Cloud Computing Services Top Providers Features 2025
Cloud computing services top providers features 2025 are a key focus as the cloud market continues to expand rapidly. Different service models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cater to various needs, each with distinct benefits and security considerations. Leading providers are vying for market share, offering diverse pricing models and global infrastructure. This analysis delves into the key features, future trends, use cases, security, and cost optimization strategies for cloud services in 2025.
The landscape of cloud computing is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging rapidly. This report provides a comprehensive overview of the top providers, their strengths, and the features that define their services in 2025. Understanding the nuances of each service model is crucial for informed decision-making. The analysis also highlights the critical role of security and cost optimization in leveraging cloud resources effectively.
Introduction to Cloud Computing Services
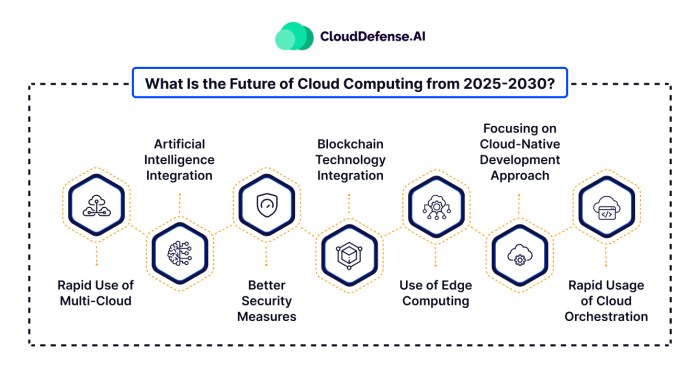
Source: clouddefense.ai
Cloud computing services are rapidly transforming how businesses and individuals store, access, and manage data and applications. Essentially, it’s the on-demand delivery of computing resources—servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the internet. This contrasts significantly with traditional on-premises computing, where hardware and software are physically housed and maintained within a company’s own facilities.Cloud computing offers a flexible and scalable alternative, allowing users to provision resources as needed, pay only for what they consume, and benefit from the management and maintenance handled by the cloud provider.
This flexibility and cost-effectiveness are driving its widespread adoption across various sectors.
Different Service Models
Cloud computing services are offered in three primary models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Understanding these models is crucial to selecting the right service for specific needs.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides the most basic level of cloud computing services. It offers virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking, enabling users to build their own applications and infrastructure. This model provides the greatest flexibility but also requires significant technical expertise. Companies using IaaS often manage their own operating systems, applications, and security.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform for developing, running, and managing applications without the need for managing the underlying infrastructure. This model simplifies the development process, allowing developers to focus on application logic rather than managing servers or operating systems. Popular examples include tools for building mobile apps, web applications, and data analytics solutions.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet. Users access and utilize the software through a web browser without needing to install or manage any software locally. This model offers the simplest and most user-friendly approach, commonly used for applications like email, CRM systems, and project management tools. Examples include Google Workspace and Salesforce.
Benefits of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Resources can be easily scaled up or down to meet fluctuating demands, reducing costs and maximizing efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Users pay only for the resources they consume, avoiding upfront investments in hardware and software.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Data and applications are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering collaboration and remote work.
- Increased Efficiency: Cloud providers handle the management and maintenance of the infrastructure, freeing up internal IT resources.
Key Factors Driving Cloud Computing Growth
Several factors contribute to the rapid growth of cloud computing:
- Increased Data Volumes: The exponential growth of data requires scalable storage and processing solutions that cloud computing offers.
- Advancements in Technology: Improved virtualization, networking, and security technologies have made cloud computing more reliable and secure.
- Cost Savings: The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing significantly reduces capital expenditures and operational costs.
- Demand for Agility and Innovation: Cloud computing allows businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions and adapt to new technologies.
Comparison of Service Models
| Service Model | Description | Typical Use Cases | Security Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| IaaS | Provides virtualized computing resources (servers, storage, networking). | Building custom applications, hosting websites, running complex data analytics workloads. | Requires significant user management and security configuration. Data encryption and access controls are crucial. |
| PaaS | Provides a platform for developing, running, and managing applications. | Rapid application development, mobile app development, web application hosting. | Security depends on the PaaS provider’s security measures and the user’s application code. |
| SaaS | Delivers software applications over the internet. | Email, CRM, project management, customer support tools. | Security is the provider’s responsibility, but users must adhere to access controls and policies. |
Top Providers in 2025
Cloud computing is poised for continued growth in 2025, with established players and new entrants vying for market share. This section examines the projected leading providers, their competitive strengths, and their anticipated market positions. Analyzing their pricing models and geographic presence provides insights into the evolving landscape of cloud services.
