Evolution Of Home Media From Vhs To Streaming
Evolution of home media from VHS to streaming represents a significant shift in how we consume entertainment. This journey chronicles the technological advancements, business models, and user experiences that transformed home media from physical tapes to digital platforms. Early formats like VHS, with their limitations in storage and playback, paved the way for the rise of streaming services.
This exploration delves into the factors behind the decline of VHS and the ascent of streaming, considering the impact on content creation, distribution, and the entertainment industry as a whole.
The transition from physical media to streaming services profoundly altered the entertainment landscape. This shift was fueled by advancements in technology, including internet bandwidth and data compression. The rise of streaming services also brought about changes in user experience, business models, and content creation. We will explore how these changes impacted different stakeholders, from consumers to content creators and industry giants.
Historical Overview of Home Media
Home media technologies have revolutionized how we consume and share content. From the earliest attempts at capturing and reproducing sound and images to the sophisticated streaming services of today, the evolution of home media has been a fascinating journey of technological advancement. This overview traces the development of home media, focusing on the key technologies that led up to the ubiquitous VHS format.The progression from rudimentary recording devices to sophisticated playback systems highlights the relentless pursuit of improved quality, portability, and accessibility.
Each new technology built upon the strengths of its predecessors, introducing innovations that significantly altered how we enjoyed films, music, and other forms of media.
Early Forms of Home Media
Early forms of home media focused primarily on capturing and reproducing sound, rather than visual images. Phonograph cylinders and wax discs allowed for the recording and playback of sound, marking a significant step towards personal entertainment. The limitations of these early technologies were substantial; sound quality was often poor, and recording time was extremely short.
The Rise of Visual Media
The introduction of visual media significantly expanded the possibilities of home entertainment. Early technologies like 8mm and Super 8mm film cameras enabled individuals to capture moving images, though the process was complex and often cumbersome. These formats offered limited storage capacity and often required specialized equipment for playback.
The Advent of Video Recording
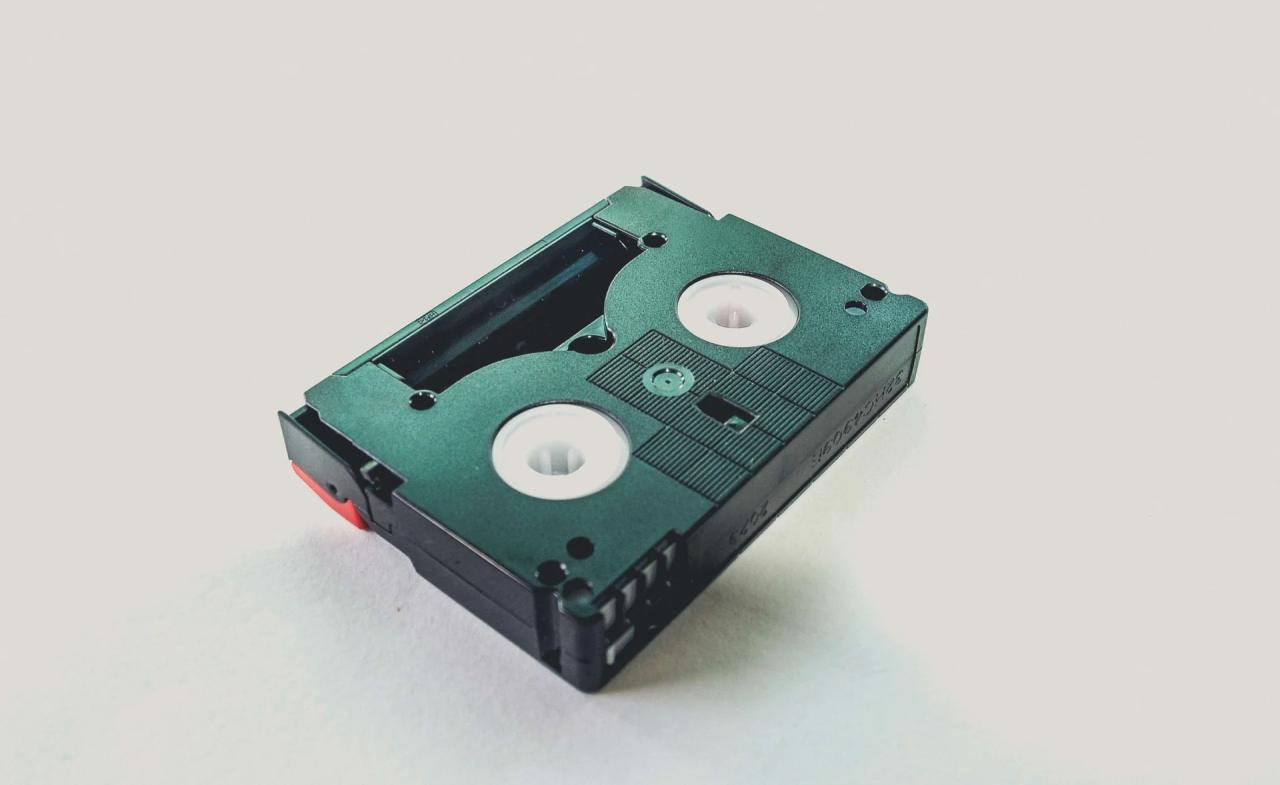
The development of video recording technologies like Betamax and VHS represented a crucial leap forward. These formats allowed for the recording and playback of moving images with sound, ushering in a new era of home entertainment. However, these early video formats had limitations, including tape handling issues, which affected the longevity and quality of recordings.
Comparison of Technologies
| Technology Name | Year of Introduction | Key Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phonograph Cylinders | Late 19th Century | Early sound recording and playback. | Poor sound quality, short recording time. |
