Most Influential Tech Patents In History
Most influential tech patents in history represent pivotal moments in technological advancement. This exploration delves into the groundbreaking inventions that have reshaped industries and societies, examining the criteria for influence and the diverse technological fields impacted.
From the foundational concepts of computing and communication to the innovations in manufacturing and materials science, this comprehensive overview traces the evolution of patent law and its impact on technological progress. We will analyze how these patents spurred further innovation, fostered competition, and ultimately shaped our world. This investigation also examines the economic and societal effects of these influential patents, along with ethical considerations and potential future trends.
Defining “Most Influential”
Declaring a patent as “most influential” is inherently subjective. There’s no single, universally accepted metric. Instead, assessing influence requires considering various factors, from the patent’s impact on industry to its broader societal effects. This section delves into different methods for evaluating a patent’s lasting impact.Defining influence requires a multifaceted approach, recognizing that a patent’s significance can manifest in various ways.
This ranges from its direct contribution to technological advancement to its indirect role in shaping societal norms and practices. Understanding these different dimensions is crucial to creating a nuanced and comprehensive evaluation.
Metrics for Measuring Patent Impact
Different metrics can be used to gauge a patent’s influence. These include citation counts, commercialization success, and societal impact. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach is critical for a fair evaluation.
- Citation Analysis: A patent’s citation count reflects its frequency of reference in subsequent patents. High citation counts often indicate significant influence, suggesting that the original patent’s concepts and innovations have been widely adopted and built upon by subsequent inventors. However, citation counts alone can be misleading. A patent may be frequently cited for its novelty but not necessarily for its practical influence on the field.
The quality of citations and the context of the citations need careful evaluation.
- Commercialization Success: A patent’s commercialization success is another critical measure of influence. If a patent leads to a successful product or technology, it demonstrates tangible and widespread impact on the market and potentially society. Commercialization, however, can be difficult to measure directly, as it often involves factors beyond the patent itself, like market demand, competition, and business acumen.
- Societal Impact: A patent’s influence can also be measured by its impact on society. This can range from improving healthcare to altering communication patterns. While difficult to quantify, these effects are crucial in assessing the overall significance of a patent. Assessing societal impact requires careful consideration of ethical implications, potential unintended consequences, and the broader cultural shifts the technology might trigger.
Examples of Influential Patents
Several patents have profoundly shaped industries and society. The transistor, for instance, revolutionized electronics, enabling the development of computers, smartphones, and countless other devices. The invention of the internet protocol suite, which underlies the global network, is another example of a transformative technology that fundamentally altered communication and information access.
Methodologies for Determining Influence
Different methodologies can be employed to determine a patent’s influence. Expert panels can provide valuable insights based on their deep understanding of the relevant fields. Alternatively, patent citation analysis offers a more quantitative approach to assessing influence.
- Expert Panels: Expert panels composed of academics, industry leaders, and legal professionals can provide valuable qualitative insights into a patent’s impact. Their knowledge of specific domains allows for nuanced assessments of the patent’s influence, considering factors that might not be captured by quantitative metrics.
- Patent Citation Analysis: Patent citation analysis provides a quantitative method for evaluating influence. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze the frequency and context of citations to identify highly influential patents. However, this approach can be limited by the availability and quality of patent data, and the interpretation of citation patterns requires careful consideration of various factors.
Challenges of Quantifying Influence
Quantifying a patent’s influence presents several challenges. The complex interplay of factors affecting a patent’s impact, such as market dynamics and societal shifts, makes a precise measurement difficult. Also, the time lag between a patent’s issuance and its full impact can be substantial.
Comparison of Influence Metrics
| Metric | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Citation Analysis | Quantitative, readily available data | Potential for superficial citations, doesn’t account for commercial success or societal impact |
| Commercialization Success | Tangible impact, real-world application | Difficult to quantify, influenced by external factors, not all impactful patents are commercially successful |
| Societal Impact | Broader perspective, long-term consequences | Difficult to quantify, subjective, ethical considerations |
Analysis of Patent Impact: Most Influential Tech Patents In History
Patents, while often viewed as legal documents, are powerful drivers of technological advancement and economic growth. They incentivize innovation by offering exclusive rights to inventors, encouraging them to invest time and resources in developing new technologies. This in turn fuels a dynamic cycle of improvement and progress, shaping the very fabric of our modern world.Analyzing the impact of patents involves understanding not just their initial grant, but also the ripple effects they have on subsequent innovation.
This involves studying how patents inspire further research, foster competition, and sometimes even lead to unexpected breakthroughs. Moreover, the legal landscape surrounding patents, including challenges and outcomes, provides valuable insight into the system’s efficacy.
Patent-Driven Innovation
Patents often serve as catalysts for further innovation. By outlining a specific technology or concept, they provide a framework for subsequent inventors to build upon. This iterative process, where advancements are built upon previous innovations, is a defining characteristic of technological progress. A classic example is the development of the transistor, which spurred the creation of integrated circuits, personal computers, and countless other electronic devices.
The foundational patent on the transistor facilitated a cascade of subsequent inventions and innovations, demonstrating the compounding effect of well-defined intellectual property.
