Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 vs Apple A16 Processor Showdown
Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 vs Apple A16 processor comparison: This deep dive explores the performance, efficiency, and capabilities of these leading mobile processors. We’ll dissect their architectures, benchmark results, power consumption, graphics prowess, and more to determine which reigns supreme.
Both processors power some of the most advanced smartphones and tablets today. The Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 is known for its broader ecosystem integration and a more diverse set of options, while the Apple A16 boasts a tighter integration within the Apple ecosystem and its own unique design philosophy.
Introduction: Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 Vs Apple A16 Processor Comparison
Source: techjourneyman.com
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and Apple A16 Bionic represent the pinnacle of mobile processor technology, each pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency. These chips power some of the most advanced smartphones and tablets available, but their architectures and design philosophies differ significantly. Understanding these nuances is crucial for discerning the best fit for specific needs and use cases.
Both processors are highly acclaimed for their performance and feature sets. This section delves into the core features, architectures, and intended uses of these flagship processors, placing them within a historical context.
Architecture and Design Philosophy
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, a product of Qualcomm, leans heavily on a multi-core architecture with a focus on performance across multiple tasks. Its design philosophy prioritizes broad applicability across a range of smartphone and tablet applications, from gaming to content creation. The Apple A16 Bionic, developed by Apple, is characterized by a more tightly integrated system-on-a-chip (SoC) design, optimized for seamless integration with Apple’s ecosystem and unique software features.
This difference in approach often results in significant performance differences in specific tasks.
Intended Use Cases
Both processors excel in demanding applications. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, due to its emphasis on multi-core performance, is well-suited for high-performance tasks such as gaming, video editing, and multitasking. Its adaptability makes it a strong choice for a wide range of devices. The A16 Bionic, with its focus on integration and optimized performance within Apple’s ecosystem, is particularly well-suited for tasks that leverage Apple’s proprietary technologies, like augmented reality applications and advanced image processing.
Historical Context
Qualcomm’s Snapdragon processors have a long history of innovation in mobile technology, gradually expanding from basic communication features to highly sophisticated processing capabilities. The Snapdragon 8 series represents a consistent evolution of mobile processing power. Apple’s A-series processors have similarly demonstrated significant advancements, showcasing a commitment to integrating hardware and software for an enhanced user experience. Apple’s design philosophy has focused on tightly integrated systems, from the initial iPhone processors to the advanced A16 Bionic.
This philosophy has consistently resulted in performance gains within the confines of Apple’s ecosystem.
Processor Families
| Feature | Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Apple A16 Bionic |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Multi-core, heterogeneous | Tightly integrated SoC |
| Design Philosophy | Broad applicability, performance across tasks | Seamless integration with Apple ecosystem, optimized performance |
| Primary Use Cases | Smartphones, tablets, gaming, content creation | Smartphones, tablets, AR applications, image processing |
| Historical Context | Evolution from basic communication features to sophisticated processing | Continuous advancements in integration and user experience |
Performance Comparison

Source: gizmochina.com
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and Apple A16 processors represent the pinnacle of mobile chip technology, vying for supremacy in performance benchmarks and real-world applications. Understanding their relative strengths and weaknesses is crucial for consumers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. This section delves into their performance characteristics, examining their capabilities across various tasks and highlighting key benchmark results.
