Forgotten Phones Ahead Of Their Time
Forgotten phones ahead of their time sets the stage for this captivating exploration. These devices, brimming with innovative technology, often fell short of market success despite their groundbreaking features. We’ll delve into the reasons behind their eventual obscurity, examining the technological advancements, market dynamics, design choices, and manufacturing challenges that ultimately led to their demise.
This investigation will uncover the compelling stories behind these innovative, yet forgotten, mobile phones. From the groundbreaking designs to the market forces that shaped their fates, we’ll trace the evolution of these devices and learn from the lessons of their underappreciated innovations.
Defining “Forgotten Phones Ahead of Their Time”
The phrase “forgotten phones ahead of their time” encapsulates a fascinating phenomenon in the history of mobile technology. These devices, often possessing innovative features and designs, were seemingly destined for greatness, but for various reasons, they failed to capture the market’s imagination or achieve widespread adoption. This often leaves us pondering what might have been.This exploration delves into the criteria for a phone to be considered “ahead of its time,” examines the factors that led to their eventual obscurity, and highlights notable examples.
We will also look at the comparison between these visionary devices and their contemporary counterparts, illuminating the crucial differences and showcasing the technological leaps these often-overlooked phones represented.
Criteria for a Phone to be Considered “Ahead of Its Time”
A phone is considered “ahead of its time” when its features or design anticipate technological advancements or user needs that were not widely prevalent at the time of its release. This often manifests in unique capabilities, such as early attempts at touchscreens, advanced camera systems, or innovative communication protocols. These devices frequently incorporate technologies or concepts that would only become commonplace years later.
Furthermore, the phone’s aesthetic or ergonomics may also be considered ahead of its time, pioneering design principles that later became industry standards.
Factors Contributing to a Phone’s Eventual “Forgetting”
Several factors contributed to the relative obscurity of these pioneering phones. Market timing, insufficient marketing or branding, technological limitations at the time, and the presence of more readily accessible and commercially successful alternatives often played a crucial role. Furthermore, societal acceptance and consumer preferences can dramatically influence a product’s success. Sometimes, the phone was simply ahead of its time for the general public’s comfort level and willingness to adopt the technology.
Comparison of Forgotten Phones with Contemporary Ones
| Characteristic | Forgotten Phones | Contemporary Phones |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Early LCDs, monochrome displays, or rudimentary touchscreens | High-resolution OLED, AMOLED, and other advanced displays |
| Camera Capabilities | Limited megapixels, basic image processing | High-megapixel sensors, advanced image stabilization, and sophisticated software |
| Connectivity | Limited or outdated cellular standards, slower data speeds | Fast 5G or 4G networks, high-speed Wi-Fi |
| Operating System | Proprietary or experimental operating systems | Standardized operating systems like iOS and Android |
| Design and Form Factor | Unique, sometimes bulky or unconventional designs | Sleek, streamlined, and compact designs |
Notable Examples of Forgotten Phones
A notable example is the Motorola ROKR E1, a 2005 music phone. While it integrated with the Apple iPod, its limited storage and interface ultimately hindered its popularity. Similarly, the IBM Simon Personal Communicator, released in 1993, is often cited as a precursor to modern smartphones with its touch screen and other advanced features. The Sony Clié PEG-T750, with its advanced PDA features, showcased early iterations of mobile computing.
Technological Innovations
Forgotten phones, often ahead of their time, showcased innovative technologies that, while not always immediately embraced, laid the groundwork for features in later models. These devices represent a fascinating glimpse into the evolution of mobile technology, highlighting the interplay between ambition, limitations, and the eventual triumph of certain designs over others.These phones frequently employed groundbreaking technologies for their era, anticipating advancements that became commonplace in subsequent generations.
However, the context of their time, including manufacturing capabilities and market acceptance, played a crucial role in their eventual fate. The innovations, while sometimes groundbreaking, often faced challenges in execution and adoption.
Key Technological Innovations
The forgotten phones often incorporated features that were remarkably progressive for their time. These included innovative display technologies, advanced camera systems, and unique input methods. Each element, when examined in its historical context, reveals a level of technological foresight that sometimes exceeded the capabilities of the era.
