TextView is one of the most basic and commonly used UI components in Android. It is used to display text to the user. Whether you need to show a title, message, label, or any static content, TextView is the go-to widget. It supports features like text styling, custom fonts, click events, and much more.
Add TextView and EditText in activity_main.xml
Open the res/layout/activity_main.xml file and replace the content with:
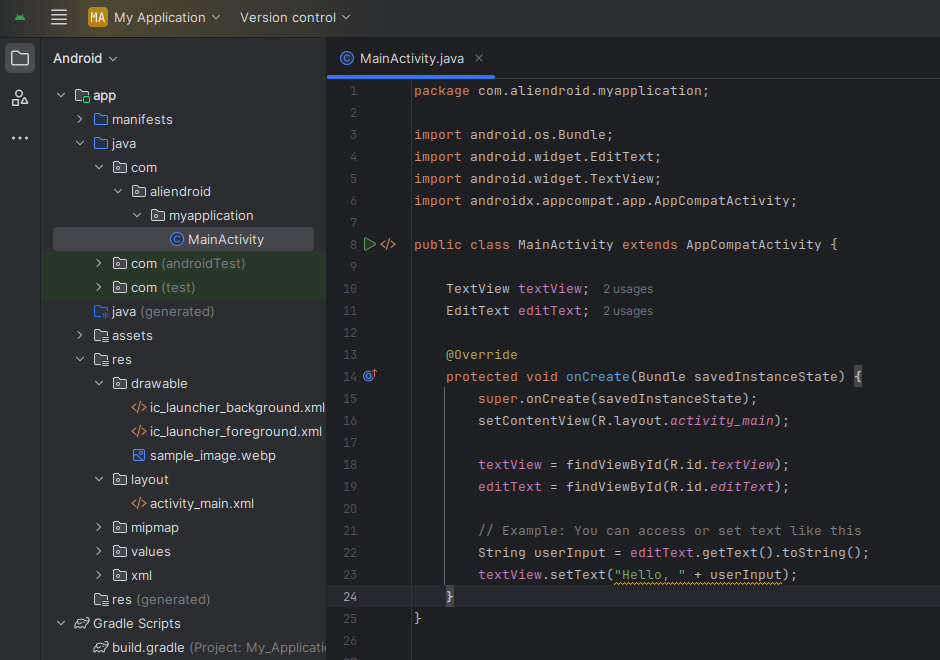
package com.example.myfirstapp;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView textView;
EditText editText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = findViewById(R.id.textView);
editText = findViewById(R.id.editText);
// Example: You can access or set text like this
String userInput = editText.getText().toString();
textView.setText("Hello, " + userInput);
}
}Note: To respond to user input dynamically, consider using a Button and adding a setOnClickListener.
Conclusion
Now you’ve successfully added and connected a TextView and an EditText in Java using Android Studio. This is the foundation of many input-related user interfaces in Android development.
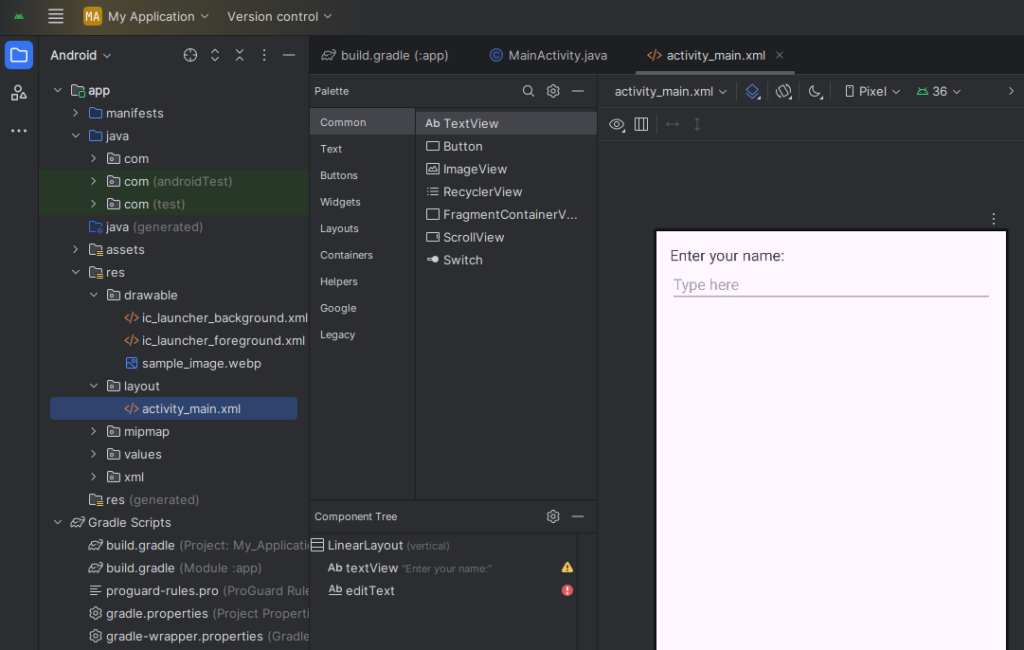
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Enter your name:"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Type here"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
android:marginTop="12dp"/>
</LinearLayout>Access TextView and EditText in Java File
Open MainActivity.java and modify as follows:

package com.example.myfirstapp;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView textView;
EditText editText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = findViewById(R.id.textView);
editText = findViewById(R.id.editText);
// Example: You can access or set text like this
String userInput = editText.getText().toString();
textView.setText("Hello, " + userInput);
}
}Note: To respond to user input dynamically, consider using a Button and adding a setOnClickListener.
Conclusion
Now you’ve successfully added and connected a TextView and an EditText in Java using Android Studio. This is the foundation of many input-related user interfaces in Android development.