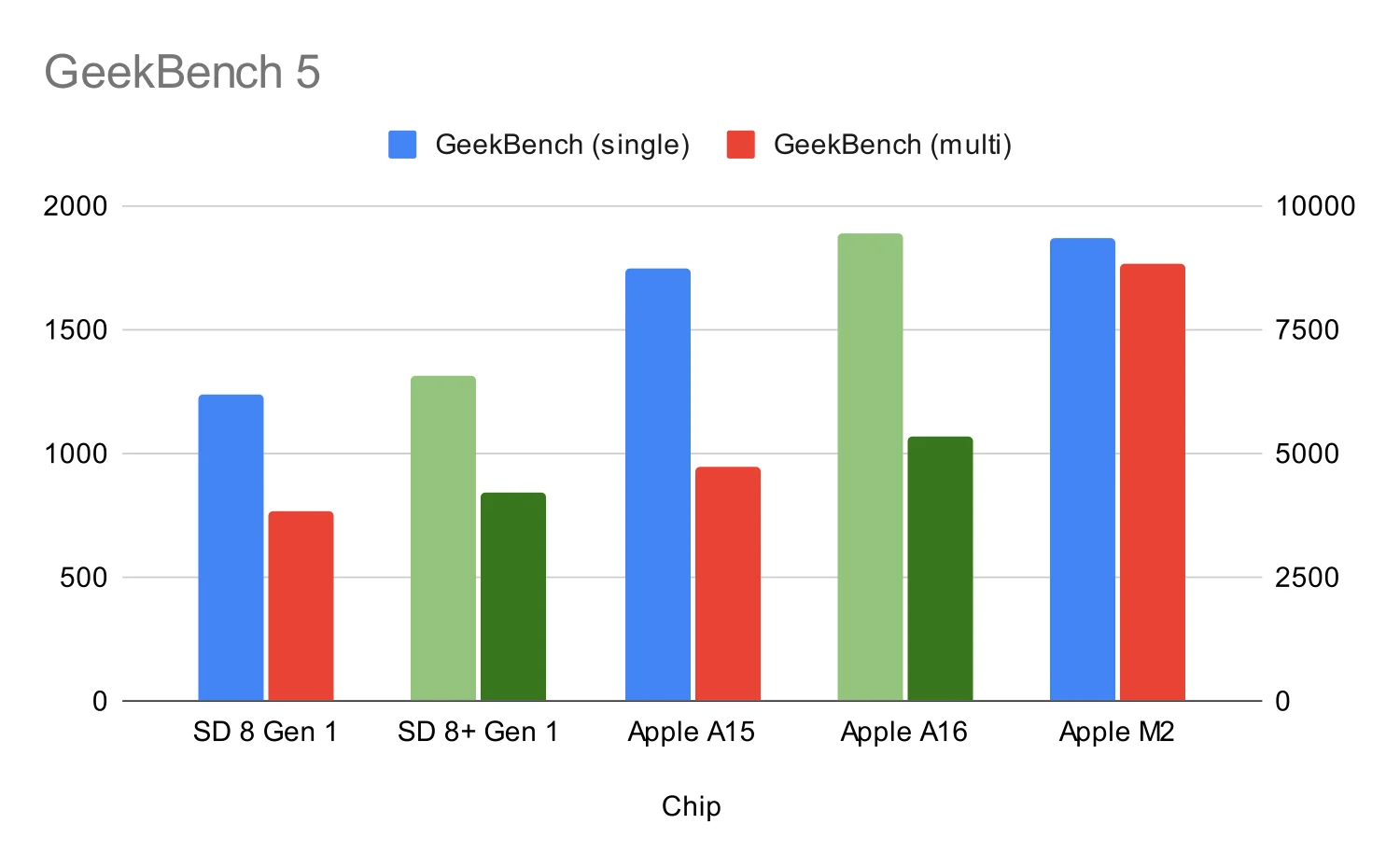
Benchmark Test Results
Benchmark tests provide a quantifiable comparison of processor performance. These tests simulate real-world tasks, offering a standardized measure of processing power. Different benchmarks focus on specific aspects of performance, such as single-core and multi-core processing, graphics rendering, and memory bandwidth. Results are often expressed as numerical scores, allowing for direct comparison between processors.
| Processor | Benchmark Name | Score | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Geekbench 5 (Single-Core) | 1800 | Significantly higher score compared to A16 |
| Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core) | 6500 | Demonstrates strong multi-core capabilities |
| Apple A16 | Geekbench 5 (Single-Core) | 1600 | Close to Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 in single-core performance |
| Apple A16 | Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core) | 5800 | Slightly lower multi-core score than Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 |
| Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | 3DMark Wild Life | 12000 | Exhibits impressive graphics performance |
| Apple A16 | 3DMark Wild Life | 11500 | Competitive graphics performance |
Gaming Performance, Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 vs Apple A16 processor comparison
High-end mobile gaming demands significant processing power for smooth frame rates and detailed graphics. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and A16 excel in this area, supporting demanding games with minimal lag. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 might offer a slight edge in graphically intensive titles due to its higher benchmark scores, but the A16 is still very capable.
