Augmented Reality And Virtual Reality Potential Applications
Augmented reality and virtual reality potential applications are transforming various sectors, from entertainment and healthcare to industrial design and architecture. These immersive technologies offer exciting possibilities for interactive experiences, from realistic simulations to enhanced learning opportunities. The potential for innovation is vast, with applications across numerous industries.
This exploration delves into the diverse uses of AR and VR, examining their current applications and future trends. We’ll analyze how these technologies are revolutionizing consumer experiences, impacting healthcare practices, and enhancing efficiency in industrial settings. The detailed overview of AR and VR will include a comparative analysis of hardware requirements, outlining the advantages and disadvantages of each technology.
Introduction to Augmented and Virtual Reality
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are rapidly evolving technologies transforming diverse industries. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, while VR creates immersive, computer-generated environments. These technologies are driving innovation in gaming, healthcare, education, and more.
Definitions of AR and VR
Augmented reality (AR) enhances the user’s perception of the real world by integrating computer-generated sensory input. Virtual reality (VR), on the other hand, immerses the user in a completely artificial environment, replacing the real world with a simulated one. The core difference lies in the degree of immersion and the presence of the real world.
Fundamental Differences Between AR and VR
AR maintains a connection to the user’s real-world surroundings, supplementing the view with digital information. VR, conversely, isolates the user from the real world, creating a completely artificial experience. This difference is reflected in the user interface, interaction methods, and the overall sensory experience. AR allows for seamless integration of digital and physical elements, while VR provides a complete digital replacement.
Key Components and Enabling Technologies
AR and VR experiences rely on several crucial components. Display technology, such as high-resolution screens and head-mounted displays (HMDs), is essential for rendering visuals. Sophisticated tracking systems, including motion sensors and cameras, are crucial for accurately overlaying or simulating the user’s position and movements within the virtual or augmented environment. Powerful processing units and high-bandwidth networks are required to manage complex calculations and ensure smooth operation.
Software development plays a vital role in creating and managing the interactive elements of these immersive environments.
Historical Evolution of AR and VR
The evolution of AR and VR spans several decades, with significant milestones shaping their current form. Early concepts of AR and VR emerged in the 1960s and 1970s, with pioneering work in computer graphics and interactive systems. The development of head-mounted displays in the 1990s marked a crucial step forward, enabling more immersive experiences. More recently, advancements in processing power, display technology, and sensor accuracy have led to significant improvements in the quality and realism of AR and VR applications.
The introduction of smartphones and tablets has also significantly democratized access to these technologies.
Comparison of Hardware Requirements
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Display | Smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses, often with a screen overlaying the real world. | Head-mounted displays (HMDs) creating a fully immersive virtual environment. |
| Processing Power | Moderate processing power needed for real-time image processing and overlays. | High processing power required for complex simulations and rendering of the virtual environment. |
| Tracking Systems | Cameras, accelerometers, and gyroscopes for tracking user movement and environment. | Sophisticated motion sensors (e.g., inside-out or outside-in tracking) for precise tracking of head and body movements within the virtual environment. |
| Networking | Generally less demanding networking requirements than VR. | Higher bandwidth and low latency networking for seamless interaction and data transfer. |
The table above summarizes the fundamental differences in hardware requirements for AR and VR experiences. The contrasting needs for processing power, display capabilities, and tracking technology highlight the distinct nature of these two technologies.
Applications in Consumer Entertainment
Augmented and virtual reality (AR and VR) technologies are rapidly transforming the consumer entertainment landscape, offering immersive and interactive experiences that were previously unimaginable. From gaming and movie-watching to education and social interaction, AR and VR are reshaping how we engage with entertainment media. This evolution is driven by advancements in hardware and software, allowing for increasingly realistic and engaging simulations.AR and VR are no longer confined to niche markets; their accessibility and affordability are driving broader adoption, particularly in entertainment applications.
This trend is expected to continue, with further innovations promising even more captivating and interactive experiences for consumers in the coming years.
