Artificial Intelligence Applications Across Industries
Artificial intelligence applications across industries are rapidly transforming various sectors, from healthcare to manufacturing. This overview explores the diverse applications of AI, highlighting its fundamental concepts and its evolving integration into different fields. We’ll examine how AI is revolutionizing processes and impacting industries across the board.
The table below provides a glimpse into the broad categories of industries benefiting from AI. From disease diagnosis in healthcare to fraud detection in finance, AI is demonstrably changing the landscape of various sectors. This report delves deeper into these specific applications, providing detailed insights into the specific AI algorithms and models used, and the associated benefits and challenges.
Introduction to AI Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, automating tasks, improving efficiency, and driving innovation. From healthcare to finance, AI is finding diverse applications, offering solutions to complex problems and creating new opportunities. The fundamental concepts of AI, such as machine learning and deep learning, are enabling these applications, and the integration of AI into different sectors is evolving at a rapid pace.The fundamental concepts of AI underpin its diverse applications.
Machine learning, a subset of AI, allows systems to learn from data without explicit programming. Deep learning, a more advanced form of machine learning, uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to analyze complex data patterns. These capabilities are crucial in automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and enabling systems to adapt to changing circumstances.
Overview of AI Applications Across Industries
AI is now prevalent across a wide range of industries, from the healthcare sector to the financial industry. Its applications are constantly expanding, leading to increased efficiency and improved outcomes. The evolving landscape of AI integration is characterized by a continuous process of development, refinement, and adaptation.
Categories of Industries Leveraging AI
Various industries are leveraging AI to enhance their operations and achieve significant improvements. The following table highlights some key sectors and the specific AI applications they are employing:
| Industry | Specific AI Application |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images (X-rays, MRIs) to detect diseases like cancer earlier and more accurately. AI can also personalize treatment plans based on individual patient data, leading to more effective outcomes. |
| Finance | AI algorithms can identify fraudulent transactions in real-time, minimizing financial losses and enhancing security. Risk assessment and personalized financial advice are also being enabled by AI. |
| Retail | AI-powered recommendation systems suggest products to customers based on their browsing history and purchase patterns, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction. Inventory management is also optimized using AI to reduce waste and enhance efficiency. |
| Manufacturing | AI-driven robots can automate manufacturing processes, increasing production speed and reducing human error. Predictive maintenance, using AI to anticipate equipment failures, reduces downtime and maintenance costs. |
| Transportation | AI is being used to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve the efficiency of logistics. Self-driving cars, utilizing AI for navigation and decision-making, are also an emerging application. |
AI in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the healthcare industry, offering innovative solutions for diagnosis, treatment, and drug discovery. Its ability to process vast amounts of data and identify patterns is revolutionizing medical practices, leading to more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatments, and faster development of new therapies.AI’s impact extends across the entire spectrum of healthcare, from basic diagnostics to complex treatments and research.
The ability to analyze medical images, patient records, and research data with unprecedented speed and accuracy allows AI to assist healthcare professionals in making informed decisions and improving patient outcomes.
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
AI is proving invaluable in medical diagnosis, assisting in the detection of diseases like cancer and cardiovascular conditions. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) with remarkable accuracy, often identifying anomalies that might be missed by human eyes. Furthermore, AI can predict patient risk factors and personalize treatment plans based on individual characteristics. This predictive capability allows for earlier interventions and potentially more effective therapies.
For example, AI can predict the likelihood of a patient experiencing a heart attack, enabling proactive measures and improved patient outcomes.
Drug Discovery and Development
AI is significantly accelerating the drug discovery and development process. By analyzing vast datasets of chemical compounds and biological information, AI algorithms can identify potential drug candidates with high efficacy and low toxicity. This accelerates the pipeline of potential new therapies, leading to faster and more efficient drug development. This process involves identifying promising drug candidates from a huge database of molecules, predicting their effectiveness, and reducing the time and resources needed for testing.
Furthermore, AI can model the behavior of drugs in the human body, simulating their interaction with different biological systems, which enables more accurate predictions of efficacy and potential side effects.
Personalized Medicine
AI plays a crucial role in personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual patient needs. By analyzing patient data, including genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle factors, AI algorithms can identify optimal treatment strategies for specific patients. This approach aims to improve treatment outcomes by matching therapies to individual patient characteristics and responses. For instance, AI can predict which cancer patients will respond favorably to specific therapies, enabling more targeted and effective treatments.
