History of Internet Development From ARPANET to 5G
History of internet development from ARPANET to 5G traces the evolution of connectivity, from the early days of packet switching networks to the ubiquitous mobile internet of today. This journey explores the key technologies, milestones, and influential figures that shaped the internet, highlighting its impact on communication, information sharing, and global culture. The story begins with the genesis of ARPANET, its architectural features, and early applications.
From there, we’ll witness the transition to the broader internet, the rise of the World Wide Web, and finally, the mobile internet revolution, culminating in the capabilities of 5G.
The development of internet access technologies, from dial-up to cable to DSL, is examined, showcasing the rapid increases in speed and accessibility. The role of Tim Berners-Lee in creating the World Wide Web, and the subsequent impact of the web on information sharing and communication, will be thoroughly detailed. The increasing integration of the internet into daily life, its impact on social interactions, and the challenges and concerns associated with its development will be covered, alongside the role of governments and organizations in shaping the internet’s evolution.
Finally, we’ll explore the future of internet development, considering emerging trends, advancements, and potential challenges.
Early Days of Networking
Source: rosehosting.com
The genesis of the internet lies in the pioneering efforts to connect computers across geographical distances. This era saw the development of fundamental networking concepts and technologies that laid the groundwork for the global network we know today. Early networks were built on the principle of packet switching, a revolutionary approach to data transmission.The development of packet switching was a crucial step in enabling communication between disparate computer systems.
It marked a significant departure from circuit switching, which reserved a dedicated communication path for the entire duration of a call. This shift allowed for more efficient utilization of network resources, as data could be broken into smaller packets and routed independently.
Packet Switching Networks
Packet switching, a fundamental concept in modern networking, enabled efficient data transmission. It involved breaking down data into smaller units, called packets, each containing source and destination information. These packets were then routed independently through the network to their destination, maximizing network utilization and resilience to failures. This approach contrasted with circuit switching, which reserved a dedicated path for communication throughout the entire transmission.
Key to packet switching’s success were the protocols and algorithms that managed the routing and reassembly of these packets.
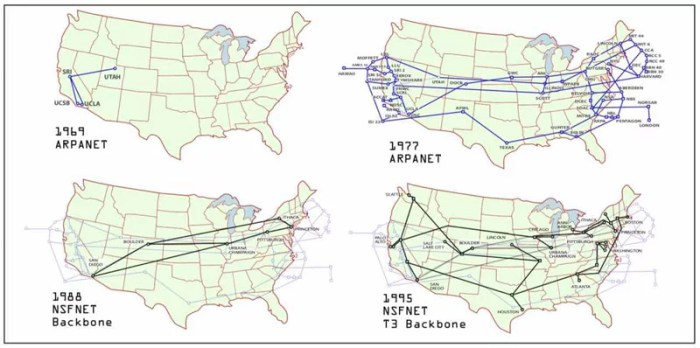
ARPANET: The Foundation of the Internet
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) stands as a pivotal moment in the history of networking. Its creation was driven by the desire to connect researchers across different institutions, fostering collaboration and accelerating research. ARPANET’s key architectural features included a distributed control structure, enabling independent operation of nodes, and the use of the TCP/IP protocol suite, which would become the backbone of the internet.
This design provided significant flexibility and scalability, crucial for the network’s future growth.
Early Networking Protocols
Early networking protocols, while foundational, differed significantly from modern protocols in their functionality and complexity. These protocols focused on basic communication tasks, such as packet routing and error handling. Modern protocols, like TCP/IP, provide a much richer set of functionalities, including reliable data transmission, security features, and support for diverse applications. The evolution of these protocols reflects the increasing complexity and demands of networked communication.
ARPANET Applications and Uses
ARPANET was initially utilized for research and development purposes, supporting communication between researchers in various institutions. Early applications included file transfer, remote login, and email. These applications were essential for collaborative research, fostering knowledge sharing, and promoting scientific progress.
Evolution of Networking Hardware
| Era | Hardware Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Early ARPANET (1960s-1970s) | Dedicated mainframe computers connected by leased lines | Limited processing power, slow transmission speeds, and reliance on dedicated lines. |
| Ethernet (1970s-1980s) | Local Area Networks (LANs) using coaxial cables | Improved transmission speeds and facilitated communication within a limited geographical area. |
| Early Internet (1980s-1990s) | Routers and modems enabling wider network connectivity | Increased network scale and speed, facilitating global communication. |
| Modern Internet (2000s-present) | High-speed fiber optic networks, sophisticated routers, and mobile devices | Extremely high speeds, ubiquitous connectivity, and a vast range of applications. |
The table above illustrates the significant advancements in networking hardware, moving from limited, dedicated systems to the ubiquitous, high-speed networks of today.