Revolutionizing Gaming and Interactive Entertainment
AR and VR are fundamentally altering the gaming experience, moving beyond traditional screens to encompass entire environments. Players can now step into virtual worlds, interact with realistic digital characters, and experience scenarios that were previously only possible in fiction. Examples include virtual reality games offering immersive combat simulations, allowing players to explore intricate landscapes and engaging in realistic challenges.
Furthermore, AR games overlay digital elements onto the real world, enhancing user engagement by integrating digital content with physical spaces. The use of motion tracking and haptic feedback systems creates an almost tangible connection to the virtual environment, creating a more dynamic and engaging experience.
Transforming the Movie-Watching Experience
AR and VR technologies are enhancing the cinematic experience, offering viewers unprecedented levels of immersion and interaction. Imagine a VR headset allowing you to be present at the film’s location, or AR overlays enhancing a film’s narrative with interactive elements. Virtual cinema experiences can place viewers in the heart of the action, offering a truly immersive perspective on the story.
AR can provide real-time translations of foreign films, creating subtitles that appear on the screen in a clear and unobstructed way. This approach enables a wider audience to enjoy international films, regardless of their language proficiency.
AR and VR in Interactive Learning
AR and VR offer compelling educational opportunities, creating interactive learning environments that go beyond traditional textbooks. AR applications can overlay educational content onto real-world objects, enabling users to learn about the world around them in a dynamic and engaging way. For instance, students can use AR apps to explore the anatomy of a human body or the details of a historical monument.
VR allows for simulations of complex scenarios or historical events, providing learners with a unique and hands-on approach to learning. These immersive learning environments can be customized to meet specific educational objectives and learning styles.
Enhancing Social Interaction and Communication
AR and VR are blurring the lines between physical and virtual interactions, opening up possibilities for new forms of social connection. Imagine using AR to virtually place yourself in a meeting with colleagues from another continent, or interacting with virtual avatars in a shared VR environment. This technology can connect individuals geographically dispersed and foster meaningful interactions, even in situations where physical presence is not possible.
VR can provide a platform for interactive storytelling and collaborative experiences that were not previously possible.
Creating Immersive and Interactive Tourist Experiences
AR and VR are reshaping the way we experience travel and tourism. AR apps can overlay information about historical sites or natural landmarks onto the real world, providing visitors with an enriched understanding of their surroundings. VR simulations can offer potential tourists a glimpse into destinations before they arrive, allowing them to experience a location virtually and prepare for their visit.
Imagine virtually touring the Colosseum or exploring the Amazon rainforest from the comfort of your home, creating immersive and memorable travel experiences.
Table of AR/VR Applications in Entertainment
| Application Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Gaming | Immersive gaming experiences with virtual worlds and AR overlays | VR games with realistic environments and AR games that superimpose digital characters into real-world settings |
| Movies/Cinema | Enhanced movie-watching experiences with immersive virtual environments | VR cinema allowing viewers to be virtually present at the film’s location and AR overlays providing interactive elements to enhance narrative |
| Education | Interactive learning experiences that go beyond traditional textbooks | AR apps overlaying educational content onto real-world objects, VR simulations of historical events or complex scenarios |
| Social Interaction | New forms of social connection and communication through virtual interactions | Virtual meetings using AR or interacting with virtual avatars in a shared VR environment |
| Tourism | Immersive and interactive travel experiences before and during a visit | AR apps overlaying information about historical sites, VR simulations of destinations |
Applications in Healthcare
Augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technologies are rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, offering innovative solutions for medical training, surgical interventions, rehabilitation, and patient care. Their immersive nature and interactive capabilities are proving valuable tools for improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall healthcare experience.
Medical Training and Education
AR and VR simulations provide realistic and safe environments for medical students and professionals to practice complex procedures and scenarios. These interactive experiences allow learners to rehearse surgical techniques, diagnose medical conditions, and manage critical situations without the risks associated with real-world patients. For instance, virtual anatomy platforms enable students to explore the human body in detail, manipulating organs and structures in a safe and controlled setting.
Surgical procedures, like laparoscopic techniques, can be practiced virtually before performing them on real patients, significantly improving the proficiency of healthcare professionals.