| Wax Discs | Early 20th Century | Improved sound quality over cylinders. | Still limited recording time, relatively fragile. |
| 8mm and Super 8mm Film | Early 20th Century | Visual recording of moving images. | Complex process, limited storage, specialized equipment needed. |
| Betamax | 1975 | Early video recording format, offered good picture quality. | Compatibility issues with other formats, limited storage. |
| VHS | 1976 | Widely adopted format, offered longer recording time, and increasing playback quality compared to Betamax. | Tape handling issues, potential for degradation with use, less refined playback quality compared to modern standards. |
VHS: A Defining Era
The VHS format, introduced in 1976, dominated the home video market for decades. Its popularity stemmed from several factors, including its relatively affordable price, longer recording time compared to Betamax, and compatibility with a wider range of playback devices. However, VHS tapes were susceptible to wear and tear, and the quality of the recordings was not as high as modern standards.
The Rise of Streaming Services: Evolution Of Home Media From VHS To Streaming
The transition from physical media like VHS to streaming services represents a significant shift in how we consume entertainment and information. This evolution was driven by a confluence of factors, including technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the emergence of new business models. The decline of VHS was not a sudden event, but rather a gradual process that paved the way for the rise of digital streaming as the dominant form of home media.The decline of VHS and the rise of streaming services were intertwined with a series of technological advancements.
Increased internet bandwidth, coupled with advancements in data compression techniques, enabled the efficient delivery of high-quality video content over the internet. This made streaming a viable and increasingly attractive alternative to the limitations of physical media like VHS.
Technological Advancements Enabling Streaming, Evolution of home media from VHS to streaming
Technological advancements played a crucial role in making streaming services a viable alternative to traditional media distribution. Improvements in internet bandwidth allowed for faster and more reliable video transmission. Data compression techniques, such as MPEG-4 and H.264, significantly reduced the file sizes of video files, allowing for quicker downloads and smoother playback. These advancements, combined with the increasing affordability and accessibility of high-speed internet connections, fostered the growth of streaming services.
Business Models of Streaming Services
Streaming services utilize a subscription-based model, fundamentally different from the traditional retail model of physical media. This subscription-based approach allows streaming services to offer a vast library of content to consumers at a recurring monthly fee. This model differs significantly from the one-time purchase of a VHS tape or DVD. The subscription model also allows for continuous content updates and a constantly evolving catalog of films, television shows, and other media.
