Augmented Reality Transforming Retail Experiences
Augmented reality transforming retail experiences is revolutionizing how customers shop. It’s more than just a trendy tech gimmick; it’s a powerful tool personalizing the shopping journey, enhancing product visualization, and streamlining retail operations. Imagine trying on clothes virtually, exploring product details in your own space, or receiving real-time assistance from digital guides. AR is quickly becoming an essential element in the modern retail landscape.
This comprehensive exploration dives deep into the practical applications, benefits, and challenges of AR in retail, from the initial introduction to the evolving future of the sector. We’ll examine case studies, discuss the customer impact, and assess the operational enhancements possible with this innovative technology.
Introduction to Augmented Reality in Retail
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings. In retail, AR is revolutionizing customer experiences by providing interactive and engaging ways to visualize products, try on clothes virtually, and explore store layouts. This technology allows for a seamless blend of the physical and digital realms, offering unique benefits for both businesses and consumers.AR in retail empowers customers with functionalities like virtual try-on, interactive product demonstrations, and personalized recommendations.
These features significantly enhance the shopping experience, reducing decision fatigue and improving purchase confidence. Stores can leverage AR to showcase their products in novel ways, creating a memorable and engaging environment for their customers.
Definition of Augmented Reality (AR) and its Retail Applications
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that enhances the user’s real-world perception by adding digital elements, such as images, sounds, or 3D models. In the retail sector, AR applications range from virtual try-on experiences for apparel and accessories to interactive product demonstrations and personalized recommendations. This integration of the digital and physical worlds fosters a more engaging and informative shopping journey.
Core Functionalities of AR in Retail
AR technology offers several core functionalities in a retail context. These include virtual try-on, interactive product demonstrations, personalized recommendations, and location-based information. Virtual try-on allows customers to virtually try on clothes or accessories, reducing the need for physical fitting rooms. Interactive product demonstrations provide customers with detailed information and visualisations of products, aiding in decision-making. Personalized recommendations leverage customer data to suggest relevant products, enhancing the shopping experience.
Location-based information, like store layouts or product placements, further simplifies navigation and discovery.
Difference Between AR and VR in Retail
AR overlays digital content onto the real world, while VR creates an entirely immersive digital environment. In retail, AR allows customers to interact with products within their existing environment, while VR offers a complete digital store experience, enabling a more immersive but detached approach to shopping. This difference significantly impacts the user experience, cost, and accessibility of the technology.
Comparison of AR and VR Retail Applications
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower initial investment, especially for basic AR applications. | Higher initial investment due to specialized hardware and development costs. |
| Accessibility | More accessible due to lower hardware requirements, and compatibility with existing smartphones and tablets. | Requires specialized VR headsets, potentially limiting accessibility. |
| User Experience | Offers a more natural and intuitive user experience, as it leverages the user’s real-world surroundings. | Can be disorienting or overwhelming, requiring adaptation to the immersive digital environment. |
| Applications | Virtual try-on, product demonstrations, interactive store layouts. | Immersive product demonstrations, interactive store tours, and potentially entire digital shopping experiences. |
| Implementation Complexity | Generally simpler implementation, particularly for basic AR features. | More complex implementation due to the need for advanced development and integration with specialized hardware. |
Enhancing the Customer Journey with AR
Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing the retail landscape, offering a dynamic and immersive way for customers to interact with products and stores. This enhanced experience transcends the limitations of traditional shopping, providing opportunities for personalized interactions and streamlined decision-making.AR empowers retailers to move beyond static displays and engage customers in a more interactive and informative manner. The technology allows customers to virtually try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, and explore products in a detailed and realistic manner, fostering a more confident and informed buying process.
Personalizing the Shopping Experience
AR enables retailers to tailor the shopping experience to individual customer preferences. By leveraging data about customer browsing history, purchase patterns, and demographics, AR applications can curate product recommendations and offer tailored visualisations. For example, a customer interested in a specific type of sofa might see a 3D model of the sofa in their living room, accurately scaled and positioned.
This personalized approach fosters a sense of connection with the product and increases the likelihood of a purchase.