Comparison of AI Algorithms in Healthcare
| Algorithm | Application | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Image analysis, prediction of patient risk, treatment planning | High accuracy in specific tasks, cost-effective in many cases, can handle large datasets | Requires large, well-labeled datasets for training, may not generalize well to unseen data, potential for bias in the training data |
| Deep Learning | Complex image analysis, natural language processing for patient records, drug discovery | High accuracy for complex tasks, capable of learning complex patterns | Requires massive datasets, computationally intensive, potential for overfitting, difficult to interpret the reasoning behind predictions |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Extracting information from patient records, analyzing clinical trial data, generating reports | Improved efficiency in extracting insights from text-based data | Challenges in understanding nuances in human language, potential for misinterpretations |
AI in Finance: Artificial Intelligence Applications Across Industries

Source: binatedigital.com
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the financial sector, automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and improving overall efficiency. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data and identify patterns allows for more accurate risk assessments, fraud detection, and personalized customer experiences. This transformative power is being widely adopted across financial institutions, driving innovation and growth.
Fraud Detection and Risk Assessment
AI algorithms excel at identifying subtle anomalies and patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity. Machine learning models, particularly neural networks, are trained on historical transaction data to learn what constitutes normal behavior. Any deviation from this norm triggers an alert, enabling financial institutions to quickly investigate and prevent potential losses. Risk assessment benefits similarly, as AI analyzes a wide range of factors – creditworthiness, market trends, and economic indicators – to predict and mitigate potential financial risks.
This proactive approach helps to avoid significant financial losses and improve portfolio performance.
Algorithmic Trading and Investment Strategies
AI plays a crucial role in algorithmic trading, automating investment decisions based on complex mathematical models. These models analyze market data, including price movements, volume, and sentiment, to identify profitable trading opportunities. AI-powered investment strategies are designed to optimize portfolio returns and manage risk effectively. High-frequency trading, for instance, leverages AI to execute trades at an incredibly fast pace, taking advantage of minuscule price fluctuations.
AI-Powered Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly used to provide 24/7 customer support in the financial sector. These tools can handle routine inquiries, such as account balance checks or transaction histories, freeing up human agents to address more complex issues. AI also personalizes customer interactions, tailoring financial advice and recommendations based on individual needs and preferences. These AI-driven customer service solutions improve efficiency and enhance the overall customer experience.
Types of AI Models in Finance
| Model Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Neural Networks | Complex algorithms that learn from data by adjusting interconnected nodes. They excel at identifying intricate patterns and correlations, making them highly effective in fraud detection and risk assessment. | Fraud detection, risk assessment, algorithmic trading, customer service (sentiment analysis). |
| Support Vector Machines (SVMs) | Algorithms that find optimal hyperplanes to separate different classes of data. They are particularly useful in classification tasks, such as separating legitimate transactions from fraudulent ones. | Fraud detection, credit scoring, customer segmentation. |
| Decision Trees | Models that break down data into a series of decisions based on rules. They are valuable for understanding the factors that contribute to a specific outcome, such as a customer defaulting on a loan. | Credit scoring, risk assessment, customer churn prediction. |
| Bayesian Networks | Models that represent probabilistic relationships between variables. They are well-suited for predicting the likelihood of future events, such as the probability of a customer defaulting on a loan. | Risk assessment, credit scoring, fraud detection. |
AI in Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the manufacturing sector, leading to increased efficiency, improved quality, and enhanced safety. AI-powered systems are automating tasks, predicting potential issues, and optimizing processes across the entire production pipeline. This results in cost savings, reduced downtime, and improved competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Enhancing Production Efficiency and Quality Control
AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including machine sensors, production logs, and historical data. This analysis allows manufacturers to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling proactive interventions to prevent defects and improve product quality. Real-time monitoring and feedback loops enable adjustments to processes as needed, ensuring consistent high-quality output. AI-powered vision systems can identify defects in products with a high degree of accuracy, reducing the need for manual inspection and accelerating the production process.
Predictive Maintenance and Automation
AI-driven predictive maintenance systems analyze machine data to anticipate potential failures before they occur. This allows manufacturers to schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and maximizing equipment lifespan. AI-powered robots and automation systems are increasingly used for repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex and strategic roles. This automation also increases production speed and consistency. For example, in automotive manufacturing, AI-powered robots can precisely weld components, leading to higher quality and reduced production time.
Supply Chain Optimization
AI can optimize supply chains by predicting demand fluctuations, identifying bottlenecks, and streamlining logistics. AI-powered algorithms can analyze market trends, inventory levels, and transportation data to optimize inventory management and reduce lead times. This allows for better responsiveness to changing market demands, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Real-time tracking of shipments using AI-powered systems provides greater visibility and control over the entire supply chain.