Leading Cloud Providers in 2025
The cloud computing market is expected to see a few dominant players in 2025. These companies are building upon their existing strengths and leveraging new technologies to maintain their positions or gain traction. Key players include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Smaller players may also achieve notable market share if they develop unique offerings that meet specific niche requirements.
Key Strengths and Competitive Advantages
Each major cloud provider possesses unique strengths that contribute to their market position. Amazon Web Services (AWS) benefits from its extensive infrastructure and established ecosystem, making it a strong choice for large enterprises. Microsoft Azure’s strengths lie in its integration with Microsoft’s product portfolio, giving it a strong advantage in enterprise deployments. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) emphasizes its innovative approach and focus on specific sectors, such as data analytics and artificial intelligence.
Market Share Projections for 2025
| Provider | Projected Market Share (2025) |
|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | 35% |
| Microsoft Azure | 28% |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | 18% |
| Other providers | 19% |
Note: Projections are based on market research and analysis and may vary. These estimates are intended as a general representation of expected market trends and should not be taken as absolute guarantees.
Pricing Models Comparison
Cloud providers offer various pricing models to cater to different needs and budgets. AWS often employs a pay-as-you-go model, which allows flexibility and control over costs. Microsoft Azure offers tiered pricing structures with varying benefits depending on usage levels. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) employs a variety of pricing strategies, including committed use discounts for larger commitments. The choice of pricing model often depends on the specific requirements of the customer and the size of their operation.
Geographic Presence
The geographic presence of cloud providers is crucial for global reach and localized support.
| Provider | Data Centers | Regions Served |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Over 85 | Global, including major regions like North America, Europe, and Asia |
| Microsoft Azure | Over 60 | Global, with a strong presence in North America, Europe, and Asia |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Over 40 | Global, with a focus on regions with high data traffic and significant cloud demand |
Each provider aims to provide robust regional coverage and support, which is vital for meeting the needs of businesses across the globe.
Features of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are rapidly evolving, offering a diverse range of features that cater to various needs and industries. These features, ranging from robust security measures to streamlined automation, are instrumental in driving efficiency and cost savings for users. Leading providers continuously enhance these services, focusing on user experience and technological advancements.
Essential Features
Cloud computing services boast a multitude of essential features designed to optimize user experience and maximize efficiency. These features, including scalability, availability, and security, are paramount for businesses of all sizes. They are also critical to ensuring a dependable and resilient service environment.
- Scalability: The ability to dynamically adjust resources—like computing power, storage, and bandwidth—is crucial for handling fluctuating workloads. This feature is essential for businesses experiencing rapid growth or seasonal peaks in demand. For instance, an e-commerce platform might need increased server capacity during holiday shopping seasons. Cloud providers offer flexible scaling options to meet these demands.
- Availability: High availability ensures continuous service access. This feature is often achieved through redundant infrastructure and geographically dispersed data centers. A reliable service ensures business continuity, preventing disruptions to critical operations. A bank, for example, needs a highly available cloud platform to process transactions 24/7.
- Security: Protecting sensitive data is paramount. Leading cloud providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. These measures are essential to safeguard against cyber threats. A healthcare organization, handling patient data, relies heavily on the security features offered by cloud providers.
Automation and Management Tools
Automation and management tools simplify cloud resource provisioning and management. These tools streamline tasks like deploying applications, monitoring performance, and updating software, freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Automated Provisioning: Cloud providers offer tools to automate the provisioning of virtual machines, storage, and networking resources. This significantly reduces the time and effort needed to set up and manage infrastructure.
- Centralized Management: Cloud management consoles provide a centralized platform for monitoring and managing various cloud resources. This offers a unified view of the entire infrastructure.
- Monitoring Tools: Monitoring tools help track the performance of applications and resources, allowing for proactive identification and resolution of potential issues.
API Integrations and Developer Tools
Cloud providers offer extensive API integrations and developer tools to facilitate seamless integration with existing systems and applications. These tools enable developers to quickly build and deploy applications on the cloud platform.
- API Integrations: APIs enable seamless integration with various third-party applications and services. This allows for streamlined workflows and enhanced functionality.
