When developing Android applications, designing the user interface (UI) is one of the most crucial steps. Android uses XML (Extensible Markup Language) to define UI layouts in a clear and structured way. Understanding XML layouts allows you to separate the UI design from your app’s logic, making development easier and more manageable.
What is an XML Layout?
An XML layout is a file that describes the visual structure of an Android user interface. These files are located in the res/layout directory of your project and usually have the .xml extension.
Example:
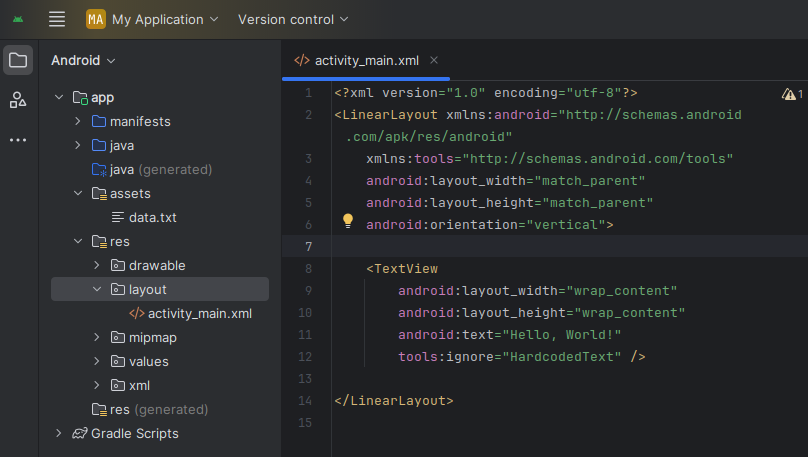
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello, World!" />
</LinearLayout>Common Layout Types in Android
- LinearLayout – Arranges child views in a single direction (horizontal or vertical).
- RelativeLayout – Positions views relative to each other or the parent.
- ConstraintLayout – Flexible and powerful layout that lets you position and size widgets in a responsive way.
- FrameLayout – Used to hold a single view; often used for overlaying views.
- TableLayout – Organizes views in rows and columns.
Key XML Attributes
layout_widthandlayout_height: Define the size of the view.id: Uniquely identifies a view.orientation: Used in LinearLayout to specify direction.paddingandmargin: Control spacing.gravityandlayout_gravity: Align content inside or within the parent.
Benefits of Using XML Layouts
- Separation of concerns: Keeps UI separate from business logic.
- Reusability: XML layouts can be reused across activities and fragments.
- Readability: XML is human-readable, making UI structure easy to understand.
- Support for Tools: Easily editable via Android Studio’s visual Layout Editor.
Best Practices
- Keep layouts simple and avoid deep nesting.
- Use
ConstraintLayoutfor complex layouts to improve performance. - Name views clearly for easier reference in your Java/Kotlin code.
- Use styles and themes to maintain design consistency.
Conclusion
XML layouts are the foundation of Android app UI design. By learning how to structure and manipulate XML layout files, developers can create beautiful, functional, and responsive Android apps. This beginner’s guide is your first step toward mastering Android UI development.