Improving Worker Safety and Productivity
AI can contribute significantly to improving worker safety. AI-powered safety systems can monitor worker behavior and identify potential hazards, alerting workers and supervisors to potential risks in real-time. This proactive approach can prevent accidents and injuries, promoting a safer work environment. AI also enhances worker productivity by automating repetitive and potentially dangerous tasks. This allows human workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks, leading to increased efficiency and overall productivity.
Stages of AI Implementation in a Manufacturing Plant
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Planning | Identifying AI use cases, defining goals, and creating a roadmap for implementation. This includes assessing existing data sources and infrastructure, and determining the necessary resources. Defining specific metrics for measuring success is also crucial at this stage. |
| Data Collection and Preparation | Gathering and preparing the data needed for AI algorithms. This involves cleaning, transforming, and integrating data from various sources. |
| Model Development and Training | Developing and training AI models tailored to specific manufacturing processes and tasks. This stage involves experimenting with different models and algorithms to find the most effective solutions. |
| Deployment and Integration | Integrating AI systems into existing manufacturing processes and workflows. Testing the AI solutions under real-world conditions is critical to ensure they function as intended. |
| Monitoring and Evaluation | Continuously monitoring the performance of AI systems, identifying areas for improvement, and refining the models over time. This iterative process ensures ongoing optimization and effectiveness. |
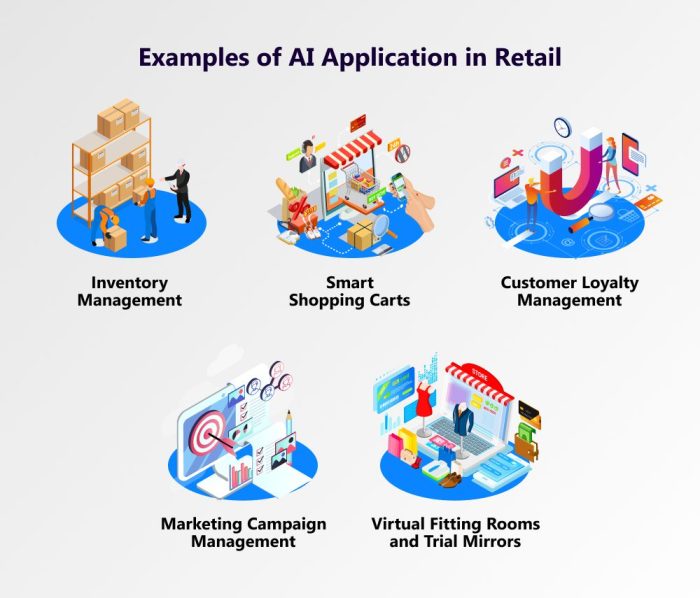
AI in Retail
Source: so-development.org
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the retail landscape, impacting everything from customer interactions to supply chain management. AI-powered systems are increasingly sophisticated, enabling retailers to offer personalized experiences, optimize operations, and enhance marketing strategies. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and increased profitability.
Personalizing Customer Experiences
AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of customer data, including purchase history, browsing behavior, and demographics, to create highly personalized shopping experiences. This includes tailoring product recommendations, offering targeted promotions, and even anticipating customer needs before they are explicitly stated. For example, an AI system might suggest complementary products based on previous purchases or recommend specific items based on browsing patterns, significantly enhancing the customer journey.
AI in Inventory Management and Supply Chain Optimization
AI plays a crucial role in optimizing inventory levels and supply chain processes. Predictive analytics models forecast demand fluctuations, allowing retailers to proactively adjust stock levels to minimize overstocking and stockouts. Real-time tracking of inventory and supply chain data enables retailers to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize logistics for faster delivery times and reduced costs. This proactive approach reduces waste and improves efficiency across the entire supply chain.
For instance, AI-powered systems can predict seasonal demand fluctuations, allowing retailers to adjust their inventory levels accordingly.
AI in Customer Service and Marketing
AI is revolutionizing customer service by automating routine tasks and providing instant support. Chatbots powered by AI can handle customer inquiries, answer frequently asked questions, and resolve simple issues, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex problems. AI also enhances marketing efforts by enabling targeted advertising campaigns and personalized product recommendations. For example, AI can analyze customer data to identify specific interests and tailor advertisements accordingly, leading to higher conversion rates.
AI-Powered Recommendations and Targeted Advertising
AI algorithms are central to recommending products to customers. These systems analyze vast datasets to identify patterns in customer preferences and suggest relevant items. This personalization extends to targeted advertising, allowing retailers to display ads for products that are likely to resonate with individual customers. For example, an AI system might recommend a specific type of shoe based on a customer’s past purchases and browsing history.