The Rise of the Internet
The transition from ARPANET to the global internet was a pivotal moment in human history. ARPANET, a pioneering network, laid the groundwork for interconnected communication, but its scope was limited. The development of crucial protocols and the adoption of these protocols by a wider range of institutions and individuals marked the true beginning of the internet as we know it today.The expansion of the internet was not a linear progression.
It was driven by a confluence of technological advancements, strategic decisions, and a growing global need for communication and information sharing. This era saw the rise of key players, from early researchers to visionary entrepreneurs, who shaped the internet’s evolution.
Key Milestones in the Transition
The development of standardized protocols, like TCP/IP, was crucial. This allowed different networks to communicate seamlessly, enabling the transition from ARPANET’s limited scope to a vast global network. The adoption of these protocols by a broader range of institutions, universities, and research organizations was a major step. This paved the way for the integration of various networks, marking the shift from a specialized network to a universally accessible platform.
Key figures in this transition include Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn, often considered the fathers of the internet.
Technological Advancements Driving Growth
Several technological advancements fueled the internet’s rapid expansion. The development of faster processors and more efficient storage solutions allowed for greater processing power and data handling capacity. Moore’s Law, demonstrating the exponential increase in computing power, played a significant role in this evolution. Increased bandwidth capabilities, enabled by advancements in fiber optic technology and wireless communication, further accelerated the growth.
These improvements made data transmission faster and more efficient, supporting the rise of multimedia content and more complex online interactions.
Regional and Demographic Differences in Internet Growth
The internet’s growth wasn’t uniform across regions and demographics. Developed nations generally experienced earlier and faster adoption rates due to factors such as higher levels of technological infrastructure and greater access to resources. Developing countries often faced challenges in bridging the digital divide, due to infrastructure limitations, economic disparities, and literacy issues. This resulted in significant disparities in internet access and usage.
However, significant progress has been made in closing this gap, with increasing internet penetration in many developing regions.
Evolution of Internet Access Technologies
The development of internet access technologies has been a defining aspect of the internet’s growth. Dial-up, a prevalent early technology, allowed users to connect via their telephone lines, although speeds were relatively slow. The emergence of cable internet offered a significant improvement in speed, using existing cable television infrastructure. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) provided another faster option over traditional phone lines, allowing for greater bandwidth.
Progression of Internet Access Speeds and Technologies
| Technology | Speed (approx.) | Year of Introduction/Widespread Adoption | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dial-up | 56 kbps | 1990s | Connected via telephone lines, slow speeds limited usage to basic applications. |
| Cable Modem | 1-10 Mbps | Late 1990s | Leveraged existing cable television infrastructure for faster connections. |
| DSL | 1-20 Mbps | 1990s-2000s | Used existing telephone lines for faster data transmission than dial-up. |
| Fiber Optic | 100 Mbps and above | 2000s-Present | High-speed connections using fiber optic cables for significant bandwidth improvements. |
| Wireless Technologies (Wi-Fi, 3G, 4G, 5G) | Variable, increasing rapidly | 2000s-Present | Provided mobile access, allowing users to connect from various locations, with 5G being the latest generation. |
The World Wide Web

Source: medium.com
The early internet, while a powerful tool for communication and data exchange, lacked a user-friendly way to navigate and access information. This is where the World Wide Web, spearheaded by Tim Berners-Lee, dramatically changed the landscape. His vision of a global information space, accessible to all, became a reality, fundamentally altering how we interact with the digital world.The web’s creation wasn’t a sudden event but a gradual evolution built on pre-existing technologies.
Berners-Lee’s ingenious work combined existing ideas into a cohesive system, making information readily available to anyone with an internet connection. This revolutionary approach transformed the internet from a network of computers into a global information network.
Tim Berners-Lee and the Genesis of the Web
Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist, is credited with inventing the World Wide Web. He developed the fundamental technologies that underpin the web, including the concept of hypertext, URLs, HTTP, and HTML. His vision was to create a system that allowed for easy access and sharing of information across the globe.
Key Concepts of the Web
The web’s architecture rests on several key concepts, enabling its global reach and user-friendliness.