- Developer Tools: Comprehensive developer tools empower developers with the necessary tools and resources for building, testing, and deploying applications on the cloud platform. This includes SDKs, libraries, and documentation.
Service Model Specific Features
The features offered vary based on the service model (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS). The following table summarizes these differences:
| Service Model | Key Features |
|---|---|
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | Virtual machines, storage, networking, and operating systems. Provides maximum flexibility and control. |
| PaaS (Platform as a Service) | Development tools, databases, and middleware. Facilitates application development and deployment. |
| SaaS (Software as a Service) | Pre-built applications. Offers ready-to-use solutions for specific tasks. |
Future Trends in Cloud Computing Services

Source: apiculus.com
Cloud computing is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the increasing need for scalable and flexible solutions. This evolution is shaping the future of data management, application development, and business operations. Key trends, including the expanding roles of AI/ML, edge computing, and serverless architectures, are redefining the cloud landscape.The convergence of these trends promises a more efficient, intelligent, and adaptable cloud infrastructure, benefiting businesses of all sizes.
The potential impacts of these advancements on existing cloud service models are significant and require careful consideration by providers and users alike.
Emerging Technologies in Cloud Computing, Cloud computing services top providers features 2025
Cloud computing is no longer solely about centralized data centers. New technologies are expanding its reach and capabilities, making it more accessible and versatile. These advancements encompass a broad spectrum of possibilities, offering opportunities for innovation and efficiency gains.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming cloud services, enabling intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and personalized experiences. Examples include AI-powered security tools that proactively identify and mitigate threats, and ML algorithms that optimize resource allocation in cloud environments. These technologies improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance user experience.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings processing power closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This is particularly crucial for applications requiring real-time data processing, such as IoT devices and autonomous vehicles. Edge computing is moving data processing away from centralized cloud servers, reducing network dependency and improving efficiency for applications demanding low latency and high bandwidth.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing abstracts away server management, allowing developers to focus on code without worrying about infrastructure. This approach promotes scalability and cost efficiency by only paying for the resources used. This removes the need for manual server management, simplifying the development process and enabling dynamic scaling to meet fluctuating demands.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing, while still in its early stages, has the potential to revolutionize certain types of complex calculations, particularly in areas like drug discovery and materials science. The impact on cloud computing could be substantial, leading to specialized cloud services tailored for quantum algorithms.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s decentralized nature can enhance cloud security and transparency. Its use in cloud storage and data management could improve trust and accountability.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Services
AI and ML are increasingly integrated into cloud services, impacting everything from security to resource management. AI-powered tools can automatically detect anomalies and prevent security breaches, while ML algorithms can optimize resource allocation in real-time, minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency. These advancements improve service reliability, reduce operational overhead, and enhance user experiences.
Edge Computing and Serverless Computing
Edge computing and serverless computing are changing the cloud landscape by distributing processing power and abstracting away server management. Edge computing shifts data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness for applications like IoT and real-time analytics. Serverless computing empowers developers to focus on code without managing infrastructure, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings.
| Feature | Traditional Cloud Computing | Edge Computing | Serverless Computing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Processing Location | Centralized data centers | Distributed at the edge of the network | Dynamically provisioned resources |
| Latency | Higher latency for real-time applications | Lower latency for real-time applications | Variable latency depending on the workload |
| Scalability | Scalable but can be complex | Scalable but can be complex | Highly scalable, automatically adjusts |
| Cost | Potentially higher costs for unused resources | Potential for lower costs due to reduced data transfer | Pay-as-you-go model, cost-effective |
| Management | Requires significant infrastructure management | Requires some edge infrastructure management | No infrastructure management required |
Use Cases and Applications
Cloud computing services are rapidly evolving, adapting to the dynamic needs of diverse industries. Its flexibility and scalability are driving widespread adoption, transforming how businesses operate and compete. This section explores key use cases and applications across various sectors, highlighting the benefits and transformative impact of cloud technology.Cloud computing offers significant advantages for businesses, particularly in terms of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and accessibility.
Its ability to handle fluctuating workloads and provide on-demand resources makes it a powerful tool for managing various operational needs, from data storage and processing to application development and deployment.
Healthcare
Cloud computing is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling secure and efficient storage and sharing of patient data. This facilitates faster access to critical information for diagnoses and treatment plans, improving patient outcomes. Cloud-based platforms support remote patient monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to track patient conditions and intervene proactively. This leads to improved patient care and reduced hospital readmissions.