This level of personalization leads to a more engaging and effective marketing strategy.
Benefits and Challenges of AI in Retail
| Benefit | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Increased sales due to personalized recommendations and targeted marketing | Data privacy concerns regarding the collection and use of customer data. Maintaining trust and transparency with customers about how their data is used is paramount. |
| Improved inventory management and supply chain optimization, reducing costs and waste | Potential job displacement in certain roles, requiring retraining and upskilling initiatives for affected employees. |
| Enhanced customer service through automated support and faster response times | Ensuring the reliability and accuracy of AI-driven systems, as errors or biases in algorithms can negatively impact customer experiences. |
| Increased efficiency in marketing campaigns and higher conversion rates | The high cost of implementing and maintaining AI systems, requiring careful planning and resource allocation. |
AI in Transportation
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the transportation sector, from autonomous vehicles to optimized logistics. This transformative power is driven by AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data, predict outcomes, and automate complex tasks, ultimately improving efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Autonomous Vehicles
AI plays a pivotal role in enabling autonomous vehicles. These vehicles leverage advanced sensor technologies and sophisticated algorithms to navigate roads and perform driving tasks without human intervention. Sensor fusion, combining data from various sensors like cameras, radar, and lidar, is crucial for creating a comprehensive understanding of the environment, enabling the vehicle to perceive and respond to obstacles and traffic conditions.
This complex process is a key element in the development of safe and reliable autonomous vehicles.
Traffic Management
AI can significantly enhance traffic management by analyzing real-time data from various sources. This data includes traffic flow, road conditions, and incident reports. By using machine learning algorithms, AI systems can predict congestion patterns and adjust traffic signals in real-time, optimizing traffic flow and reducing delays. This proactive approach to traffic management leads to smoother traffic conditions and increased efficiency.
Logistics and Delivery Optimization
AI is revolutionizing logistics and delivery by optimizing routes and scheduling. AI algorithms can analyze various factors, such as traffic patterns, delivery windows, and vehicle availability, to develop the most efficient delivery routes. This optimization minimizes travel time and fuel consumption, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Navigation and Route Planning Systems
AI-powered navigation and route planning systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated. These systems analyze real-time data, such as traffic conditions and road closures, to suggest the fastest or most efficient routes. Advanced systems can even account for factors like weather conditions, allowing users to make informed decisions about their travel plans. Examples include Google Maps, Waze, and other similar applications.
Safety Implications
The safety implications of AI in transportation are substantial. Autonomous vehicles must be meticulously tested and validated to ensure their ability to respond appropriately to various scenarios. Human oversight and safety protocols are also crucial to mitigate potential risks and ensure the safe operation of autonomous vehicles. Real-world testing and rigorous simulations are necessary to refine AI algorithms and prevent unforeseen incidents.
Comparison of Autonomous Vehicle Types
| Vehicle Type | Technology | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Self-driving cars | Sensor fusion, machine learning algorithms | Urban driving, highway driving, and potentially even specialized applications like delivery or ride-sharing services. |
| Autonomous trucks | Sensor fusion, route optimization algorithms | Long-haul trucking, freight delivery, and potentially other specialized transport needs. |
| Autonomous buses | Sensor fusion, passenger management systems | Public transportation routes, optimized for passenger flow and efficiency. |
| Autonomous drones | Advanced sensor systems, flight control algorithms | Delivery of goods, inspection of infrastructure, aerial photography, and potentially even passenger transport in specific environments. |
AI in Customer Service
AI is rapidly transforming customer service interactions, offering businesses new ways to engage with their clientele and enhance the overall experience. By automating tasks and providing personalized support, AI-powered systems are proving invaluable in optimizing customer service workflows.
How AI Powers Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are designed to mimic human conversation, understanding and responding to customer inquiries. Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms are crucial in enabling these systems to comprehend the nuances of human language, interpreting intents and extracting relevant information from customer queries. Machine learning models are trained on vast datasets of customer interactions to identify patterns and predict likely responses, allowing the systems to learn and improve over time.
This allows for efficient handling of routine queries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Sentiment Analysis and Customer Feedback
AI plays a pivotal role in analyzing customer feedback and sentiment. By employing NLP, AI systems can discern the emotional tone behind customer comments, identifying positive, negative, or neutral sentiments. This allows businesses to track customer satisfaction levels and proactively address concerns. Sentiment analysis enables companies to understand what aspects of their service are appreciated and where improvements are needed.
This data-driven approach can be invaluable in guiding strategic decisions and refining customer service strategies.