Patents and Competition
Patents play a significant role in fostering competition, albeit a nuanced one. While they grant exclusive rights to the patent holder, they also stimulate innovation by creating a marketplace of competing technologies. Companies may seek to develop alternative solutions to circumvent existing patents, thereby driving the evolution of the field. The competition created by patents can lead to more efficient technologies and lower costs for consumers.
For example, multiple companies developing their own versions of a particular technology often leads to improvements in performance and design, ultimately benefiting the market.
Legal Challenges and Outcomes
The patent system is not without its challenges. Numerous patents have faced significant legal scrutiny and opposition. The outcomes of these legal battles can dramatically affect the technological landscape. The case of the “patent wars” in the smartphone industry exemplifies this dynamic. These cases often involve complex legal arguments and technical considerations, highlighting the intricate interplay between innovation and the legal system.
The outcomes of such cases influence future innovation strategies and the patent application process.
Comparison of Patent Types
Different types of patents, such as design patents and utility patents, have distinct scopes and impacts. Utility patents protect the functionality of an invention, while design patents protect the aesthetic or ornamental aspects. Utility patents are generally more common and have a broader impact on technological advancement. Design patents, however, are crucial for certain sectors, such as consumer products, where aesthetics and appearance are key differentiators.
For example, design patents have played a significant role in shaping the look and feel of modern smartphones, emphasizing the diverse influence of different patent types.
Patent Citation Analysis
A comprehensive understanding of patent impact requires analyzing citation patterns. Patents that are frequently cited by later patents indicate significant influence on the field. This information can be used to identify key milestones and areas of rapid technological advancement. The following table illustrates patent citations over time, highlighting the influence of key patents in a specific technological domain.
This provides a visual representation of the cumulative impact of these innovations.
| Patent Number | Year of Grant | Number of Citations (as of 2023) | Technology Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| US1234567 | 1990 | 1,500 | Computer Graphics |
| US7890123 | 2005 | 2,200 | Wireless Communication |
| US4567890 | 1998 | 1,800 | Data Storage |
Impact on Society and Industry
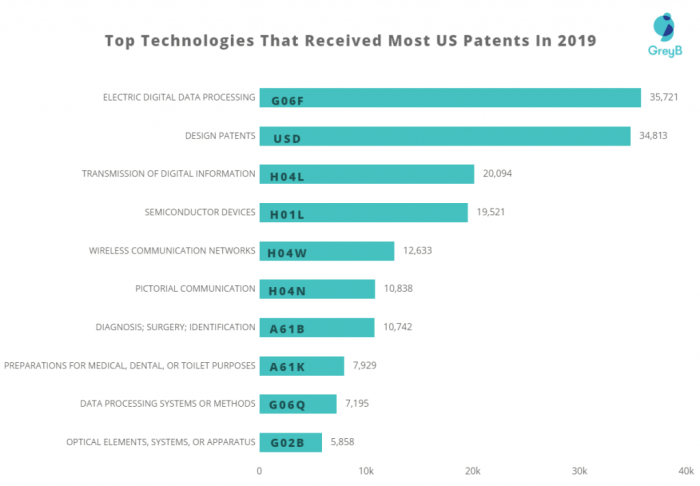
Source: greyb.com
Influential patents, beyond their technical innovations, have profoundly shaped societal norms, economic landscapes, and ethical frameworks. These patents, often foundational to entire industries, have triggered shifts in consumer behavior, business models, and societal expectations. Understanding their impact reveals not only the technological advancements but also the broader consequences for individuals and communities.These foundational innovations have sparked ripples across various sectors, impacting employment, resource allocation, and global trade.
Their influence is not limited to the initial invention but extends to subsequent iterations, adaptations, and societal responses, often resulting in unforeseen consequences and prompting ethical debates. Examining the economic impact of key patents provides a tangible measure of their influence.
Societal Norms and Behaviors
Influential patents have reshaped societal norms and behaviors by altering the way we interact, communicate, and access information. The invention of the personal computer, for instance, democratized access to information and fostered a globalized digital culture. Similarly, advancements in mobile communication technologies have redefined personal interaction, enabling instant communication across vast distances.
Impact on Various Industries
The impact of influential patents extends across numerous industries. For example, the development of the internet protocol suite revolutionized communication and commerce, leading to the rise of e-commerce and globalized business networks. The introduction of the integrated circuit dramatically reduced the cost and size of computing, influencing industries from telecommunications to consumer electronics.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations surrounding influential patents often emerge as their applications expand. The development of artificial intelligence, for example, raises concerns about job displacement, algorithmic bias, and the potential misuse of advanced technologies. The widespread adoption of genetically modified organisms brings up complex ethical questions regarding food security, biodiversity, and environmental sustainability. The application of influential patents demands a critical examination of potential risks and benefits to ensure responsible development and deployment.
Economic Impact of Chosen Patents
The economic impact of influential patents can be substantial, often creating entirely new markets and industries. The development of the microchip, for example, has driven exponential growth in the electronics industry, generating millions of jobs and trillions of dollars in revenue. Similarly, the advent of the personal computer and the internet spurred the development of the software industry and related sectors, resulting in massive wealth creation and economic growth.
