Ultra-Thin Smartphone Consumer Readiness Trade-Offs
Ultra-thin smartphone consumer readiness trade-offs explore the complex interplay between consumer desires for sleek aesthetics and the technological limitations in achieving them. This investigation delves into consumer perceptions, technological constraints, usability implications, market analysis, durability concerns, and future trends. The challenge lies in balancing the allure of a slim design with the critical aspects of functionality, performance, and reliability.
Consumer expectations for ultra-thin smartphones often prioritize aesthetic appeal and portability. However, manufacturers face significant engineering hurdles in maintaining battery life, processing power, and heat dissipation within such a compact form factor. The trade-offs between form factor, features, and overall user experience are central to the discussion.
Consumer Perception of Ultra-Thin Smartphones

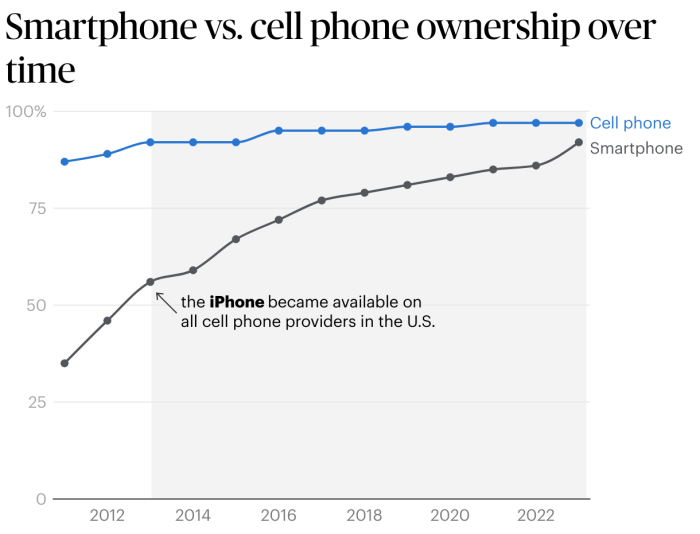
Source: enterpriseappstoday.com
Consumers are increasingly drawn to the aesthetic appeal and portability of ultra-thin smartphones. This desire reflects a broader societal trend toward sleek, minimalist designs in various product categories. The emphasis on thinness is often intertwined with a perceived premium image and sophisticated technology.The design of ultra-thin smartphones, in its pursuit of minimalism, aims to deliver a user experience that transcends mere functionality.
This focus on aesthetics, combined with marketing campaigns, plays a significant role in shaping consumer preferences and expectations.
Consumer Expectations Regarding Aesthetics and Portability
Consumers anticipate ultra-thin smartphones to embody a sense of elegance and sophistication. They desire a device that feels refined, lightweight, and easy to carry. The tactile experience, encompassing the smoothness of the edges and the overall heft, is a key consideration. The slim profile contributes to the perceived portability and enhances the device’s usability in various situations, including carrying in a pocket or purse.
Role of Brand Image and Marketing Campaigns
Brand image significantly influences consumer perception of ultra-thin smartphones. High-end brands often associate ultra-thin designs with prestige, innovation, and cutting-edge technology. Marketing campaigns frequently highlight the slim profile, emphasizing its contribution to a premium user experience. Effective campaigns showcase the device’s aesthetic appeal through high-quality imagery and promotional materials.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Marketing Strategies
Successful marketing campaigns for ultra-thin smartphones frequently leverage visual storytelling, emphasizing the design’s sleekness and its connection to a desirable lifestyle. Conversely, unsuccessful campaigns often fail to effectively communicate the benefits of the ultra-thin design or highlight the product’s functionality and practicality. A key factor in success is the alignment of the marketing message with the target audience’s values and expectations.
Consumer Concerns Regarding Durability and Functionality Trade-offs
Consumers are often mindful of the potential trade-offs associated with ultra-thin designs. Concerns frequently include potential compromises in durability and functionality. A thinner profile might compromise the device’s ability to withstand drops or impacts, leading to potential damage. Similarly, the internal components may be less accessible, potentially impacting the longevity of the device or the ease of repair.