AI-Powered Customer Support Tools
Several tools leverage AI to enhance customer service. These include automated chatbots that handle routine inquiries, virtual assistants that schedule appointments or provide information, and AI-powered systems that analyze customer interactions to identify trends and potential problems. A notable example is the use of AI in email management, where systems can prioritize emails, categorize them based on subject, and even compose responses based on the content.
This streamlines the workflow and enables more effective responses.
Benefits and Limitations of AI in Customer Service
The benefits of AI in customer service are substantial. AI can provide 24/7 support, handle large volumes of inquiries simultaneously, and offer personalized experiences. This can significantly reduce response times and improve customer satisfaction. However, limitations exist. AI systems may struggle with complex or nuanced issues that require human judgment and empathy.
The accuracy of AI responses depends heavily on the quality and quantity of the training data. Furthermore, maintaining customer trust and ensuring ethical use of AI in interactions is crucial.
Comparison of AI-Powered Customer Service Platforms
| Platform | Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered chatbot | 24/7 support, automated responses to common queries, escalation to human agents when needed, integration with various communication channels | Variable, dependent on features, usage, and support level. Some platforms offer freemium models or pay-as-you-go options. |
| Virtual assistant | Scheduling appointments, providing information, answering basic questions, routing calls to relevant agents | Variable, dependent on the scope of services offered and the level of customization required. |
| AI-powered feedback analysis platform | Sentiment analysis of customer feedback, identification of recurring themes and issues, reporting and visualization of trends, recommendations for improvement | Variable, often based on the volume of data processed and the level of sophistication in the analysis. |
Emerging Trends in AI Applications
Artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving, impacting numerous industries and reshaping the future of work and society. This evolution brings about new trends, promising advancements, and crucial considerations regarding ethical implications and workforce adaptation. Understanding these emerging trends is essential for navigating the changing landscape.
Future Potential of AI Integration
AI’s potential for enhancing productivity and efficiency is significant across diverse sectors. Automation of repetitive tasks, predictive modeling, and data-driven insights can lead to substantial gains in efficiency. In healthcare, AI can aid in diagnosis and treatment planning. Finance can benefit from fraud detection and risk assessment. Furthermore, personalized recommendations in retail and targeted marketing can optimize customer engagement.
The possibilities extend to optimizing transportation routes and improving customer service response times.
Limitations of AI Integration
Despite the potential benefits, AI integration presents limitations. Data bias can lead to inaccurate or unfair outcomes. Privacy concerns regarding data collection and usage are significant, necessitating robust ethical frameworks. The need for skilled professionals to manage and maintain AI systems is a crucial aspect to address. Moreover, the potential displacement of human workers in certain roles necessitates careful planning for retraining and reskilling initiatives.
Impact of AI on the Workforce and Society
The integration of AI has the potential to reshape the job market. Certain roles may become automated, while new roles requiring AI expertise will emerge. Adaptability and continuous learning will be crucial for workers to thrive in this evolving landscape. The societal impact is multifaceted, encompassing concerns about job displacement, income inequality, and the need for robust social safety nets.
This transformation requires careful consideration and proactive measures to mitigate potential negative consequences.
Innovative AI Applications in Specific Industries, Artificial intelligence applications across industries
Several industries are already leveraging AI for innovative applications. In agriculture, precision farming techniques using AI-powered sensors and data analysis can optimize resource utilization and increase crop yields. In transportation, AI-powered navigation systems can optimize routes and reduce fuel consumption. Retail businesses can leverage AI for personalized recommendations and inventory management.
Ethical Considerations of AI Deployment
Ethical considerations surrounding AI deployment are paramount. Bias in algorithms, data privacy, and the potential for misuse necessitate careful consideration. Transparency in AI decision-making processes is crucial to building trust and addressing concerns. Robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines are essential for ensuring responsible AI development and deployment.
Examples of New AI Applications
| Industry | New Application |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Precision farming |
| Healthcare | AI-powered diagnostics, personalized medicine |
| Finance | Fraud detection, risk assessment |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance, quality control |
| Retail | Personalized recommendations, inventory optimization |
| Transportation | Autonomous vehicles, optimized logistics |
| Customer Service | Chatbots, automated support |
Conclusive Thoughts
Source: itechindia.co
In conclusion, the pervasive adoption of artificial intelligence across various industries presents both exciting opportunities and considerable challenges. While AI offers the potential for increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation, it’s crucial to address the ethical implications and societal impact of this transformative technology. The future of AI in these industries hinges on responsible development and implementation.













Post Comment