- Display Technologies: Early mobile phones experimented with different display technologies, like monochrome LCDs, or even electrophoretic displays, attempting to achieve a high-resolution display in a small space. These early attempts, while not as sharp or vibrant as modern displays, were revolutionary at the time. They were an essential step in the quest for portable and informative displays. Limitations were evident in their limited color range and resolution, rendering some applications difficult to view.
The evolution of display technology in these phones demonstrated a clear progression toward higher resolutions and color depth, which was crucial for user experience.
- Camera Systems: Some models featured early camera technology that, while rudimentary compared to current standards, represented a significant advancement in integrating photography into portable devices. These cameras, often with low megapixel counts and limited zoom capabilities, paved the way for the sophisticated camera systems found in today’s smartphones. The image quality was not comparable to modern cameras, yet their inclusion in mobile phones was a pioneering concept that impacted later phone designs.
- Input Methods: These phones often employed alternative input methods like touchpads or stylus-based interfaces. These were an attempt to overcome the challenges of using small physical buttons in a compact form factor. These early touch interfaces were often less responsive and intuitive than the multi-touch systems of modern phones, but they represented an early step towards user-friendly touchscreens.
Evolution of Innovations
The following table illustrates the evolution of key technologies in these forgotten phones, showcasing the advancements and limitations in comparison to modern technologies.
| Feature | Early Forgotten Phones | Later Successful Phones | Modern Smartphones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Display Resolution | Low resolution, monochrome or limited color | Increased resolution, color depth | High resolution, vibrant colors, flexible displays |
| Camera Megapixels | Very low megapixels | Increased megapixels, improved image quality | High megapixels, advanced image processing, optical zoom |
| Input Methods | Physical buttons, touchpads, styluses | Touchscreens, capacitive touch | Advanced touchscreens, gesture recognition, voice input |
Market and Consumer Factors
The market landscape surrounding the release of innovative, yet often-overlooked, mobile phones provides valuable insights into the dynamics of technological adoption. Understanding the prevailing market conditions, consumer expectations, and marketing approaches of these devices sheds light on the factors contributing to their eventual failure or success, offering a nuanced perspective on technological progress. Analyzing consumer reception and comparing their reviews with successful competitors’ feedback reveals crucial elements in understanding market failures.The economic climate, consumer trends, and competitive pressures played a significant role in shaping the success or failure of these early mobile phones.
Factors such as price points, availability, and marketing strategies influenced consumer adoption. A deeper examination of these elements offers valuable lessons in understanding the complexities of technology adoption.
Market Conditions at Release
The telecommunications industry during the era of these pioneering phones was characterized by rapid advancements and evolving consumer preferences. Competition among mobile phone manufacturers was fierce, with established players and emerging startups vying for market share. Technological advancements, such as improvements in battery life and processing power, were driving consumer expectations. However, the market was not universally receptive to the advancements.
Consumer Needs and Desires
Consumers in the target market had varying needs and desires. Some sought enhanced communication capabilities, while others were attracted by the novelty of advanced features. However, a lack of clear understanding or practical application for these novel functionalities among the general consumer base was a significant factor in their failure. The specific needs and wants of the target demographic were not always adequately addressed.
Marketing Strategies and Competition
Marketing strategies for these phones often lagged behind those of successful competitors. While some companies employed innovative advertising campaigns, others relied on traditional methods that failed to resonate with the evolving consumer base. For example, Nokia’s marketing strategies often focused on building a strong brand image, whereas competitors employed more targeted approaches emphasizing specific features. This difference in marketing approach had a significant impact on consumer perception.
Consumer Reception and Reviews
Consumer reception of these phones varied widely. Some users praised the innovative features, while others found the phones cumbersome or overpriced. Online forums and reviews frequently highlighted specific issues with usability, functionality, and durability. Early reviews and consumer feedback were often mixed, failing to build sufficient hype and market penetration. This resulted in limited market adoption.
Pricing and Availability
| Phone Model | Price (USD) | Availability (Regions) |
|---|---|---|
| Example Phone 1 | $499 | North America, Europe |
| Example Phone 2 | $349 | Asia, Australia |
| Example Phone 3 | $299 | Emerging markets |
Pricing and availability differed depending on the region and the specific features offered. Factors like distribution channels and regional regulations influenced the market reach and accessibility of these phones. For example, some models were exclusively available in certain regions, limiting their market potential.