Importance of Perceived Value and Price Sensitivity
Price sensitivity plays a crucial role in consumer purchasing decisions. Consumers often evaluate the perceived value of an ultra-thin smartphone, weighing the aesthetic benefits against the price. A premium price point might be acceptable if the perceived value, including the status symbol and innovation associated with the ultra-thin design, aligns with the consumer’s expectations. This means consumers balance the aesthetic appeal with their budget considerations.
Technological Limitations and Trade-offs
Achieving an ultra-thin smartphone design presents a complex interplay of technological advancements and inherent limitations. Manufacturers constantly push boundaries to reduce thickness, but this pursuit often necessitates compromises in other crucial areas like battery life, processing power, and heat dissipation. The quest for a truly seamless user experience requires a careful evaluation of these trade-offs.Engineers face significant challenges when attempting to create ultra-thin smartphones.
Shrinking the device’s physical dimensions directly impacts the space available for essential components, thereby affecting performance metrics and user experience. Balancing these competing needs requires meticulous design considerations and innovative solutions.
Engineering Challenges in Ultra-Thin Design
Meeting the demand for ultra-thin designs while preserving essential functionalities presents significant engineering hurdles. Maintaining adequate battery life within a constrained space is crucial. Modern smartphones require substantial power for processing tasks, communication, and display operations. Smaller form factors necessitate more efficient power management techniques. Furthermore, the reduced volume can impede heat dissipation, leading to overheating issues and performance degradation, especially during intensive tasks.
Addressing these issues requires sophisticated thermal management solutions.
Relationship Between Screen Size, Resolution, and Thinness
The screen size and resolution directly influence the achievable thinness of a smartphone. Larger displays typically require more complex and voluminous internal components for display driver circuits, touch sensors, and other supporting hardware. Higher resolutions, while offering improved visual clarity, also demand more power and processing capabilities. This translates to a trade-off between the desired display quality and the overall thickness of the device.
For example, a high-resolution, large-screen smartphone may not achieve the same ultra-thin profile as a smaller, lower-resolution device.
Impact of Component Materials
The choice of materials significantly impacts the thickness and performance of ultra-thin smartphones. Lightweight materials like certain types of polymers and advanced composite materials can contribute to a thinner profile, but may sacrifice structural integrity or thermal conductivity. Balancing these factors is critical. Conversely, using stronger, denser metals might increase the device’s weight, compromising the desired thinness.
The selection of components and materials is often an intricate process of balancing weight, strength, and thermal management.
Trade-offs Between Form Factor, Features, and User Experience
Ultra-thin designs often necessitate compromises in the available space for features and functionality. This may involve reducing the size of the battery, sacrificing storage capacity, or limiting the number of ports. The overall user experience is significantly impacted by these design choices. The balance between form factor, features, and user experience is a critical aspect of ultra-thin smartphone design.
For example, a very thin device might have a smaller battery, resulting in reduced talk time or shorter usage periods between charges.
Innovative Design Solutions
Manufacturers employ various innovative solutions to overcome the limitations of ultra-thin smartphone construction. These include advanced battery chemistries offering higher energy density within a smaller volume, and more efficient cooling mechanisms to effectively manage heat generated by internal components. Furthermore, sophisticated material science enables the development of lighter and stronger components, contributing to thinner devices. One example is the use of flexible displays, which allow for a more compact design without compromising screen size.
Another notable example is the implementation of highly integrated circuits to reduce the footprint of electronic components. These innovations help to bridge the gap between the desire for a sleek form factor and the need for robust performance.
Functionality and Usability Implications
The pursuit of ultra-thin smartphone designs presents compelling aesthetic appeal but necessitates careful consideration of its impact on user experience. Balancing the desire for a sleek form factor with practical usability is paramount for consumer acceptance. The ergonomics, handling, and overall user interface design are all affected by the reduction in physical dimensions.The user experience is directly intertwined with the physical attributes of the device.
