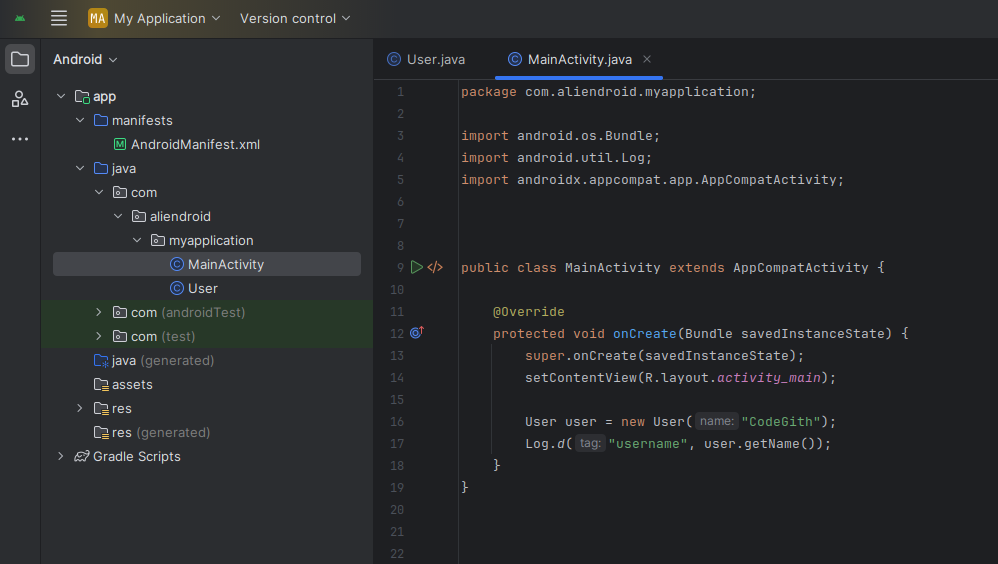
Best Practices
- Use clear class and variable names.
- Keep classes focused (Single Responsibility Principle).
- Reuse code through inheritance or interfaces.
- Always consider using modifiers like
private,public, andprotected.
Conclusion
Understanding and using Classes and Objects in Java is critical for Android development. It helps you write scalable, reusable, and clean code inside Android Studio.