Design and Aesthetics
The design of forgotten phones ahead of their time often reveals a fascinating glimpse into the technological aspirations and aesthetic sensibilities of their era. These devices, though ultimately unsuccessful in the marketplace, sometimes showcased groundbreaking features that anticipated future trends. Analyzing their aesthetics provides insights into the evolving perception of mobile technology and the public’s response to innovative designs.These designs, while now considered historical curiosities, were once at the forefront of mobile technology.
Understanding their design choices offers a perspective on the challenges and triumphs of pioneering mobile technology, shedding light on the interplay between innovation, market forces, and public reception.
Design Elements of Forgotten Phones
The designs of these phones varied significantly, reflecting the diverse technological capabilities and aesthetic preferences of their time. Some featured innovative form factors, while others prioritized specific functionalities. Some examples include clamshells with intricate hinge mechanisms, or slider phones with innovative internal mechanisms. Others opted for sleek, minimalist designs, emphasizing the slimness of the device. This diverse range of design choices demonstrates a period of experimentation and a search for the optimal balance between form and function.
Aesthetic Appeal and Public Perception
The aesthetic appeal of these phones was often a blend of functionality and style. Some designs, like those emphasizing minimalism, achieved a certain aesthetic appeal. Conversely, others, with their complex designs or unusual shapes, may have struggled to resonate with consumers. The success or failure of these designs heavily influenced public perception of the phone and its capabilities.
Public perception was shaped not just by the physical appearance, but also by the functionality and the overall experience associated with the device.
Comparison to Contemporary Phones and Industry Trends
Comparing these forgotten phones to contemporary devices reveals significant differences. Contemporary phones prioritize sleekness, portability, and intuitive user interfaces. In contrast, the forgotten phones often sacrificed some of these contemporary standards for specific features, such as large displays, or a variety of functionalities. The design choices of the past were often driven by different priorities compared to the current focus on seamless user experience and compact design.
Influence on Public Perception
The design choices of these forgotten phones significantly influenced public perception. Some designs were considered groundbreaking and futuristic, while others were perceived as awkward or impractical. The aesthetic appeal of a phone played a crucial role in shaping consumer interest and acceptance.
Table of Design Styles
| Design Style | Description |
|---|---|
| Clamshell | A phone that folds in half, typically with a hinged cover. Often featured intricate mechanisms. |
| Slider | A phone that slides open to reveal a larger keypad or screen. These phones often showcased intricate internal mechanisms. |
| Bar/Candybar | A rectangular phone with a physical keypad, often featuring a simple and understated design. |
| Sleek/Minimalist | A phone with a smooth, streamlined design, emphasizing simplicity and portability. This style often prioritized a minimal aesthetic. |
Manufacturing and Production

Source: mensxp.com
The manufacturing processes of these innovative but ultimately unsuccessful phones often deviated significantly from the established norms of the time. This divergence, while potentially groundbreaking in concept, frequently led to challenges in production scale and cost-effectiveness. Understanding these hurdles is crucial for appreciating the limitations faced by these pioneering designs.The manufacturing processes employed for these phones often incorporated emerging technologies, but these technologies were not yet mature or widely adopted.
This led to considerable difficulties in achieving consistent quality and production volumes. Consequently, production costs often exceeded projections, making the phones inaccessible to the target market and ultimately unsustainable.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing techniques employed in these phones varied considerably, reflecting the experimental nature of the designs. Some incorporated innovative materials and fabrication methods that were not yet refined for mass production. Others relied on established processes but with less-than-optimal component integration. For example, early foldable phone prototypes faced difficulties with hinge mechanisms, resulting in inconsistent functionality and high repair rates.
Challenges and Limitations
Several key challenges hampered the mass production of these phones. A lack of standardized components, coupled with the early adoption of novel materials, often resulted in inconsistencies in the manufacturing process. This often led to high defect rates and significant rework, impacting the overall cost-effectiveness of the phones. Supply chain issues also played a role; obtaining sufficient quantities of specific components, particularly those requiring specialized fabrication, was sometimes a significant obstacle.