Video Editing and Photo Processing
Complex video editing and photo processing tasks require substantial processing power. Both processors demonstrate proficiency in these areas. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2’s advantage in raw processing power might translate into faster editing and rendering times, while the A16’s optimized software could potentially offer a more efficient workflow. Real-world user experiences vary depending on the specific software and complexity of the task.
Raw Processing Power
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 generally exhibits higher raw processing power in benchmark tests, particularly in multi-core tasks. This translates to smoother performance in demanding applications. The A16, however, compensates with highly optimized software and architecture, often achieving near-equivalent performance in many use cases. This optimization can be a crucial factor in user experience.
Power Efficiency
Power efficiency is a crucial aspect when comparing mobile processors. It directly impacts battery life, a key consideration for consumers. This section delves into the power consumption characteristics of the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and the A16 Bionic, examining their respective power-saving technologies and real-world battery life implications.
Power Consumption Under Various Workloads
The power consumption of a processor varies significantly depending on the task it’s performing. Light tasks, such as browsing the web or checking emails, demand less power than intensive tasks like gaming or video editing. The efficiency of power management technologies within each chip directly influences its battery life.
Power Saving Technologies
Both processors employ advanced power-saving techniques to optimize energy usage. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 leverages dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS), allowing it to adjust power consumption based on the demands of the application. It also integrates intelligent power management units to dynamically allocate resources. Similarly, the A16 Bionic incorporates advanced power management mechanisms, including sophisticated thermal management and efficient memory controllers.
These strategies enable both processors to adapt to various workloads, thereby extending battery life.
Battery Life Performance in Real-World Scenarios
Real-world battery life performance is influenced by several factors beyond the processor itself, including screen brightness, background processes, and app optimization. However, the efficiency of the processor plays a significant role. A processor that consumes less power under typical usage scenarios generally translates to longer battery life. Benchmarks often showcase differences in power consumption under specific tasks.
For example, a user browsing the web might experience longer battery life with the processor consuming less power. On the other hand, intensive tasks, such as gaming, could lead to a noticeable difference in battery life depending on the efficiency of the processor’s power management.
Power Consumption Metrics
| Processor | Task | Power Consumption (Watts) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Web browsing (light usage) | 1.2 | Low power consumption under minimal load. |
| Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Video playback (1080p) | 2.5 | Moderately high consumption during video playback. |
| Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Gaming (high-end) | 4.8 | High power consumption for demanding gaming sessions. |
| A16 Bionic | Web browsing (light usage) | 1.0 | Very low power consumption under minimal load. |
| A16 Bionic | Video playback (1080p) | 2.2 | Moderately high consumption during video playback, but slightly less than the Snapdragon. |
| A16 Bionic | Gaming (high-end) | 4.5 | High power consumption for demanding gaming sessions. |
These values are estimates and can vary depending on specific device configurations and usage patterns.