Finance
Financial institutions leverage cloud services for secure data processing and analysis. This allows for faster transaction processing, fraud detection, and risk management. Cloud-based solutions also provide enhanced security and compliance features, mitigating financial risks and adhering to stringent regulations. Moreover, cloud platforms allow for rapid deployment of new financial products and services, enabling financial institutions to adapt to market changes swiftly.
Retail
Cloud-based solutions are transforming retail operations by enabling personalized customer experiences and optimized inventory management. Real-time data analysis empowers retailers to understand customer preferences and tailor marketing strategies effectively. Cloud platforms also support seamless order fulfillment and logistics, enhancing customer satisfaction. The scalability of cloud solutions allows retailers to easily adjust their operations to meet seasonal demand fluctuations.
Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
Cloud computing offers significant benefits for SMEs by reducing capital expenditures and providing access to advanced technologies previously unavailable. The cost-effective nature of cloud services enables SMEs to scale their operations without significant upfront investments in infrastructure. Cloud platforms empower SMEs with robust data storage and processing capabilities, enhancing their competitiveness. Furthermore, cloud computing facilitates collaboration among team members, regardless of location, improving productivity and efficiency.
Examples of Successful Implementations
- Netflix utilizes cloud computing for its vast streaming library and real-time content delivery, ensuring seamless access to a global audience. This scalable solution supports the streaming of high-definition content to millions of users concurrently.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a robust cloud platform for a diverse range of businesses, including e-commerce giants, media companies, and financial institutions. Its comprehensive suite of services enables seamless scalability and secure data management.
- Salesforce utilizes cloud computing to deliver a customer relationship management (CRM) platform, empowering businesses to manage customer interactions effectively. This platform facilitates data-driven insights and enhances customer engagement.
Security Considerations in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing, while offering numerous advantages, presents unique security challenges. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of cloud services are paramount concerns for organizations and individuals alike. Maintaining robust security measures across the entire cloud lifecycle is crucial to mitigate risks and build trust in cloud-based solutions.Cloud providers employ a range of security measures, but the shared responsibility model mandates that both the provider and the user take proactive steps to safeguard data.
Understanding the potential vulnerabilities and adopting appropriate security practices are vital to preventing breaches and maintaining data integrity.
Security Challenges and Risks
Cloud computing environments present several security risks, including data breaches, unauthorized access, and malicious attacks. These threats can arise from vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure, misconfigurations of cloud resources, and the inherent complexity of managing multiple interconnected systems. Furthermore, the shared responsibility model requires careful consideration of security controls on both the provider and user sides.
Importance of Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount in cloud computing. Sensitive information stored or processed in the cloud must be protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. Compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is critical for organizations handling personal data in cloud environments. The potential consequences of a data breach can be severe, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties.
Security Measures Taken by Cloud Providers
Cloud providers implement various security measures to protect data. These include encryption of data at rest and in transit, access control mechanisms, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and regular security audits. They often leverage advanced technologies and expertise to safeguard their infrastructure and mitigate risks. Specific security measures can vary between providers, and customers should carefully evaluate these differences when selecting a cloud service.
Potential Security Breaches and Vulnerabilities
Potential security breaches and vulnerabilities in cloud environments can arise from various sources. These include vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure, misconfigurations of cloud resources, and inadequate security controls implemented by users. Human error, such as weak passwords or phishing attacks, also poses a significant risk. The interconnected nature of cloud systems makes it crucial to address vulnerabilities in any part of the system, whether in the provider’s infrastructure or the user’s configuration.
Additionally, the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks necessitates continuous vigilance and adaptation of security measures.
Comparison of Security Features Offered by Different Providers
| Cloud Provider | Encryption | Access Control | Vulnerability Management | Compliance Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Strong encryption at rest and in transit | Fine-grained access controls | Automated vulnerability scanning | ISO 27001, SOC 2 |
| Microsoft Azure | Robust encryption mechanisms | Role-based access control | Regular security updates | ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Advanced encryption features | Identity and access management (IAM) | Continuous security monitoring | ISO 27001, SOC 2, FedRAMP |
This table provides a simplified comparison. The specific security features and their implementation details can vary based on the specific services and configurations chosen by users. Thorough research and evaluation of the security posture of each provider are crucial.