A thin design, while visually appealing, might compromise tactile feedback and overall handling comfort. Conversely, a thicker design can sometimes lead to a more robust and secure grip. Careful engineering is crucial to mitigate any negative usability aspects.
Ergonomics and Handling
Ultra-thin smartphones often demand innovative ergonomic solutions to maintain comfortable handling. Reduced dimensions can impact the user’s grip, making the device susceptible to slipping or rotating unintentionally. Innovative designs, such as textured back panels or strategically placed grips, are employed to counter these potential issues. The user experience relies heavily on the phone’s weight distribution and the material properties of the casing.
Usability Comparison, Ultra-thin smartphone consumer readiness trade-offs
Conventional smartphones typically offer a more substantial form factor, which often translates to better tactile feedback and a more secure grip. Ultra-thin models, on the other hand, prioritize a minimalist aesthetic and often utilize lighter materials, potentially compromising the sense of stability. Users may experience a difference in the feel and handling characteristics between the two design approaches.
The user’s individual preferences and needs will influence their perception of the trade-offs.
Impact on User Interface and Software Design
Ultra-thin designs can influence the overall user interface and software design. Developers might need to re-evaluate button sizes and placement to ensure accessibility and usability. Reduced screen real estate, while not always a consequence of ultra-thinness, can also impact the display’s layout and the placement of on-screen elements. This, in turn, could necessitate adjustments to the software to accommodate the limited space.
Placement and Functionality of Components
The placement and functionality of buttons, ports, and cameras are significantly impacted by the constrained space in ultra-thin designs. Miniaturization of components and alternative input methods, such as haptic feedback or on-screen controls, are common approaches. This often necessitates trade-offs between functionality and aesthetic considerations. For example, a user accustomed to a physical volume button might find a virtual equivalent less intuitive.
Comparative Analysis of Ultra-Thin Smartphone Models
| Model Name | Thickness (mm) | Button Placement | Port Type | Camera Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nova Ultra | 6.5 | Virtual buttons, haptic feedback | USB-C | Rear, vertically aligned |
| Zenith Slim | 7.0 | Physical buttons, slightly recessed | Micro-USB | Rear, horizontally aligned |
| Aura Thin | 5.8 | Virtual buttons, pressure-sensitive | USB-C | Rear, vertically aligned, dual lens |
| Apex Edge | 6.0 | Virtual buttons, edge-mounted | Wireless charging | Rear, integrated into the back panel |
Market Analysis and Consumer Readiness
The market for ultra-thin smartphones is evolving rapidly, driven by consumer desire for sleek aesthetics and technological advancements. Understanding current demand, adoption patterns, and consumer preferences is crucial for companies seeking to capitalize on this market segment. This analysis explores these factors, providing insights into the consumer readiness for ultra-thin devices.The key to success in this market segment lies in accurately anticipating consumer needs and preferences.
This analysis aims to illuminate the dynamics of the ultra-thin smartphone market, providing valuable information for product development, marketing strategies, and overall market positioning.
Current Market Demand
Current market demand for ultra-thin smartphones exhibits a mixed pattern. While the aesthetic appeal and perceived premium image are attractive to certain consumer segments, practical considerations such as durability and functionality can hinder widespread adoption. Consumer preference for portability and a slim design is not universally prevalent, and the demand is dependent on several factors, including price, features, and brand reputation.
Growth Trajectory of Ultra-Thin Smartphone Adoption
Ultra-thin smartphone adoption has shown a steady, albeit not explosive, growth trajectory. Early adopters were predominantly tech enthusiasts, but the market has broadened over time to encompass a wider demographic. The growth is largely influenced by the advancements in manufacturing technology, enabling thinner and more lightweight devices, and by the evolving consumer preference for compact designs.