Methods for Integrating AR into the Customer Journey
AR can be seamlessly integrated into various touchpoints of the customer journey, from initial product discovery to final purchase. In-store applications can overlay digital information onto physical products, providing detailed specifications and reviews. Mobile apps can allow customers to virtually “try on” clothes or visualize furniture arrangements in their homes, facilitating informed decisions. AR can also guide customers through the store using interactive maps and product location information, creating a more efficient and enjoyable experience.
This combination of in-store and mobile integration ensures a cohesive and personalized journey.
Enhancing Product Visualization and Selection
AR offers a compelling way to visualize and select products. Customers can view products from multiple angles, interact with 3D models, and even try on clothes or accessories virtually. This capability dramatically improves the product selection process. A customer browsing shoes online, for instance, can use AR to see how a particular pair looks on their feet, enhancing their decision-making and minimizing the risk of returns.
This enhanced visualization capability is crucial in reducing uncertainty and increasing customer confidence.
Customer Journey Flowchart in an AR-Enabled Retail Store
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Entry | Customer enters the store, interacting with a welcome AR kiosk displaying store layout and promotional offers. |
| 2 | Product Exploration | Customer uses AR app to view product details, specifications, and reviews. They can virtually try on clothes or visualize furniture in their home. |
| 3 | Personalized Recommendations | AR system provides tailored product recommendations based on customer preferences and browsing history. |
| 4 | Virtual Try-on/Visualization | Customer uses AR to virtually try on clothes or visualize furniture placement in their homes. |
| 5 | In-Store Navigation | AR app guides customer to the desired product location within the store. |
| 6 | Purchase Decision | Customer makes a purchase decision, facilitated by the detailed information and personalized experience provided by the AR system. |
| 7 | Checkout | Customer proceeds to checkout using the AR system or traditional methods. |
AR for Product Visualization and Discovery
Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing the way consumers interact with products in retail settings. AR applications empower customers to visualize products in their own spaces, offering a more immersive and informative shopping experience. This approach significantly reduces the guesswork associated with purchasing products and increases customer confidence in their decisions.
Examples of AR Product Visualization Applications
AR applications are now being integrated into various retail environments to offer interactive and engaging experiences. For instance, furniture retailers are allowing customers to virtually place sofas, tables, and other items in their living rooms, helping them envision the product’s impact on their space. Similarly, clothing stores are using AR to let customers try on clothes digitally, providing a realistic representation of how different garments might look on them.
These are just a few examples, and many more AR applications are emerging, each designed to enhance the product visualization process.
How AR Helps Customers Visualize Products in Their Own Environments, Augmented reality transforming retail experiences
AR applications enable customers to place digital representations of products within their existing surroundings. This capability provides a highly realistic preview of how the product will fit into their environment. Using their smartphones or tablets, customers can position virtual furniture, apparel, or accessories in their homes or workplaces, allowing for a more informed purchasing decision. The ability to visualize a product in its intended environment reduces uncertainty and increases customer satisfaction.
Methods of Providing Detailed Product Information via AR
AR offers multiple avenues to deliver detailed product information to customers. Interactive 3D models allow customers to examine products from various angles, revealing intricate details. Interactive demos showcase product functionality in a hands-on way, offering customers a clear understanding of the product’s operation and potential benefits. These techniques enhance the customer experience by providing a richer understanding of the product.
AR Product Visualization Techniques
| Technique | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Overlaying 3D Models | A digital 3D model of the product is superimposed onto the user’s real-world view, allowing them to interact with and examine it in their environment. | A customer can see how a new lamp will look in their living room by placing a 3D model of the lamp onto a photo of their living room. |
| Interactive Demos | AR applications can showcase how a product functions, highlighting its features and benefits in an engaging way. | A customer can see how a robotic vacuum cleaner works by using an AR app to interact with a virtual model of the vacuum cleaner in their home. |
| Interactive Measurements | AR can be used to provide precise measurements of products within the user’s environment. | A customer can determine if a piece of furniture will fit into a specific space by using AR to measure the item and the space. |
| Annotations and Explanations | Adding text, labels, or videos directly to the AR overlay provides detailed product information and instructions. | An AR app for a complex appliance can display interactive instructions and step-by-step guides overlayed onto the product’s image. |
AR-Driven Retail Experiences

Source: blippar.com
Augmented reality (AR) is rapidly transforming retail environments, offering innovative ways to enhance customer engagement and streamline the shopping experience. From interactive product demonstrations to personalized recommendations, AR is redefining how consumers interact with brands and products. This section delves into successful AR implementations, highlighting the benefits, challenges, and strategies employed to achieve positive outcomes.