Surgical Procedures and Interventions
AR overlays vital information onto the patient’s anatomy during surgical procedures, guiding surgeons with real-time data. This augmented reality support can include anatomical models, patient-specific imaging, and instrument guidance, enhancing precision and reducing the risk of complications. VR can simulate complex surgical procedures in a virtual environment, allowing surgeons to refine their techniques and strategize before operating on actual patients.
Examples include virtual rehearsals for complex craniotomies or cardiac surgeries.
Rehabilitation and Therapy
AR and VR therapies provide immersive and engaging rehabilitation exercises for patients recovering from injuries or illnesses. Virtual environments can be tailored to specific needs, allowing patients to practice movements, improve balance, and regain lost function. VR can create interactive games and exercises, motivating patients to participate actively in their recovery. For instance, patients recovering from stroke can use VR games to improve their hand-eye coordination and motor skills.
Patient Engagement and Education
AR and VR offer innovative ways to educate patients about their conditions and treatment options. Interactive simulations can illustrate complex medical concepts in an accessible manner, improving patient understanding and empowering them to actively participate in their care. Patients can visualize their surgical procedures or treatments in a virtual environment, fostering confidence and reducing anxiety. For example, VR applications can provide patients with a realistic view of their own anatomy before surgery, enabling them to better understand their condition.
Remote Diagnostics and Consultations
AR and VR can aid in remote diagnostics and consultations, allowing healthcare professionals to virtually examine patients and provide remote support. AR overlays can provide healthcare professionals with a comprehensive view of a patient’s condition, enabling them to diagnose issues remotely and provide effective recommendations. VR simulations can be used to simulate patient symptoms or medical scenarios for remote consultations.
This approach is particularly useful in underserved areas or for patients with mobility limitations.
Benefits of AR/VR in Healthcare Settings
| Healthcare Setting | Benefits of AR/VR |
|---|---|
| Medical Training | Enhanced skill development, reduced risk, immersive learning |
| Surgical Procedures | Increased precision, reduced complications, improved visualization |
| Rehabilitation | Engaging therapy, personalized exercises, improved patient motivation |
| Patient Education | Improved understanding, reduced anxiety, active patient participation |
| Remote Diagnostics | Improved access to care, comprehensive examinations, remote support |
Applications in Industrial and Manufacturing
Augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technologies are rapidly transforming industrial processes, offering significant advantages in training, maintenance, design, and quality control. Their immersive nature and interactive capabilities allow for realistic simulations and hands-on experiences, reducing risks and enhancing efficiency in the industrial setting.AR/VR technologies provide a unique opportunity to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, enhancing learning and retention in industrial training.
The immersive experiences allow trainees to practice complex procedures in a safe and controlled environment, significantly reducing the potential for errors and accidents.
Industrial Training Programs
AR and VR offer compelling methods for training industrial personnel. Immersive simulations can replicate real-world scenarios, allowing trainees to practice complex procedures without the risks associated with live equipment. This not only improves safety but also accelerates learning and knowledge retention. For example, a VR training module could simulate operating heavy machinery or performing intricate assembly tasks in a risk-free environment.
This approach can drastically reduce the time needed for personnel to reach proficiency, leading to substantial cost savings.
Complex Machinery Maintenance and Repair
AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, enabling technicians to access real-time instructions, diagrams, and maintenance manuals while working on machinery. This allows for more efficient troubleshooting and repair, reducing downtime and potential errors. VR simulations can replicate the internal workings of complex machinery, offering technicians a visual guide to intricate components and systems. This can prove invaluable in diagnosing problems, especially in scenarios involving hard-to-reach areas or delicate components.
The result is improved diagnostic accuracy and quicker repair times.
Product Design and Prototyping
AR and VR tools facilitate rapid prototyping and design iterations. Engineers can visualize products in 3D environments, enabling interactive exploration and adjustments to designs. VR environments allow for testing product usability and ergonomics, leading to more user-friendly designs. By experimenting with different design iterations within a virtual space, companies can minimize costly physical prototyping cycles. AR can also be used for real-time design reviews, enabling remote collaboration and faster feedback loops.