Cost Optimization and Management
Optimizing cloud computing costs is crucial for businesses leveraging cloud services. Effective cost management in cloud environments hinges on understanding and utilizing available tools and strategies to minimize expenses without sacrificing performance or functionality. This involves careful resource allocation, proactive monitoring, and a well-defined cost-saving strategy.A well-structured cost optimization strategy is paramount for long-term cloud sustainability and profitability.
This approach ensures that cloud services align with business needs, minimizing unnecessary expenses and maximizing return on investment. The right tools and strategies can significantly reduce cloud spending while maintaining service reliability.
Strategies for Effective Cloud Resource Management
Effective cloud resource management is essential for cost optimization. This involves proactively monitoring resource utilization, identifying areas for potential savings, and adjusting resources based on fluctuating demands. Implementing automated scaling solutions can further reduce costs by dynamically allocating resources only when needed.
- Rightsizing Resources: Analyzing current resource usage to ensure that the allocated resources align with the actual needs of applications and workloads. This often involves transitioning from over-provisioned instances to instances with optimized configurations.
- Automated Scaling: Implementing automated scaling solutions that adjust resources dynamically based on fluctuating demands. This avoids paying for unused resources during low-activity periods and ensures sufficient resources during peak demands. Examples include automatically scaling up compute instances during peak hours and scaling down during off-peak periods.
- Reserved Instances: Utilizing reserved instances for predictable workloads. Reserved instances offer significant discounts compared to on-demand instances for commitments over a specific period. The decision to use reserved instances hinges on the predictability of workloads. This often provides significant savings if the workload pattern is known in advance.
Cost-Saving Tools and Strategies in Cloud Computing
Cloud providers offer various tools and strategies for cost optimization. These tools provide detailed insights into resource utilization, helping identify areas for cost reduction. Strategies include leveraging cloud provider’s cost optimization tools and implementing internal cost management processes.
- Cloud Provider Tools: Utilizing cloud provider-specific tools for cost analysis, forecasting, and optimization. These tools often provide granular views of spending, allowing for identification of specific areas where costs can be reduced. Examples include AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud Cost Management.
- Internal Cost Management Processes: Implementing internal cost management processes for cloud spending, including budgeting, tracking, and reporting. This involves defining clear cost allocation policies and regularly reviewing cloud spend to identify potential savings.
- Rightsizing Instances: Rightsizing instances based on usage patterns and needs. This involves migrating workloads to smaller or larger instances depending on the current workload requirements. This ensures that resources are optimized to match current needs, preventing unnecessary expenditure.
Best Practices for Cost Management in Cloud Environments
Implementing best practices is crucial for maintaining control and minimizing costs in cloud environments. This includes implementing tagging, developing clear cost allocation policies, and employing appropriate security measures.
- Tagging Resources: Tagging resources for clear identification and cost allocation. This enables better visibility into resource utilization and allows for easier tracking of costs associated with specific projects or departments.
- Cost Allocation Policies: Establishing clear cost allocation policies for cloud services to ensure accountability and transparency. These policies define who is responsible for specific cloud costs and how costs are tracked and reported.
- Security Measures: Implementing appropriate security measures to avoid accidental or malicious use of resources, thereby reducing potential costs. This involves monitoring for and promptly addressing security incidents to prevent unauthorized resource consumption.
Cost Optimization Strategies Effectiveness
A structured analysis of various cost optimization strategies provides insights into their effectiveness. This allows for informed decisions based on potential ROI and impact on operational efficiency.
| Strategy | Effectiveness | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Reserved Instances | High | Significant discounts for predictable workloads. |
| Automated Scaling | Medium to High | Dynamic resource allocation based on demand. |
| Rightsizing Instances | Medium | Optimizing instance types to match workload needs. |
| Spot Instances | Variable | Lower-cost instances for flexible workloads. |
| Cloud Provider Tools | High | Detailed insights into resource utilization and cost analysis. |
Epilogue: Cloud Computing Services Top Providers Features 2025
In conclusion, the cloud computing landscape in 2025 is characterized by intense competition among top providers, offering a range of features tailored to diverse needs. Understanding the benefits, security considerations, and cost optimization strategies associated with cloud computing is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage its potential. The future of cloud computing promises continued innovation and growth, driven by emerging technologies and the increasing demand for scalable and secure solutions.













Post Comment