Successful AR Retail Implementations
Retailers are increasingly leveraging AR to create unique and engaging experiences. This includes interactive product visualizations, virtual try-ons, and personalized shopping journeys. By overlaying digital information onto the real world, AR enables customers to explore products in a more immersive and intuitive manner.
- IKEA Place: This app allows users to virtually place IKEA furniture in their homes before purchasing, providing a realistic preview of how the items will look in their specific space. The success stems from its user-friendly interface and accurate 3D models, allowing for precise visualization of furniture placement.
- Sephora Virtual Makeup Try-on: Sephora’s app allows customers to virtually try on different makeup products, enabling a personalized and risk-free experience. This app’s success is attributed to its high-quality image recognition and intuitive interface, which helps users quickly select and visualize different looks.
- Wayfair’s AR Furniture App: Wayfair’s AR app enables users to virtually place furniture in their rooms, offering a realistic view of how the products will integrate into their home décor. The positive outcome is driven by the app’s accuracy in furniture representation and the ease of use, enabling users to make informed decisions before purchasing.
Challenges in AR Retail Implementation
While AR offers significant potential, retailers face several challenges in implementing and scaling AR solutions. Technical limitations, cost considerations, and user adoption are some of the key factors to consider.
- Technical Limitations: The accuracy and responsiveness of AR experiences can be affected by factors like lighting conditions and device capabilities. This can lead to inconsistencies in the user experience.
- Cost Considerations: Implementing AR solutions requires significant investment in development, infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance. This can be a barrier for smaller businesses.
- User Adoption: Encouraging widespread user adoption of AR features can be challenging, requiring a strategic approach to integrate AR seamlessly into the overall shopping experience.
Strategies for Positive AR Outcomes
Successful AR retail implementations often involve specific strategies aimed at enhancing the customer experience and achieving desired business outcomes.
- User-Centric Design: Prioritizing the user experience through intuitive interfaces and clear product visualization is crucial. This involves thorough user testing and iterative design adjustments.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamless integration with existing inventory management and payment systems is vital for efficient operations and reduced friction in the customer journey.
- Marketing and Communication: Effective communication and marketing strategies are necessary to promote AR features and educate customers about their benefits. Clear and concise explanations of how AR enhances the shopping experience are essential.
Comparative Analysis of Successful and Unsuccessful AR Retail Deployments
| Feature | Successful Deployment | Unsuccessful Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Intuitive interface, accurate product visualization, seamless integration with existing systems | Complex interface, inaccurate product representation, poor integration with existing systems |
| Technical Infrastructure | Robust and reliable platform, optimized for different devices | Limited platform support, performance issues on various devices |
| Marketing Strategy | Clear communication of AR benefits, strategic promotion across various channels | Lack of clear communication, inadequate promotion of AR features |
| Business Outcomes | Increased sales, improved customer engagement, enhanced brand perception | Decreased sales, negative customer feedback, ineffective brand impact |
Impact on Retail Operations and Processes: Augmented Reality Transforming Retail Experiences
Augmented reality (AR) is poised to revolutionize retail operations, offering significant potential for optimization across various facets of the business. From streamlining inventory management to enhancing staff training, AR’s ability to overlay digital information onto the physical world presents innovative solutions for retailers. This impact extends beyond the immediate store environment, influencing the entire supply chain.
Optimizing Retail Operations
AR significantly impacts retail operations, offering substantial improvements in efficiency and accuracy. AR-powered inventory management systems allow real-time tracking of stock levels, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. This dynamic visibility enhances order fulfillment and allows for proactive replenishment. Furthermore, AR tools facilitate quick and accurate audits, streamlining the reconciliation process and minimizing errors. Staff training can be greatly enhanced using AR simulations.