Quality Control and Inspection
AR applications facilitate real-time quality checks and inspections by overlaying digital data onto physical products. This enables technicians to compare real-world objects against digital models and specifications, identifying defects and deviations with ease. VR can be used to simulate complex inspection processes, allowing technicians to practice their skills in a controlled environment before applying them to real-world scenarios.
This enhances accuracy and consistency in quality control, leading to reduced rework and improved product quality.
Immersive Simulations for Industrial Scenarios
Virtual reality environments provide a realistic simulation of various industrial scenarios. Engineers and technicians can test and evaluate the safety and effectiveness of procedures and responses in simulated hazardous environments, which is invaluable in preventing accidents. This capability is particularly beneficial for testing disaster response protocols or emergency situations, training employees for immediate and appropriate responses. Immersive VR simulations also aid in risk assessment and the development of contingency plans.
Potential Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains in Industrial Applications
| Application | Potential Cost Savings | Potential Efficiency Gains |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Training | Reduced training time, lower injury rates, reduced need for specialized instructors | Faster skill development, increased employee proficiency, reduced on-the-job errors |
| Maintenance and Repair | Reduced downtime, lower repair costs, reduced need for expert technicians | Faster troubleshooting, improved diagnostic accuracy, reduced maintenance time |
| Product Design and Prototyping | Reduced physical prototyping costs, faster design iterations, minimized design errors | Improved product usability, faster product development cycles, increased design innovation |
| Quality Control and Inspection | Reduced rework costs, improved product quality, minimized defects | Increased accuracy in inspections, faster inspection processes, improved product consistency |
| Immersive Simulations | Reduced risk of accidents in real-world scenarios, lower cost of safety training | Improved disaster response, enhanced risk assessment, more effective contingency plans |
Applications in Architecture and Design
Augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technologies are rapidly transforming the architecture and design industry, offering unprecedented possibilities for visualization, collaboration, and client communication. These immersive technologies allow designers to create realistic and interactive models of spaces, enabling clients to experience proposed designs before construction begins. This leads to improved decision-making and a more streamlined design process.AR/VR tools empower architects and designers with enhanced capabilities for creating, experimenting, and presenting their work.
The immersive nature of these tools fosters a deeper understanding of the design, enabling both the creators and the recipients to experience the space in a way that traditional methods cannot replicate.
Interactive Architectural Visualization
AR and VR enable interactive architectural visualization, allowing users to explore designs from any angle, virtually walk through spaces, and even manipulate elements like furniture and lighting. This immersive experience goes beyond static blueprints and renders, providing a far more intuitive understanding of the final product. Users can explore various design options in a virtual environment, providing invaluable feedback and facilitating crucial design decisions.
Interior Design and Space Planning
VR is instrumental in interior design and space planning, enabling designers to virtually furnish and decorate spaces, experiment with different layouts, and assess the impact of color schemes and materials. This process allows for a more thorough and efficient design process, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming physical iterations. The ability to visualize furniture placement, lighting, and spatial flow within a realistic 3D environment significantly aids in the creation of functional and aesthetically pleasing interiors.
Real-time Collaboration among Designers
AR and VR foster real-time collaboration among designers, enabling remote teams to work together on projects simultaneously. This collaborative approach promotes a more streamlined design process. Virtual meetings and shared design environments facilitate the exchange of ideas and feedback, leading to more innovative and effective design solutions. Using collaborative AR/VR platforms, architects and designers can virtually meet and interact, share designs, and make changes in real-time, regardless of geographical location.
Presenting Architectural Models to Clients
AR and VR offer powerful tools for presenting architectural models to clients. Instead of static presentations, clients can experience a building or space in an interactive virtual environment. This immersive experience allows clients to better visualize the design, understand its features, and provide feedback more effectively. Clients can virtually walk through a building, explore different spaces, and make informed decisions about the design.