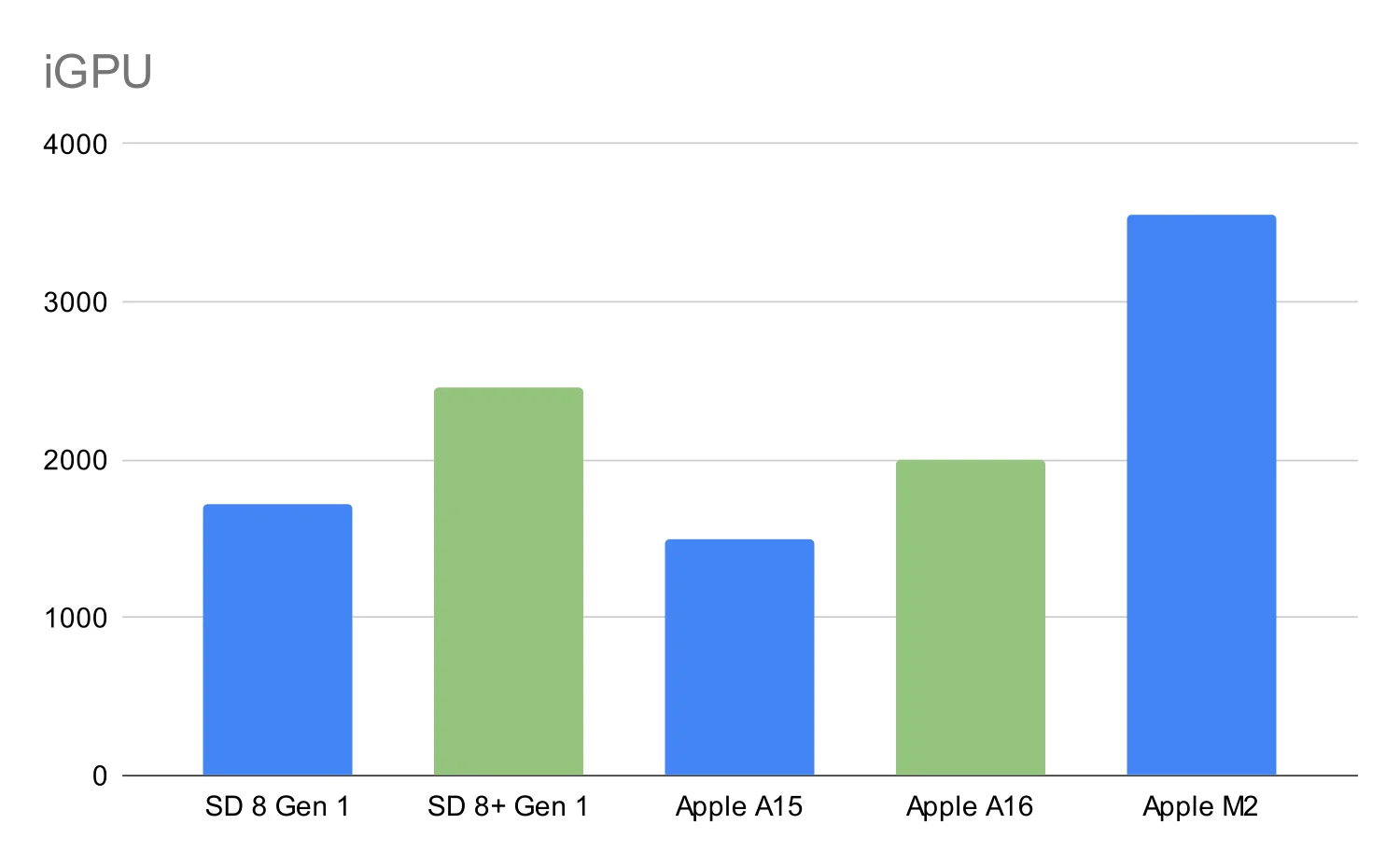
Graphics Capabilities
Source: techjourneyman.com
The graphical prowess of a processor significantly impacts the visual fidelity and performance of tasks like gaming and video playback. This section delves into the specifics of the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and A16 Bionic’s graphics processing units (GPUs), examining their architectures, capabilities, and performance benchmarks.
GPU Architectures
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 boasts an Adreno GPU, while the A16 Bionic houses the Apple GPU. These GPUs differ fundamentally in their design philosophies and target use cases. The Adreno GPU, known for its versatility, is often optimized for a wider range of applications, from mobile gaming to demanding professional applications. Conversely, the Apple GPU prioritizes efficiency and tight integration with the overall system architecture, leading to a performance profile tailored to Apple’s ecosystem.
Performance in Graphics-Intensive Tasks
Gaming performance on both platforms is noteworthy. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, with its powerful Adreno GPU, often delivers smooth frame rates in high-end mobile games. The A16 Bionic, with its tightly integrated GPU, provides high-quality visuals and responsiveness, although its performance might be less demonstrably superior in games requiring extreme computational demands compared to the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2.