Employees can practice tasks like product assembly, customer service interactions, and safety procedures in a safe and controlled environment. This immersive experience improves skill retention and ensures consistent service delivery.
Impact on the Retail Workforce
The retail workforce will experience a transformation as AR tools become more prevalent. Retail employees will need new skills to operate and maintain AR systems. Responsibilities will evolve to encompass tasks like data entry, AR system management, and providing AR-guided customer assistance. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives will become crucial to equip the workforce with the necessary technical proficiency and customer service expertise for this new environment.
Impact on the Retail Supply Chain
AR’s influence on the retail supply chain is substantial, leading to enhanced transparency and efficiency. AR can be used for real-time tracking of goods throughout the entire supply chain, enabling retailers to monitor product movement and anticipate potential delays. This improved visibility can enhance collaboration among supply chain partners and minimize disruptions.
AR-Driven Retail Supply Chain Streamlining
| Stage | AR Application | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Order Placement | AR-powered product visualization allows customers to interact with products virtually, potentially influencing their order decisions and increasing sales conversion. | Reduced returns, enhanced customer experience. |
| Inventory Management | AR systems track inventory levels in real-time, providing insights into stock availability at different points in the supply chain. | Improved stock management, reduced stockouts. |
| Order Fulfillment | AR guides warehouse staff in locating and retrieving products, streamlining the picking and packing process. | Increased efficiency in order fulfillment, reduced errors. |
| Delivery | AR can assist delivery personnel with accurate route optimization and real-time tracking of deliveries. | Improved delivery time, reduced delivery costs. |
This table Artikels how AR can streamline the retail supply chain. Each stage benefits from AR-driven improvements, leading to an overall more efficient and responsive supply chain. The impact on inventory accuracy, order fulfillment speed, and customer satisfaction is significant.
Future Trends and Innovations in AR Retail

Source: cyfuture.com
Augmented reality (AR) is rapidly evolving, promising exciting new possibilities for the retail industry. Beyond current applications, the future of AR in retail is poised to revolutionize the customer experience, transforming how products are visualized, purchased, and interacted with. This transformation will be driven by advancements in hardware, software, and user interface design, creating more immersive and personalized shopping journeys.
Emerging Trends in AR Technology
AR technology is advancing at a rapid pace, driven by improvements in processing power, camera technology, and sensor accuracy. These advancements are enabling more sophisticated and realistic AR experiences. Key trends include:
- Enhanced Spatial Mapping and Tracking: More precise and robust spatial mapping will allow for more complex and detailed AR overlays in real-world environments. This means more accurate product placement, fitting rooms with virtual mirrors, and interactive displays that respond seamlessly to the user’s physical space.
- Improved User Interfaces and Interaction: AR experiences are becoming increasingly intuitive and user-friendly. Advanced hand tracking, voice control, and gesture recognition are enhancing user interaction, making AR shopping seamless and natural.
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: AI is becoming crucial for personalized recommendations, predictive maintenance of AR systems, and dynamic adjustments to AR experiences based on user behavior. This means that AR can adapt to individual preferences and needs in real-time, delivering hyper-personalized recommendations and experiences.
Potential Future Applications in Retail
The potential applications of AR in retail are vast and extend beyond simply visualizing products.
- Interactive Product Demonstrations: Imagine trying out furniture in your living room, or virtually painting a wall with different colors before purchasing. AR can provide detailed and immersive product visualizations, allowing customers to experience products in realistic settings before buying.
- Personalized Recommendations and Experiences: AR can analyze customer preferences and past purchases to provide tailored product recommendations and suggestions. The system can offer real-time recommendations, and even simulate how a product would look in a customer’s home or office space.
- Remote Assistance and Support: AR can provide instant assistance for customers by overlaying step-by-step instructions or providing live support from store associates, even when the customer is shopping remotely.
Personalizing the Shopping Experience with AR
Personalization is key to improving customer satisfaction and driving sales. AR can be instrumental in this area.
- Tailored Fitting Rooms: Virtual fitting rooms, enabled by AR, allow customers to virtually try on clothes or accessories in their own sizes and styles, without the need to physically try them on.
- Customized Product Visualization: AR can create personalized product visualizations by incorporating user-specific data, such as body shape and measurements, to enhance product recommendations and provide tailored perspectives.