Examples of Early Streaming Services and Their Impact
Several early streaming services played a pivotal role in shaping the current streaming landscape. Netflix, for instance, initially focused on delivering DVD rentals by mail. Its transition to a streaming service was a key turning point, marking a significant shift in the entertainment industry. Other early pioneers, like Hulu and YouTube, introduced different approaches to content distribution and consumption, reflecting a wider variety of user needs and preferences.
These services helped establish the streaming platform as a new normal for accessing movies and TV shows, while also creating new opportunities for creators and distributors.
Impact of Streaming Services on Consumers
Streaming services have significantly impacted consumers by providing access to a vast library of content from around the world. This accessibility has democratized entertainment, making it more affordable and convenient for consumers. The ability to stream content on-demand has also given consumers greater control over their viewing experience. Consumers can watch movies and TV shows whenever and wherever they choose, leading to a more personalized and flexible entertainment experience.
User Experience and Accessibility
The transition from physical media like VHS to streaming services fundamentally reshaped the home media experience. This shift brought about significant changes in how users interacted with content, impacting accessibility and convenience in profound ways. The evolution wasn’t just technological; it was a transformation in the very nature of entertainment consumption.The user experience of accessing and enjoying media has undergone a dramatic evolution, moving from a largely linear and physically constrained experience to a highly flexible and on-demand one.
Streaming services have democratized access to a vast library of content, opening up new possibilities for viewers.
VHS Compared to Streaming: User Experience
The user experience between VHS and streaming differs drastically. VHS involved physical handling of tapes, requiring precise insertion and rewinding, while streaming offers instant access and a vast library at the touch of a button. This shift dramatically altered how people consumed media, fundamentally changing the way we engage with entertainment.
Ease of Use and Convenience
Streaming services significantly improved the ease of use and convenience of accessing media. Gone are the days of fumbling with tapes, searching for specific scenes, or dealing with the constraints of physical storage. Streaming platforms offer intuitive interfaces, search functionalities, and personalized recommendations, streamlining the user experience and simplifying the process of finding desired content. The ease of use in streaming also reduces the time spent searching for a particular show or movie, allowing users to spend more time enjoying the content.
Accessibility of Different Media Formats
The accessibility of different media formats varies significantly. VHS, while readily available in many homes, presented challenges in terms of physical limitations. Streaming, on the other hand, often relies on internet access, creating an accessibility hurdle for those without reliable internet connections or the necessary devices.
Comparison Table: VHS vs. Streaming Media
| Feature | VHS | Streaming |
|---|---|---|
| On-demand viewing | No | Yes |
| Portability | Limited (requires tapes) | High (accessible from various devices) |
| User control | Limited (playback speed, pausing, rewinding) | High (speed control, pausing, rewinding, seeking, etc.) |
| Content library | Limited, often regional | Vast, global |
| Cost | Relatively low for individual purchases; high for renting/subscriptions | Variable; subscription-based models common |
Impact of Streaming on Accessibility for Diverse User Groups
Streaming has significantly impacted accessibility for diverse user groups. Features like closed captions, audio descriptions, and subtitles greatly benefit individuals with visual or auditory impairments, broadening access to a wider range of content. However, disparities in internet access and digital literacy remain a challenge. Streaming services have also made it possible to access content from anywhere in the world, expanding cultural exposure and opportunities for people from diverse backgrounds.
The ability to pause, rewind, and access subtitles has been a significant improvement over VHS.
Content Creation and Distribution
The transition from physical media like VHS to digital streaming fundamentally reshaped the landscape of content creation and distribution. This shift involved a complex interplay of technological advancements, evolving business models, and shifts in audience expectations. The ease of digital distribution, coupled with the vast potential of streaming platforms, dramatically altered the creative process and the pathways to consumers.The methods of content creation and distribution varied significantly between the VHS era and the streaming era.
VHS, reliant on physical tapes, dictated a more localized and often less accessible distribution process. Streaming, on the other hand, leverages the internet’s global reach, allowing for near-instantaneous access to a wider audience.