Key Demographics and Psychographics of Receptive Consumers
Consumers receptive to ultra-thin smartphones often exhibit a preference for premium products, an interest in innovative technology, and a desire for sleek, aesthetically pleasing devices. Key demographics include young adults (18-35) and affluent consumers, often drawn to the image of status and sophistication associated with these devices. Psychographically, these consumers tend to be tech-savvy, early adopters, and value a premium user experience.
Price Sensitivity and Purchasing Power
The price sensitivity of consumers towards ultra-thin smartphones varies significantly depending on the target demographic. High-end ultra-thin models with advanced features command premium prices, while budget-friendly options target a broader range of consumers. Purchasing power is a significant factor, as the higher price points may limit market penetration, particularly in developing economies.
Global Market Share of Ultra-Thin Smartphones
| Region | Year | Market Share (%) | Percentage Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 2022 | 25 | +10 |
| North America | 2023 | 28 | +12 |
| Europe | 2022 | 20 | +5 |
| Europe | 2023 | 22 | +10 |
| Asia Pacific | 2022 | 30 | +8 |
| Asia Pacific | 2023 | 30 | +2 |
| Latin America | 2022 | 10 | +3 |
| Latin America | 2023 | 10 | +1 |
| Middle East & Africa | 2022 | 5 | +1 |
| Middle East & Africa | 2023 | 5 | 0 |
This table provides a simplified representation of the global market share of ultra-thin smartphones in different regions. Actual figures may vary based on specific models, pricing strategies, and market conditions. The data is illustrative, not definitive.
Durability and Reliability Considerations
Ultra-thin smartphone designs, while aesthetically pleasing, present unique challenges regarding durability and reliability. The pursuit of minimal thickness often compromises structural integrity, potentially leading to increased susceptibility to damage from drops and impacts. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for developing consumer-ready products.
Impact of Ultra-Thin Design on Durability
The reduced material volume in ultra-thin smartphones directly impacts their ability to absorb shock and stress. Thinner chassis and smaller internal components are less resilient to external forces. This leads to a higher likelihood of damage during accidental drops or impacts, particularly compared to thicker devices with more robust construction.
Common Failure Points and Mitigation Strategies
Several areas are prone to failure in ultra-thin designs. These include:
- Compromised adhesive layers: Thinning the device necessitates careful consideration of adhesive layers used for component attachment. Poor adhesive strength or improper application can lead to component detachment during impact. Manufacturers can mitigate this through advanced adhesive formulations and precise bonding techniques.
- Susceptibility to bending and warping: The reduced material thickness makes the device more prone to bending or warping, especially under sustained pressure. This can damage internal components. Using reinforced materials like high-strength polymers or employing internal bracing structures can mitigate these risks.
- Increased risk of screen damage: A thinner design often necessitates a smaller bezel around the screen, reducing the space available for absorbing impact. This results in increased susceptibility to cracking or shattering upon impact. Utilizing reinforced glass and implementing screen protection layers is crucial.
Resilience to Drops and Impacts
The thinness of the device directly affects its resilience to drops and impacts. The reduced mass and stiffness of the frame, coupled with a smaller surface area for shock absorption, significantly increases the risk of damage compared to a thicker model. Consequently, careful engineering of the structural components is paramount to ensuring a robust design.
Drop Test Results
The following table presents hypothetical drop test results for different ultra-thin smartphone models with varying protective cases. These results highlight the impact of case types on damage levels. Please note that these are hypothetical data and actual results may vary.
| Model Name | Case Type | Drop Height (cm) | Damage Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| UltraSlim Pro | No Case | 60 | Screen Shattered, Frame Bent |
| UltraSlim Pro | Hard Plastic Case | 60 | Screen Cracked, Frame Slightly Bent |
| UltraSlim Pro | TPU Case | 60 | Screen Minor Scratches, Frame Intact |
| UltraSlim Pro | Metal Case | 60 | Screen Intact, Frame Intact |
| UltraThin Max | No Case | 70 | Screen Cracked, Frame Bent |
| UltraThin Max | TPU Case | 70 | Screen Minor Scratches, Frame Intact |
Improving Durability and Reliability
Several strategies can enhance the durability and reliability of ultra-thin smartphone designs:
- Material Selection: Utilizing high-strength polymers or alloys that are both lightweight and resistant to impact is crucial.