Applications in Urban Planning and Development
AR and VR can be used for urban planning and development by allowing planners to virtually model and test different urban designs. This virtual environment enables the assessment of traffic flow, pedestrian movement, and the impact of new infrastructure projects on existing urban environments. The ability to simulate and visualize potential scenarios allows for more informed decision-making in urban planning.
Virtual prototypes can be tested and refined to address concerns and optimize the urban design, before any physical implementation.
Features and Functionalities of AR/VR Tools for Architects and Designers, Augmented reality and virtual reality potential applications
| Feature | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Interactive 3D Modeling | Allows creation and manipulation of architectural models in 3D, enabling precise design modifications and detailed visualization. |
| Virtual Walkthroughs | Enables clients and stakeholders to experience the design from different perspectives, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the space. |
| Material and Lighting Visualization | Allows for realistic rendering of materials and lighting effects, showcasing the design’s aesthetics and functionality. |
| Real-time Collaboration | Enables multiple users to work together on a project simultaneously, facilitating communication and idea sharing. |
| Integration with BIM | Facilitates seamless integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, enabling a cohesive workflow for design and construction. |
| Simulation and Analysis | Enables simulations of different scenarios, such as traffic flow or energy consumption, to optimize design solutions. |
Potential Challenges and Limitations: Augmented Reality And Virtual Reality Potential Applications
Augmented and virtual reality, while promising transformative potential, face significant hurdles in widespread adoption. These limitations span technical capabilities, health concerns, financial considerations, and societal implications. Understanding these challenges is crucial for realistic expectations and responsible development.
Technical Limitations
AR and VR technologies still grapple with limitations in processing power, rendering fidelity, and device portability. Current hardware often struggles with complex environments or large datasets, leading to performance issues like lag or decreased frame rates. The need for high-resolution displays and sophisticated sensors creates bulky and expensive devices, impacting usability and accessibility. Furthermore, accurate tracking and interaction with the real or virtual world remain challenging, leading to occasional inaccuracies and user frustration.
Health Risks
Extended use of AR and VR devices can potentially contribute to various health problems. Prolonged immersion can induce motion sickness, eye strain, and headaches, particularly for users unaccustomed to the technology. Furthermore, there’s concern about potential long-term impacts on cognitive function and social interaction if overuse becomes a norm. Ergonomic issues, such as poor posture and repetitive strain injuries, can also result from prolonged periods of use.
Cost Factors
Implementing AR and VR solutions involves significant upfront investment. High-end hardware, specialized software, and skilled personnel are often required, making these technologies inaccessible for many consumers and businesses. The development and maintenance costs for complex AR/VR applications can also be substantial. Additionally, the ongoing need for software updates and hardware upgrades can add to the long-term financial burden.
Social Implications
The widespread adoption of AR and VR could reshape social interaction and communication. The potential for social isolation, the emergence of new forms of social interaction, and the potential for misuse in digital spaces are all critical factors to consider. The creation of entirely virtual communities could lead to the erosion of traditional social structures, necessitating careful consideration of ethical and societal implications.
Security Concerns
The potential for security breaches and misuse in AR and VR applications presents a significant challenge. Hacking into AR/VR systems could lead to data breaches, the creation of malicious virtual environments, or even the manipulation of user experiences. The integration of AR/VR with other technologies, like IoT devices, amplifies the potential for vulnerabilities. This calls for robust security protocols and stringent data protection measures.