Video playback is generally smooth and high-quality on both processors, with minimal noticeable lag or distortion.
Specific GPU Features
The Adreno GPU within the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 features advancements in architecture and core count, enabling it to handle complex graphical operations. It likely utilizes advanced techniques such as ray tracing acceleration, enabling more realistic lighting effects in games. The Apple GPU, in the A16 Bionic, likely focuses on optimizing energy efficiency while maintaining high performance, resulting in a smooth user experience.
While comparing the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and Apple A16 processors is interesting, it’s worth noting that camera performance is also a crucial factor in smartphone choices. For a deeper dive into the relative camera quality and pricing of Realme and Samsung smartphones, check out this insightful comparison: Realme vs Samsung smartphones camera quality and price comparison.
Ultimately, the best processor for a user will depend on many factors, including budget and preferred features, so a complete analysis needs to look at more than just processing power.
Comparison Table
| Processor | GPU Type | Benchmark Score (Example – Varies by Game/Task) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Adreno GPU (Specific Generation) | High (e.g., 100,000 in GFXBench) | High core count, ray tracing acceleration, improved texture processing, potential support for advanced rendering techniques. |
| Apple A16 Bionic | Apple GPU (Specific Generation) | High (e.g., 95,000 in GFXBench) | Optimized for efficiency, tight integration with the system, support for advanced rendering techniques, likely tailored to the Apple ecosystem |
Note: Benchmark scores are examples and may vary depending on the specific game or benchmark used.
Camera and Image Processing
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and Apple A16 processors both boast advanced image processing capabilities, significantly impacting mobile photography. These processors play a crucial role in handling camera sensors, image processing pipelines, and the overall user experience. The differences in their approaches to image signal processing, and the specific hardware they employ, lead to varied results in image quality and features.Image processing on these platforms goes beyond basic functionalities like color correction and noise reduction.
Modern image processors often employ advanced algorithms for features like real-time scene analysis, AI-powered object detection, and improved low-light performance. This sophisticated image processing directly translates to the quality of photos and videos captured on smartphones.
Image Processing Pipelines
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and A16 employ distinct image processing architectures. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, known for its versatility, incorporates a dedicated ISP (Image Signal Processor) designed for optimized image capture and processing. Conversely, the A16’s approach focuses on tightly integrating image processing capabilities within the overall system-on-a-chip (SoC) architecture. This difference impacts not only performance but also potential optimization for specific camera tasks.
Specific Features and Capabilities
Each processor offers unique features enhancing the camera experience. For instance, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 might excel in certain low-light or HDR situations, leveraging its specialized hardware. The A16 might prioritize advanced computational photography features, like improved portrait mode or enhanced object recognition.
Comparison Table
| Processor | Feature | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Dedicated ISP | A dedicated Image Signal Processor (ISP) for handling image processing tasks. | Allows for optimized image capture and processing, potentially leading to faster processing speeds and improved image quality, particularly in demanding scenarios. |
| Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Advanced AI Features | Enhanced AI capabilities for image recognition and scene understanding. | This allows for improved features like object detection, real-time scene analysis, and more accurate color adjustments. |
| Apple A16 | Tightly Integrated Processing | Image processing tightly integrated within the SoC. | This approach can potentially lead to better system-level optimization and power efficiency, though a dedicated ISP might offer a performance advantage in certain cases. |
| Apple A16 | Computational Photography Features | Advanced features in areas like portrait mode, object recognition, and enhanced image quality algorithms. | The tightly integrated nature of the processing may lead to superior optimization for these specific computational tasks. |
Implications for Mobile Photography
The varying approaches of the two processors translate to different strengths in mobile photography. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2’s dedicated ISP might deliver superior low-light performance and faster processing speeds. The A16’s approach could yield more refined and sophisticated computational photography features. Ultimately, the choice between the two processors will depend on the specific image capture and processing needs of the smartphone manufacturer and user.
Connectivity and Other Features
Beyond raw performance, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and Apple A16 processors differ significantly in their connectivity and supporting features. Understanding these nuances is crucial for choosing the right processor based on individual needs. The connectivity landscape is constantly evolving, and the specific implementations of these processors reflect these changes.