Content Creation Methods
The VHS era, with its physical constraints, encouraged a more controlled and often studio-centric approach to content creation. Film studios and television networks maintained significant control over production and distribution. Independent filmmakers faced greater hurdles in reaching audiences.The streaming era, in contrast, empowered a wider range of content creators. Lower production costs and easier distribution channels enabled independent creators and smaller production companies to enter the market, contributing a more diverse range of content.
The rise of user-generated content further democratized the process, allowing individuals to create and distribute their own content through platforms like YouTube.
Distribution Methods
VHS distribution relied on a network of retailers, distributors, and rental stores. Content was packaged and shipped, creating delays in release and distribution.Streaming services, in contrast, distribute content directly to consumers through the internet. This eliminates the intermediaries and allows for instant access and global reach. This direct-to-consumer model dramatically shortened the time from production to consumption, fostering quicker feedback loops and enabling rapid response to viewer preferences.
Comparison of Challenges and Opportunities
| Characteristic | VHS Era | Streaming Era |
|---|---|---|
| Content Production Costs | Higher, due to physical media production and distribution costs. | Potentially lower, with the use of digital tools and fewer intermediaries, but production costs can vary based on the complexity of the content. |
| Distribution Reach | Limited by geographical constraints and retailer networks. | Global reach, potentially reaching millions or even billions of users worldwide. |
| Distribution Speed | Longer time from production to consumer access, due to physical shipping and distribution processes. | Near-instantaneous access, enabling quick release and update cycles. |
| Content Variety | More limited by studio budgets and distribution constraints. | Increased variety and diverse content due to the ease of entry for new creators. |
Copyright and Licensing Models
The VHS era saw copyright and licensing models largely centered on physical media and physical distribution. The streaming era necessitated a more complex framework to manage digital rights and access. Digital rights management (DRM) and streaming licenses have become crucial in protecting content and facilitating fair compensation for creators.The transition to streaming brought challenges to the traditional copyright and licensing models.
The ease of copying and distributing digital content made piracy a significant issue. This prompted the development of new technological safeguards and stricter legal frameworks to combat infringement. Simultaneously, new licensing models, such as subscription-based services, emerged, offering alternative revenue streams for creators and distributors. The emergence of creative commons licensing has also allowed for more flexibility and accessibility of content.
Impact on the Entertainment Industry
The transition from physical media like VHS to streaming services has dramatically reshaped the entertainment landscape, impacting everything from studio operations to consumer habits. This shift has introduced new revenue streams and challenges, forcing traditional players to adapt to survive in the digital age. The economic and social effects are multifaceted and far-reaching, touching on the creative process, distribution methods, and ultimately, the consumer experience.The entertainment industry, once largely reliant on physical product sales, has been fundamentally transformed by the rise of streaming.
This transition has triggered a cascade of adjustments across all sectors, from the production of content to its distribution and consumption. Studios, distributors, and retailers have had to recalibrate their business strategies to thrive in this new environment, and this has led to both exciting opportunities and significant hurdles.
Economic Effects of the Shift
The shift from physical media to streaming has dramatically altered the economic dynamics of the entertainment industry. Streaming platforms have disrupted traditional revenue models, particularly for distributors and retailers. Studios have seen new avenues for revenue, but the precise financial implications remain complex and evolving. The subscription-based model, while offering long-term revenue potential, necessitates significant investment in content creation and infrastructure.
Social Effects of the Shift
The accessibility of streaming has democratized access to entertainment, allowing audiences to consume content from around the globe. This global reach has fostered a sense of interconnectedness and cultural exchange. However, concerns about the homogenization of content and the impact on local industries are valid points of discussion.
Impact on Studios, Distributors, and Retailers
The transition from physical media to streaming has dramatically altered the roles and responsibilities of studios, distributors, and retailers. Studios now have the opportunity to distribute their content directly to consumers, bypassing traditional distributors. This direct-to-consumer model offers significant potential for revenue generation but also introduces challenges in managing global distribution networks and maintaining brand reputation. Distributors, once pivotal in the supply chain, have had to adapt to the new reality of streaming platforms, either by partnering with them or by finding alternative revenue streams.
Retailers, such as video rental stores, faced significant economic hardship as demand for physical media plummeted.