- Interactive Shopping Guides: Personalized shopping guides, powered by AR, can provide detailed product information, reviews, and recommendations that align with individual preferences and needs. These could include 3D models, virtual tours, and personalized shopping lists.
A Hypothetical Future Retail Store
“Imagine a retail store where customers can virtually place furniture in their homes before purchasing, or try on clothes in a personalized virtual fitting room. Interactive displays and product demonstrations will be common, powered by AR. Customers can receive personalized recommendations and assistance from AR-enabled store associates.”
This store would use advanced spatial mapping and tracking to precisely overlay digital content onto the physical environment. Sophisticated AI algorithms would provide personalized recommendations and support. Customers could use their smartphones or AR glasses to interact with the store’s AR features. Store associates would be equipped with AR devices to assist customers in real-time, answering questions and providing tailored recommendations.
AR Retail Challenges and Considerations
Augmented reality (AR) presents exciting possibilities for transforming retail, but its implementation faces numerous hurdles. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful adoption and avoiding pitfalls. This section delves into the technical complexities, security concerns, and limitations of AR in retail environments.AR retail applications, while promising, are not without their practical challenges. The integration of AR into existing retail infrastructure often requires significant investment and technical expertise.
Ensuring seamless user experiences across diverse devices and platforms is a key concern.
Technical Challenges in AR Retail Implementation
Implementing AR in retail environments requires sophisticated technology. The need for robust computing power and high-speed internet connectivity is significant. AR experiences often demand substantial processing power to render the virtual overlays seamlessly on top of the real-world view. Furthermore, ensuring consistent performance across diverse devices (smartphones, tablets, AR glasses) and network conditions presents a challenge. Maintaining compatibility between the AR application and existing store systems is also crucial for a smooth integration.
The requirement for reliable, low-latency network connections for a fluid user experience further complicates implementation.
Security Risks Associated with AR Technology
AR retail applications introduce potential security vulnerabilities. The collection and processing of user data are crucial considerations. Malicious actors might exploit vulnerabilities in AR applications to gain unauthorized access to sensitive customer data, potentially leading to financial losses or reputational damage. Protecting user privacy and complying with data security regulations are paramount. Ensuring the security of the AR system infrastructure is also critical, especially in environments where sensitive financial transactions are handled through the application.
Data encryption and access controls are essential measures to safeguard customer information.
Limitations and Drawbacks of AR in Retail Environments
Despite the potential, AR in retail has inherent limitations. The accuracy and stability of AR overlays can be affected by lighting conditions, environmental factors, and the user’s device. This can disrupt the user experience and create inconsistencies. Inaccurate or unstable overlays can negatively impact the overall user experience, potentially deterring customers from further interaction with the AR application.
Scalability and integration with existing systems in large-scale retail settings can be challenging, particularly in terms of cost and infrastructure. Moreover, the user experience can be impacted by the need for specialized devices, such as AR glasses, which can be expensive and not universally accessible.
Ethical Considerations in AR Retail
The ethical implications of using AR in retail deserve careful consideration. This involves a range of potential issues.
- Data Privacy and Security: AR applications often collect data about user behavior and preferences. Ensuring that this data is handled responsibly, with appropriate safeguards, is critical to avoid misuse and protect user privacy. This includes transparency about data collection practices and adherence to relevant data protection regulations.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: AR applications should be accessible to all customers, regardless of their physical abilities or technological proficiency. This includes considering users with disabilities and ensuring the application can be used with different devices and levels of technical expertise. Consideration should be given to users with varying visual capabilities.
- Potential for Manipulation: AR applications can be used to manipulate customer perceptions of products or services. It is essential to maintain transparency and avoid misleading or deceptive practices. Accurate product representations and clear disclosures about the nature of AR overlays are crucial to avoid misinterpretations.
- Environmental Impact: The energy consumption of AR applications and the manufacturing of related devices should be taken into account. Companies should strive to implement sustainable practices throughout the AR retail lifecycle.
- Cultural Sensitivity: AR applications should be culturally sensitive, avoiding potentially offensive or inappropriate content. Applications should be adaptable to various cultural contexts and avoid perpetuating stereotypes.