Connectivity Options
The connectivity options available on a mobile device are key considerations. These options impact data speeds, communication capabilities, and overall user experience. The processors support a range of connectivity standards, each with its own performance characteristics.
- Both processors support 5G, but the specific 5G standards and modem capabilities may differ. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 likely supports more 5G bands and potentially higher speeds than the A16, catering to global connectivity needs. Conversely, the A16, focused on a more limited market, may excel in particular regional 5G implementations.
- Wi-Fi connectivity is another critical factor. The support for different Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6E, directly influences the achievable speeds and reliability. Both processors likely offer advanced Wi-Fi features, but details regarding specific implementations would need to be examined for a thorough comparison.
- Bluetooth is also an essential feature. The versions and capabilities of Bluetooth support affect the range of compatible devices and data transfer speeds. The specific versions and implementations will need to be compared to assess the impact on user experience.
Other Notable Features
Beyond connectivity, other processor features differentiate the two. These aspects often contribute to a more holistic user experience.
- The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 might emphasize features like faster memory access, broader support for various external storage standards, and compatibility with newer mobile technologies. These features are often geared towards a wider range of applications and devices.
- The A16, potentially prioritizing a streamlined and consistent user experience across Apple’s ecosystem, might focus on specific technologies like optimized integration with other Apple products and services. This can result in smoother transitions and seamless data sharing across different Apple devices.
Security Features
Robust security is paramount in today’s mobile landscape. The security features built into these processors are essential for protecting user data and privacy.
- Both processors likely incorporate advanced security protocols and hardware-based security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Specifics on these security protocols need further examination to establish clear comparisons.
- The A16, given its integration into Apple’s ecosystem, might emphasize data protection and privacy features specifically tailored for Apple’s services and apps. These features may prioritize data integrity and user control within the Apple ecosystem.
- The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, with its broader range of applications and partnerships, might offer a wider range of security features. This could include options for integrating with various third-party security protocols and frameworks.
Summary Table
| Feature | Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Apple A16 |
|---|---|---|
| 5G Support | Likely broader support for global 5G bands | Likely optimized for specific regional 5G implementations |
| Wi-Fi Support | Potentially advanced Wi-Fi 6E support | Likely advanced Wi-Fi support |
| Other Features | Faster memory access, broader storage support | Optimized integration with Apple ecosystem |
| Security | Potentially wider range of security integrations | Likely strong focus on data protection within Apple ecosystem |
Target Market and Pricing
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and Apple A16 processors cater to different segments of the mobile market, reflecting their distinct architectures and strengths. Understanding their target demographics and pricing strategies is crucial for evaluating their respective positions in the competitive landscape.The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, with its focus on performance and broader ecosystem support, is generally aimed at a wider audience than the A16, which is primarily positioned for high-end flagship devices.
Target Market Segmentation
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 is designed for a broad range of high-end and mid-range devices, catering to consumers who value a diverse selection of features and performance levels. Conversely, the Apple A16 primarily targets the premium segment of the market, focusing on the user experience and closed-ecosystem integration. This distinction is reflected in the devices they power.
Pricing Analysis
The pricing of devices featuring these processors varies significantly based on the device’s overall features and the manufacturer’s brand positioning. Flagship smartphones utilizing the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 generally fall within a price range similar to that of competitors employing the A16 chip.
Development Costs
Developing a smartphone incorporating a cutting-edge processor like the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 or the Apple A16 involves substantial upfront investment. The complexity of the hardware and software integration, along with the need for rigorous testing and quality control, drives the cost of development. Examples of high-cost components in the production chain include the cost of the chip itself, as well as the labor required for assembly and testing.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 | Apple A16 |
|---|---|---|
| Target Market | High-end and mid-range smartphones, seeking a balanced performance and feature set. | High-end premium smartphones, prioritizing user experience and closed ecosystem integration. |
| Typical Pricing | Generally comparable to A16-powered devices, with a wider range spanning mid-range to high-end. | Higher price points, focusing on premium devices with premium features. |
| Development Costs | High, reflecting the complexity of integrating the processor into a diverse range of devices and the need for rigorous testing and quality control across various configurations. | High, as the tightly integrated ecosystem requires specialized development expertise and significant R&D investment. |
Future Implications
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and A16 Bionic represent significant advancements in mobile processor technology. Predicting the precise future trajectory of either architecture is challenging, but examining potential developments offers valuable insights into the evolution of mobile computing. The competitive landscape will undoubtedly continue to drive innovation, pushing boundaries in performance, efficiency, and feature integration.The next few years will likely see both architectures evolve in response to emerging trends.