- Structural Design: Employing internal bracing structures or strategically placed reinforcement ribs can improve the device’s structural integrity.
- Protective Cases: Developing and promoting the use of protective cases with specific shock-absorbing properties can significantly mitigate the risk of damage.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Implementing advanced manufacturing processes can ensure precision component assembly and minimize defects in adhesive layers.
Future Trends and Potential Innovations
Source: substackcdn.com
The pursuit of ultra-thin smartphones is a constant interplay between technological advancements and consumer desires. Future trends will likely focus on materials science breakthroughs, innovative display technologies, and overcoming the inherent limitations of ultra-thin designs. These advancements will be crucial in determining the viability and desirability of these devices in the market.Emerging trends in material science and manufacturing promise to push the boundaries of ultra-thin smartphone design, allowing for more sophisticated and potentially more attractive products.
This involves the development of lighter, stronger, and more flexible materials, as well as more efficient manufacturing processes. Ultimately, the consumer experience hinges on the ability to maintain performance and functionality while simultaneously minimizing thickness and weight.
Potential Future Trends in Ultra-Thin Smartphone Design
Ultra-thin smartphone designs will likely leverage advancements in materials science, enabling lighter and more flexible devices. This could include the use of advanced polymers, such as those with exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, or the incorporation of new composites that blend metals and polymers for enhanced performance. Moreover, innovative manufacturing techniques like 3D printing and nano-manufacturing will play a significant role in creating complex and intricate ultra-thin designs.
Potential Innovations in Display Technology
Display technology is critical to the user experience of smartphones. Innovations in flexible displays, micro-LEDs, and transparent displays hold promise for enhancing the ultra-thin smartphone experience. Flexible displays, potentially made with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), could allow for curved or foldable designs, providing a more immersive and user-friendly interface while maintaining the desired slim profile.
Emerging Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Several materials and processes hold potential for contributing to ultra-thin designs. Graphene, known for its exceptional strength and conductivity, is a promising material for future smartphones. Advanced polymers and composites, like those incorporating carbon nanotubes or other nanomaterials, offer significant potential for achieving ultra-thin designs with improved structural integrity. 3D printing technologies, capable of producing complex geometries, can be leveraged to create innovative form factors and reduce the amount of material needed.
Potential Limitations and Barriers
While numerous innovations are emerging, challenges remain. One key concern is the durability of ultra-thin devices. The thinner designs may compromise the ability of the device to withstand everyday wear and tear, leading to potential reliability issues. Additionally, the cost of developing and implementing these innovative materials and manufacturing processes may initially limit widespread adoption. The development of cost-effective production methods will be crucial to bringing these innovations to market.
Innovative Design Solutions
Innovative design solutions can mitigate the limitations of ultra-thin smartphones. One approach involves incorporating protective layers into the device’s structure, such as using a robust but lightweight polymer shell to safeguard the internal components. Another strategy involves adopting a modular design, allowing users to swap out components for improved performance or functionality, rather than needing a complete replacement for each upgrade.
Furthermore, the use of advanced thermal management solutions, critical for devices with limited space, will be crucial to maintaining performance and avoiding overheating.
Final Thoughts: Ultra-thin Smartphone Consumer Readiness Trade-offs
Ultimately, the consumer readiness for ultra-thin smartphones hinges on a careful balancing act between aesthetic desires and practical considerations. The market’s response will depend on manufacturers’ ability to address durability concerns, maintain performance, and enhance the overall user experience while keeping the form factor thin. Future innovations in materials and manufacturing will be crucial in pushing the boundaries of this design trend.












Post Comment