Summary Table of Drawbacks and Limitations
| Category | Specific Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Technical | Limited processing power, rendering fidelity, device portability, tracking accuracy, and interaction precision. |
| Health | Motion sickness, eye strain, headaches, potential long-term cognitive effects, ergonomic issues. |
| Cost | High upfront investment in hardware, software, and skilled personnel; ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs. |
| Social | Potential for social isolation, reshaping social interaction, and ethical/societal implications of virtual communities. |
| Security | Data breaches, malicious virtual environments, manipulation of user experiences, vulnerabilities in integrated systems. |
Future Trends and Developments
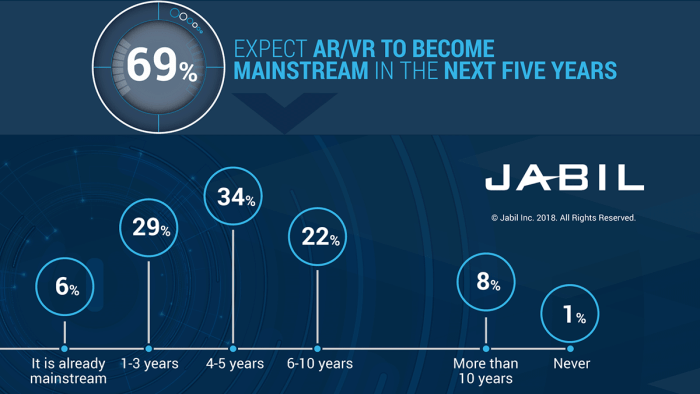
Source: jabil.com
The future of augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) is poised for significant advancements, driven by continuous innovation in hardware, software, and content creation. This evolution promises to integrate AR/VR more deeply into various aspects of daily life, from entertainment to professional applications. Expect a paradigm shift in how we interact with digital information and the physical world.The integration of AR/VR with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), will be a key factor in shaping the future landscape.
This synergistic approach will unlock new possibilities for immersive experiences and intelligent interactions. Already, we see examples of AR overlaying real-world data onto our view, enabling real-time information access.
Future Directions of AR and VR Technology Development
The evolution of AR/VR technology is expected to focus on improved processing power, enhanced sensory immersion, and more intuitive interaction methods. This will involve advancements in algorithms for rendering realistic and detailed virtual environments and creating smoother, more responsive user experiences. The current emphasis on reducing latency and increasing resolution is expected to continue.
Integration of AR and VR with Other Technologies
The convergence of AR/VR with other technologies will create new opportunities for innovation and application. AI-powered AR applications, for instance, will allow for personalized recommendations and interactive experiences tailored to individual needs. Furthermore, AR will seamlessly integrate with IoT devices, enabling real-time feedback and control over physical environments.
Emerging Trends in AR and VR Content Creation
A significant trend in content creation will be the increasing use of interactive and dynamic experiences. This will involve more sophisticated 3D modeling, improved animation, and user-generated content platforms. The demand for high-quality 3D models and animations is already evident, driving the development of more sophisticated software and tools for content creators. This shift towards user-generated content also indicates a shift towards democratization in content creation.
Potential for Personalized AR and VR Experiences
Personalization will be a crucial element in the development of AR/VR experiences. AI algorithms will analyze user preferences and behaviors to tailor content and interactions to individual needs and preferences. For example, an AR application for furniture shopping might suggest furniture pieces based on the user’s past purchases or home design style. This will lead to highly tailored and engaging experiences, improving user satisfaction.
Advancements in AR/VR Hardware
Hardware advancements will play a crucial role in improving the user experience. Expect smaller, lighter, and more affordable headsets with higher resolutions, wider fields of view, and more comfortable designs. Improved tracking technology will enable more precise and natural interactions with the virtual environment. The ongoing evolution of AR glasses and headsets is crucial to wider adoption.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of AR and VR
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Sensory Immersion | Development of more sophisticated haptic feedback, advanced visual displays, and more natural auditory interactions. | Improved realism and engagement in AR/VR experiences. |
| Increased Accessibility | Reduced cost of hardware, improved software interfaces, and development of more intuitive interaction methods. | Wider adoption of AR/VR across diverse user groups and industries. |
| Integration with Existing Technologies | Seamless integration with IoT devices, AI-powered features, and cloud-based platforms. | Expanding the possibilities of AR/VR applications in various sectors. |
| Personalized Experiences | AI-driven customization of content, interactions, and user interfaces. | Creating more engaging and relevant experiences for individual users. |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, augmented reality and virtual reality potential applications are poised to reshape industries and enrich daily life. From entertainment to healthcare, and industrial design to architecture, these immersive technologies are creating new avenues for interaction, learning, and innovation. While challenges and limitations exist, the potential for continued development and integration with other technologies is immense. The future of AR and VR promises exciting advancements and a more immersive, interactive world.









Post Comment