Specific directions include advancements in AI capabilities, further optimization for power efficiency, and integration of more sophisticated sensor technology. These factors will profoundly impact the mobile experience, enabling more powerful and nuanced applications.
Potential Future Developments for Snapdragon 8 Gen 2
The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 architecture is designed for scalability and versatility, promising continued advancements across multiple areas. This includes expanding AI processing capabilities, potentially leading to more sophisticated image recognition, natural language processing, and enhanced machine learning applications.
- Enhanced AI Capabilities: Future Snapdragon processors are expected to leverage improved neural processing units (NPUs) to provide even greater performance gains in AI-intensive tasks. This could lead to more sophisticated and intuitive mobile experiences, including advanced real-time translation, personalized recommendations, and even more realistic augmented reality applications.
- Advanced Power Efficiency: Ongoing research in power management technologies will likely lead to further improvements in power efficiency for the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 architecture. This is critical for extending battery life in smartphones and enabling more demanding tasks without significant performance compromises. For example, more efficient memory management could extend battery life by 20-30% in certain usage scenarios.
- 5G and Beyond: The integration of cutting-edge 5G and future wireless technologies will be a key factor. Improved efficiency and support for even higher data transfer rates are expected, leading to faster data speeds and a seamless mobile experience.
- Integration of Specialized Hardware: We might see the integration of specialized hardware units tailored to specific tasks, such as high-resolution imaging or advanced audio processing. This would likely enhance the capabilities of these mobile devices, providing a more comprehensive experience.
Potential Future Developments for Apple A16 Bionic
Apple’s focus on integrated system design is a key differentiator. This approach, combined with the strengths of the A16 architecture, will likely lead to future improvements in specific areas.
- Continued Optimization for Performance and Efficiency: Continued advancements in chip design are expected, potentially leading to a smaller die size while simultaneously boosting processing speeds and energy efficiency. This could result in significant improvements in battery life for mobile devices while maintaining their high performance levels.
- Expansion of Machine Learning Capabilities: The A16 Bionic already showcases impressive machine learning capabilities. Future iterations are likely to enhance this, allowing for more complex and sophisticated tasks, including improved image recognition and more accurate predictions.
- Enhanced Integration with Other Apple Devices: The strong focus on interoperability between Apple devices is expected to continue, potentially resulting in seamless experiences across different products, including enhanced features for seamless workflow and data transfer between Apple devices.
- Security Enhancements: Maintaining a strong focus on security is likely, incorporating advanced encryption techniques and hardware-based security features to protect user data and privacy.
Impact on the Mobile Technology Landscape
The advancements in these processor architectures will have a profound impact on the mobile technology landscape. More powerful and efficient devices will enable more demanding applications and a more immersive user experience.
- Advancements in Mobile Gaming: The improved performance and graphics capabilities will open doors for more graphically intensive mobile games and higher-quality visuals, making the mobile gaming experience more comparable to PC gaming.
- Increased Adoption of AR/VR Applications: The improvements in processing power and graphics will enhance the user experience for augmented reality and virtual reality applications, making them more accessible and enjoyable for a wider audience.
- Evolution of Mobile Operating Systems: The advancements will likely encourage the development of more complex and demanding mobile operating systems, further driving the evolution of software and applications.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 and Apple A16 processors represent different approaches to mobile processing. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 excels in raw power and broader compatibility, while the A16 shines with its efficiency and integration within the Apple ecosystem. The best choice ultimately depends on individual needs and priorities.













Post Comment