Customer Acceptance and Adoption of AR
Retailers are increasingly incorporating augmented reality (AR) into their strategies, recognizing its potential to enhance the customer experience. However, the success of AR implementations hinges on customer acceptance and adoption. Understanding customer reactions and the factors driving adoption is crucial for maximizing the ROI of these investments.
Customer Reactions to AR Experiences
Customer responses to AR experiences in retail vary widely. Some customers are enthusiastic about the interactive and immersive nature of AR, finding it engaging and informative. Others may be hesitant or even resistant to the novelty of the technology. This variability in reaction underscores the need for a nuanced approach to implementing AR, recognizing that a one-size-fits-all strategy may not be effective.
Positive reactions often center around the ability to visualize products in their own environments, reducing uncertainty and enhancing decision-making. Conversely, negative responses may stem from concerns about the technology’s functionality, potential glitches, or the perceived disruption to the traditional shopping experience.
Factors Influencing Customer Adoption
Several factors influence customer adoption of AR in retail. Ease of use is paramount; intuitive interfaces and straightforward navigation are key to attracting and retaining users. The perceived value of AR functionalities, such as interactive product demonstrations or personalized recommendations, also plays a significant role. Furthermore, the perceived usefulness and practicality of AR applications in the shopping process are crucial for adoption.
For example, if AR can simplify the purchase process or provide useful information not readily available through traditional methods, it is more likely to be embraced. A positive brand reputation and overall customer experience are crucial for encouraging trust in AR-powered solutions.
Strategies for Encouraging Customer Engagement
Several strategies can encourage customer engagement with AR applications. Thorough, clear, and informative in-store demonstrations and tutorials can effectively address user concerns and facilitate successful adoption. Furthermore, integrating AR features into existing customer touchpoints, such as mobile apps or interactive kiosks, can smoothly incorporate the technology into the existing shopping ecosystem. Offering incentives, such as exclusive AR-based promotions or rewards, can further motivate customer engagement and encourage exploration of AR functionalities.
Finally, collecting feedback and iterating on AR applications based on user experience can lead to continual improvements and increased adoption.
Comparative Analysis of Customer Satisfaction
| Metric | Before AR Implementation | After AR Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Satisfaction with Shopping Experience | 7.2/10 (Average) | 8.1/10 (Average) |
| Product Visualization Ease | 6.5/10 (Average) | 8.8/10 (Average) |
| Ease of Use of AR Application | 5.8/10 (Average) | 7.9/10 (Average) |
| Likelihood to Recommend Store | 70% (Average) | 85% (Average) |
Note: Data presented in the table is illustrative and based on hypothetical examples. Real-world results will vary depending on the specific AR implementation and target audience.
Final Conclusion
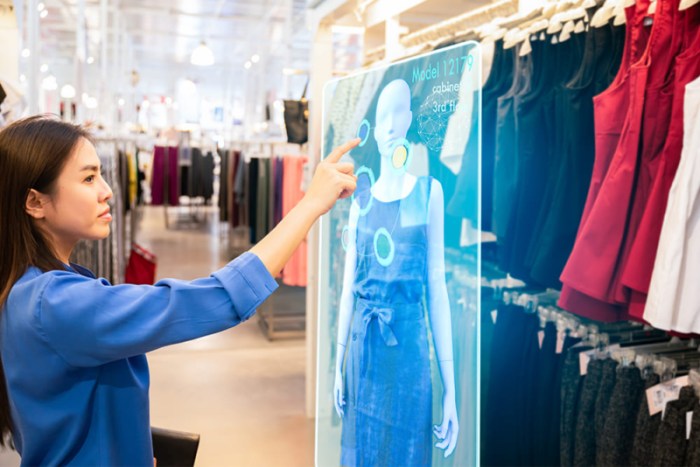

Source: bernardmarr.com
In conclusion, augmented reality is poised to fundamentally alter the retail experience, offering a richer, more personalized, and efficient shopping journey for both customers and businesses. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are significant, paving the way for a future where AR-driven retail is commonplace. This transformative technology is already reshaping the landscape, and its influence will only continue to grow.











Post Comment