Comparison of Business Models
| Feature | Traditional Media Companies | Streaming Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Content Acquisition | Primarily through film festivals, acquisitions from other studios, and production agreements | Often through original productions and acquisitions, focusing on exclusive content |
| Distribution | Through physical retailers (e.g., Blockbuster, Best Buy) and distributors (e.g., Warner Bros. Home Entertainment) | Direct-to-consumer through online platforms |
| Revenue Model | Primarily from sales of physical media (DVDs, Blu-rays) and licensing fees | Subscription fees, advertising revenue, and transactional purchases |
| Content Ownership | Studios typically retain ownership of the physical media | Streaming platforms often own the content or have exclusive streaming rights |
| Cost Structure | High costs associated with physical production, storage, and distribution | High costs associated with content creation and infrastructure (servers, bandwidth) |
Impact on the Entertainment Landscape
The widespread adoption of streaming services has significantly altered the entertainment landscape. The rise of independent filmmakers and creators has been facilitated by platforms that offer distribution avenues beyond traditional channels. Consumers now have unprecedented access to a vast library of content, but this has also led to concerns about the future of independent cinemas and local movie theaters.
The accessibility of streaming services has fostered a global entertainment market, blurring geographical boundaries and providing a platform for diverse voices and perspectives.
Technological Advancements

Source: capture.com
The evolution of home media from physical formats to streaming services is intrinsically linked to crucial technological advancements. These innovations have significantly altered storage capacity, data compression, and network infrastructure, ultimately shaping the user experience and the entertainment industry. The interplay between these advancements has driven a paradigm shift in how we consume media.Technological breakthroughs have been pivotal in making streaming services accessible and ubiquitous.
These improvements have broadened the spectrum of content available, leading to a richer and more diverse entertainment landscape. The relentless pursuit of enhanced efficiency and accessibility in technology has been a defining factor in this transformation.
Key Innovations in Storage Capacity
Early home media formats, like VHS tapes, were limited by the physical space they occupied. The development of more compact and high-density storage technologies, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and later solid-state drives (SSDs), dramatically increased storage capacity. This crucial advancement allowed for the archiving and playback of more extensive libraries of content. The significant increase in storage capacity was a prerequisite for the growth of digital libraries and the subsequent shift to streaming.
Improvements in Data Compression
The sheer volume of data required for high-quality video and audio necessitated the development of efficient data compression techniques. These advancements were crucial to making streaming services feasible. Algorithms like MPEG and H.264, and later advancements like HEVC, reduced the file sizes of video and audio content, thereby significantly decreasing bandwidth requirements and allowing for quicker downloads and smoother streaming.
This improvement in data compression was a major factor in the widespread adoption of streaming services.
Data Compression Techniques and their Impact
- MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group): Early standards for video compression, enabling the storage of high-quality video in smaller files. These standards laid the foundation for future compression technologies.
- H.264 (Advanced Video Coding): A more advanced video compression standard, significantly improving compression efficiency compared to MPEG. This improvement enabled higher-quality video streaming with lower bandwidth requirements.
- HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding): A newer standard that further enhanced compression efficiency, enabling even higher-quality video streaming and more complex content, such as 4K resolution, with minimal impact on bandwidth usage.
Network Infrastructure Advancements
The rise of streaming services is inextricably linked to the evolution of network infrastructure. Faster internet speeds and wider network coverage became essential for delivering high-definition video content to users seamlessly. Improvements in fiber optic cables, wireless technologies, and cloud computing have created the infrastructure needed to support the global demand for streaming.
Examples of Technological Innovations
- Fiber Optic Cables: These high-bandwidth cables significantly increased internet speeds, allowing for the transmission of large amounts of data required for high-definition video streaming.
- Wireless Technologies (Wi-Fi, 3G, 4G, 5G): These advancements expanded internet access beyond wired connections, enabling streaming from mobile devices and in various locations. The evolution of mobile internet technologies, particularly 4G and 5G, played a significant role in making streaming accessible on the go.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud storage and servers are essential for storing and distributing streaming content, allowing for scalability and global reach. The scalability and accessibility offered by cloud computing are essential for handling the ever-increasing demand for streaming services.