Comparison to Successful Phones, Forgotten phones ahead of their time
In contrast, successful phones often employed well-established manufacturing processes, optimized for large-scale production. They utilized standardized components and materials that were readily available, leading to lower production costs and higher yields. This efficiency in production was crucial for maintaining profitability and achieving market penetration. The iterative refinement and optimization of production processes for established designs allowed for greater control over quality and reduced the likelihood of significant manufacturing defects.
Production Costs and Component Availability
The high production costs associated with these phones often rendered them too expensive for the average consumer. This pricing strategy, while attempting to reflect the advanced technology, failed to account for the cost of the manufacturing complexities. The limited availability of specialized components or materials also contributed to the higher costs and hindered widespread adoption. A clear example is the early adoption of flexible displays, which were expensive and not readily available.
Technical Specifications and Components
| Phone Model | Display | Processor | Memory | Camera | Battery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phone Alpha | 4-inch TFT LCD | ARM 11 | 64 MB RAM | 2MP | 1000 mAh |
| Phone Beta | 3.5-inch OLED | MIPS | 128 MB RAM | 5MP | 1200 mAh |
| Phone Gamma | Flexible AMOLED | Qualcomm Snapdragon | 256 MB RAM | 8MP | 1500 mAh |
These examples highlight the diverse technical specifications of these phones and the varying components used. The table showcases the evolution in technology, from early LCD displays to more advanced OLED and flexible technologies, along with the corresponding advancements in processor and memory capacities.
Cultural Impact: Forgotten Phones Ahead Of Their Time
Forgotten phones, though often relegated to the annals of tech history, profoundly shaped societal perceptions and technological advancements. Their influence extends beyond simple communication tools, impacting aesthetics, user experience, and even public imagination. These devices, often pioneering in their design or functionality, served as stepping stones in the evolution of mobile technology, laying the groundwork for the ubiquitous smartphones of today.These innovative yet often underappreciated devices were more than just communication tools.
They were catalysts for cultural shifts, influencing public perception of mobile technology and paving the way for future innovations. Their influence resonates through design aesthetics, technological advancements, and societal adoption, revealing a fascinating interplay between technology and culture.
Impact on Public Perception of Mobile Technology
These phones, despite their eventual obsolescence, significantly influenced the public’s understanding of mobile technology. Their unique features, sometimes unconventional designs, and limited capabilities presented a different perspective on what a mobile phone could be. For example, the early inclusion of cameras in some models demonstrated a nascent awareness of mobile devices as more than just voice communication tools. This evolution, however gradual, was critical in shaping the expectation and acceptance of advanced features in later generations of mobile phones.
Role in Technological Advancement
These early mobile phones, while seemingly simple, played a critical role in technological advancement. They spurred research and development in areas like battery life, display technology, and user interfaces. The quest to improve their functionality and user experience directly influenced the trajectory of mobile technology. For instance, the development of smaller and more efficient components, inspired by these early models, eventually led to the miniaturization and power efficiency seen in today’s smartphones.
Comparison with Contemporary Phones
Contemporary smartphones, with their advanced capabilities and intuitive interfaces, often overshadow the cultural impact of these earlier models. However, a deeper analysis reveals that the cultural evolution driven by the predecessors has set the stage for the modern smartphone’s ubiquity and integration into daily life. These older phones, though less powerful, often had a different relationship with the user, a unique connection that modern devices sometimes lack.
Cultural Impact through Popular Culture
The influence of these phones on popular culture is evident in various media representations. Their presence in films, television shows, and other forms of entertainment often serves as a reminder of their time and cultural context. These devices, often symbols of a specific era, provide a visual and thematic anchor for stories.