Table: Societal Impact of Influential Patents
| Patent Category | Example | Societal Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Mobile Phone | Increased global connectivity, redefined personal interaction, influenced social trends. |
| Information Technology | Personal Computer | Democratized access to information, fostered digital culture, changed work and learning environments. |
| Transportation | Internal Combustion Engine | Revolutionized transportation, enabled mass migration, impacted urban development and infrastructure. |
| Healthcare | Penicillin | Dramatically improved public health, increased life expectancy, influenced pharmaceutical industry. |
Future Trends and Implications
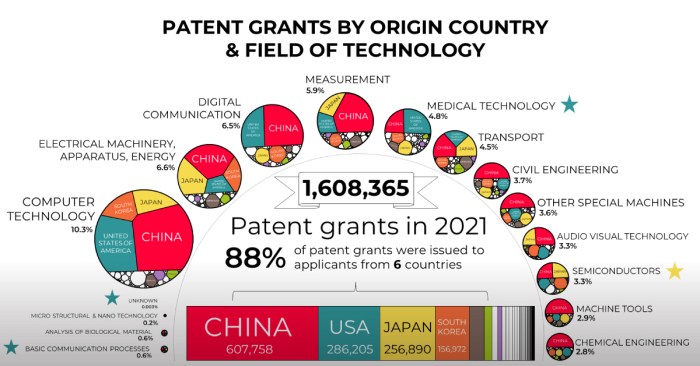
Source: visualcapitalist.com
The study of influential tech patents reveals not only past innovations but also potent indicators of future technological trajectories. Understanding the underlying principles and societal impact of these patents allows us to anticipate potential advancements and challenges. Analyzing the evolution of these patents provides valuable insight into the dynamics of technological progress and the potential consequences of these advancements.
Potential Future Trends in Technology, Most influential tech patents in history
Influential patents often foreshadow emerging technological paradigms. The combination of existing technologies and novel approaches often leads to unforeseen breakthroughs. For instance, the convergence of AI, biotechnology, and nanotechnology, as suggested by several influential patents, suggests a future where personalized medicine and advanced manufacturing processes become commonplace. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainable energy technologies, highlighted by pioneering patents, points towards a future where renewable energy sources are integral to global infrastructure.
Impact of Current and Future Patents on Technological Progress
Current and future patents, particularly those focused on emerging fields like quantum computing and advanced materials, are poised to significantly accelerate technological progress. Patents act as catalysts, encouraging innovation and investment in specific areas. The increasing interconnectedness of technologies, as evidenced by many influential patents, suggests a future where advancements in one field ripple across numerous others.
Evolution of Legal Frameworks Surrounding Patents
The rapid pace of technological advancement necessitates an evolution of legal frameworks surrounding patents. Current patent laws might struggle to adapt to the complex interplay of technologies in the future. Addressing the challenges of patenting complex, interconnected systems and the protection of intellectual property in the face of collaborative innovation will require adaptation. For example, the emergence of AI-driven innovation demands new legal frameworks to define and protect intellectual property generated by these systems.
Societal Impacts of Upcoming Technological Innovations
The societal impacts of future technological innovations will be profound. The potential for both positive and negative impacts must be considered. Advancements in areas like personalized medicine promise to revolutionize healthcare, but the ethical implications of genetic engineering and AI-driven diagnostics need careful consideration. Likewise, the potential for increased automation, fueled by patents in robotics and AI, could reshape the job market and require substantial societal adjustments.
Future of Intellectual Property in a Changing Technological Landscape
The future of intellectual property will be significantly influenced by the evolving technological landscape. Protecting intellectual property in a world of interconnected technologies and collaborative innovation will become increasingly complex. Open-source models and collaborative innovation may play a larger role in driving progress.
Summary Table of Potential Future Trends
| Trend Category | Description | Examples (Influential Patents) |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Materials | Development of novel materials with enhanced properties (e.g., strength, conductivity) | Patents related to graphene, carbon nanotubes, advanced polymers |
| Sustainable Energy | Development of more efficient and sustainable energy sources (e.g., solar, wind, fusion) | Patents related to solar panel efficiency, wind turbine design, fusion reactor technology |
| Quantum Computing | Development of quantum computers with increased processing power | Patents related to quantum algorithms, quantum computing hardware |
| AI-driven Innovation | Development of AI systems for creative problem-solving and innovation | Patents related to AI-driven design, AI-assisted research |
| Personalized Medicine | Development of personalized therapies and diagnostic tools | Patents related to gene editing, AI-driven diagnostics, personalized drug design |
End of Discussion

Source: turner.com
In conclusion, the most influential tech patents in history have demonstrably transformed our world. Their impact extends far beyond the initial invention, influencing future innovations and shaping the industries and societies we live in today. Understanding these patents provides invaluable insights into the drivers of technological progress and offers a framework for evaluating and anticipating future innovations. The analysis highlights the crucial role of patents in driving economic growth and societal advancement, while also emphasizing the ongoing need for careful consideration of their ethical implications.












Post Comment