The Future of Home Media
The evolution of home media has been a fascinating journey, marked by significant technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. From the clunky VHS tapes to the seamless streaming experiences of today, the journey has reflected broader societal trends in entertainment consumption. Looking ahead, the future of home media promises even more transformative changes, driven by emerging technologies and evolving user expectations.The convergence of technology and entertainment is likely to lead to immersive and personalized experiences.
Users will increasingly expect tailored content and interactive engagement, shaping the future of how we interact with media in our homes.
Potential Future Trends in Home Media Technologies
The future of home media will be shaped by several key trends. These trends encompass not only advancements in display technology and content delivery but also the integration of interactive elements and personalized experiences.
- Immersive Experiences: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies are poised to redefine home entertainment. Imagine watching a movie in a fully immersive VR environment, or interacting with characters in an AR-enhanced game within your living room. The potential for these technologies to transform home entertainment is significant, moving beyond passive consumption to interactive participation.
- Personalized Content Recommendations: Advanced algorithms will continue to personalize content recommendations, creating highly tailored viewing experiences. AI-powered systems will analyze viewing habits, preferences, and even emotional responses to suggest content relevant to individual users. This level of personalization will be crucial in maintaining user engagement in a saturated media landscape.
- AI-Powered Content Creation: Artificial intelligence is already impacting content creation. AI-generated visuals, music, and even storylines are becoming more sophisticated. In the future, AI could assist in crafting personalized content tailored to individual users, enabling more unique and engaging viewing experiences.
- Interactive and Personalized Home Entertainment Systems: Home entertainment systems will become increasingly integrated with other smart home devices, offering seamless control and interaction with the home media experience. Imagine controlling your home theatre system and smart lighting simultaneously through a single, intuitive interface.
Emerging Technologies Shaping Home Entertainment
Several technologies hold the potential to revolutionize the way we consume home entertainment.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR headsets, combined with high-resolution displays and sophisticated tracking technology, will enable viewers to experience films, games, and live events in a truly immersive 360-degree environment. Early adopters of VR technology are already experiencing the benefits of immersive experiences.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR technology will overlay digital information and interactive elements onto the real world, enriching home entertainment experiences. Imagine using AR filters to interact with characters in a video game, or overlaying interactive information on a movie screen to gain deeper insights. These applications have the potential to become integrated into our daily lives, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
Societal Shifts Reflected in Home Media Evolution
The evolution of home media mirrors broader societal shifts in entertainment consumption. The move from physical media to digital streaming, for example, reflects the growing demand for convenience, accessibility, and on-demand content.
- Demand for Convenience and Accessibility: Consumers increasingly value the convenience and accessibility of on-demand entertainment. Streaming services have capitalized on this trend, offering instant access to a vast library of content from anywhere with an internet connection. The desire for easy access and immediate gratification has fueled the shift towards digital platforms.
- Emphasis on Personalized Experiences: The shift toward personalized experiences in home media reflects a broader societal trend toward customization and self-expression. Consumers are seeking entertainment options tailored to their individual preferences, shaping the demand for interactive and adaptive entertainment experiences.
Disruptive Media Technologies
Several emerging technologies could potentially disrupt the current streaming landscape.
- Personalized AI-Driven Content Creation and Distribution: AI-powered systems could revolutionize content creation and distribution, offering customized entertainment experiences. This could lead to a rise of personalized content tailored to individual tastes, further segmenting the market and potentially creating new niche entertainment services.
- Metaverse Integration: The integration of the metaverse into home entertainment could create immersive virtual worlds where users can interact with content in entirely new ways. This could lead to a shift from passive consumption to active participation, potentially transforming the entertainment industry.
Last Word
In conclusion, the evolution of home media from VHS to streaming is a compelling narrative of technological progress and its impact on society. The transition wasn’t merely a technological upgrade; it was a cultural shift. The convenience and accessibility of streaming have reshaped how we interact with entertainment, demanding new approaches to content creation, distribution, and consumption. This evolution continues to shape the future of home entertainment.









Post Comment