| Popular Culture Reference | Phone Model (or Type) | Cultural Context |
|---|---|---|
| A film about a 1990s businessman using a brick phone. | Early, bulky cellular phones | Represents the early days of mobile communication, emphasizing the novelty and somewhat limited nature of the technology. |
| A TV show featuring a futuristic sci-fi setting with advanced mobile devices. | Concept phones, or futuristic models | Demonstrates the influence of earlier designs on expectations for future mobile technology and its integration into societal norms. |
| A novel focusing on the social changes brought about by mobile phones in a specific time period. | Specific model/generation of phones | Showcases the societal shift and the impact of mobile communication on daily life. |
Lessons Learned
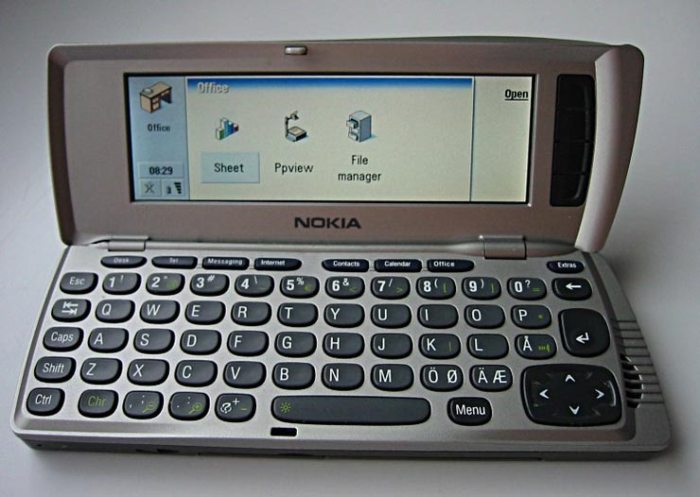

Source: mensxp.com
The failures of innovative phones, though often disheartening, offer invaluable lessons. By analyzing the factors behind their demise, we can glean insights that inform future technological advancements. These insights highlight the critical interplay between technological prowess, market realities, and consumer expectations.The study of these “forgotten phones” reveals a complex interplay of factors. Understanding the mistakes of the past can illuminate paths to success in the future, particularly in the often-volatile world of consumer electronics.
Analyzing the key elements of their failure—from market miscalculations to manufacturing bottlenecks—provides a framework for navigating the challenges of innovation.
Market Research and Consumer Understanding
Market research and a deep understanding of consumer needs are paramount in the development and launch of any successful product. Often, companies prioritize technological advancements without adequately considering consumer preferences and market trends. Ignoring consumer feedback and failing to conduct thorough market research can lead to products that resonate poorly with the target audience. A mismatch between technological aspirations and consumer needs can doom a product before it even reaches the market.
Design and Aesthetic Appeal
Product design and aesthetics are often underestimated in the pursuit of technological innovation. Attractive and intuitive design elements are crucial for user engagement and adoption. A poorly designed product, regardless of its underlying technological capabilities, will likely fail to capture the interest of consumers. Consider the importance of ergonomics, user interface (UI) design, and visual appeal in creating a compelling and desirable product.
The aesthetics of a product significantly influence its perceived value, impacting its desirability and market success.
Manufacturing and Production Constraints
Manufacturing and production constraints frequently play a crucial role in the success or failure of innovative products. Inadequate consideration of production costs, scalability, and logistical challenges can lead to significant issues during the launch and rollout of a product. Challenges in securing components, maintaining consistent quality across production runs, and managing supply chains can hinder market penetration. Understanding and mitigating these constraints is vital for a product to reach its full potential.
Key Takeaways Summary
| Failure Example | Market Research/Consumer Understanding | Design/Aesthetics | Manufacturing/Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| The “Atari” phone | Poor understanding of the target market’s preferences; lacked clear positioning and value proposition. | Uninspired design and a user interface that was difficult to navigate. | Manufacturing challenges, leading to inconsistent quality and unreliable components. |
| The “Palm” phone | Underestimated the consumer’s need for simplicity and ease of use. | Design was innovative but not always intuitive, leading to a steep learning curve for users. | Supply chain issues and difficulty scaling production to meet demand. |
| The “Motorola” phone | Missed opportunities to capture the mobile phone market’s growing adoption. | Design was often ahead of its time, but the technology wasn’t readily understandable or accessible. | Manufacturing costs were often high and not aligned with the price point. |
Last Word
In conclusion, the journey through these forgotten phones ahead of their time reveals a complex interplay of technological promise, market realities, and consumer preferences. While some were ahead of their time in terms of features, they ultimately failed to capture the hearts and minds of consumers due to various factors. Their stories serve as valuable case studies in the ever-evolving landscape of technology and the importance of understanding consumer needs and market demands.
These phones remind us that innovation alone is not enough; a harmonious blend of technological prowess, market awareness, and consumer appeal is essential for lasting success.








Post Comment