- Uniform Resource Locators (URLs): URLs provide unique addresses for every resource on the web, enabling users to easily locate and access specific documents or pages. This standardized addressing system allows for efficient navigation through the vast expanse of online information. Examples include https://www.example.com and file:///path/to/file.html. These addresses are crucial for directing users to specific content on the web.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP): HTTP defines the rules for communication between web browsers and web servers. It specifies how requests for web pages are sent and how responses are returned, enabling a standardized interaction between clients and servers.
- HyperText Markup Language (HTML): HTML is the language used to structure and format web pages. It defines the elements and layout of web content, making it readable and navigable by web browsers. HTML uses tags to specify different parts of a document, such as headings, paragraphs, and images. For example,
defines a main heading,
defines a paragraph, and
defines an image.
Early Websites and their Impact
The early web saw a proliferation of simple websites, often showcasing basic information or personal profiles. These early sites laid the foundation for the complex websites we see today. Examples of early websites, though rudimentary by modern standards, included personal pages, organizational information, and early e-commerce platforms. These early sites, though limited in functionality, demonstrated the potential of the web as a platform for information sharing and communication.
They showcased how simple web pages could be used to convey information and interact with the world.
Revolutionizing Information Sharing and Communication
The World Wide Web revolutionized information sharing and communication by creating a global, interconnected network accessible to virtually anyone. Prior to the web, accessing and sharing information was often cumbersome and limited by geographical boundaries. The web, with its ease of use and global reach, democratized information access and fostered communication across cultures and continents. It connected individuals, organizations, and ideas in unprecedented ways.
Development of Web Browsers, History of internet development from arpanet to 5g
The emergence of web browsers was crucial to the web’s widespread adoption. These applications facilitated user interaction with web content, making the internet accessible and navigable.
| Browser | Key Features and Impact |
|---|---|
| Mosaic | One of the earliest graphical web browsers, Mosaic made web browsing more intuitive and user-friendly by introducing graphical interfaces. This significantly broadened the accessibility and appeal of the internet, leading to a surge in user adoption. |
| Netscape Navigator | Netscape Navigator built upon Mosaic’s success by incorporating advanced features, including support for JavaScript and plugins. Its popularity helped solidify the web as a platform for interactive experiences. |
| Internet Explorer | Internet Explorer’s dominance as a browser in the early 2000s helped establish a standard for web development and usage, despite its design choices and sometimes controversial market strategies. |
| Firefox | Firefox emerged as an open-source alternative, emphasizing user privacy and control. This browser became popular due to its flexibility and customization options. |
| Chrome | Chrome’s rise to prominence is attributed to its speed, efficiency, and extensive feature set. It quickly became the most widely used browser, impacting the development and direction of the web. |
Mobile Internet and 5G
The internet has transitioned from a primarily desktop-based phenomenon to a ubiquitous mobile experience. Mobile internet access has become increasingly crucial for personal and professional communication, entertainment, and commerce, driving a rapid evolution in mobile technologies. This shift highlights the pivotal role of mobile devices in shaping modern society and the economy.
The Increasing Importance of Mobile Internet Access
Mobile internet access has become indispensable in modern life. Its pervasive availability enables real-time communication, instant access to information, and seamless engagement with online services, regardless of location. This constant connectivity has profound implications for education, employment, and social interaction, fostering global interconnectedness and enabling remote work, education, and healthcare.
Evolution of Mobile Internet Technologies (2G to 4G)
Mobile internet technology has progressed significantly from its early stages. 2G introduced the ability to send text messages and make calls, laying the groundwork for mobile communication. Subsequent generations, 3G and 4G, enhanced data speeds and capabilities, enabling video streaming, online gaming, and more complex applications. This progression demonstrates the continuous drive for faster and more reliable mobile internet access.
Key Features and Benefits of 5G Technology
5G represents a significant leap forward in mobile internet technology. Its key features include dramatically increased speeds, significantly lower latency, and enhanced network capacity, enabling faster data transfer rates and more reliable connections. This allows for seamless streaming of high-definition video, low-latency gaming experiences, and the support of advanced applications like the Internet of Things (IoT). The benefits extend to various sectors, enabling new possibilities and efficiencies.
Comparison of 5G with Previous Generations
Compared to its predecessors, 5G offers unparalleled speed and capacity. While 2G and 3G were primarily focused on voice and basic data, 4G provided faster speeds for data-intensive tasks. 5G builds upon this foundation by providing vastly superior speeds and lower latency, opening up a new era of possibilities for applications and services that were previously unimaginable.
Potential Impacts of 5G on Various Sectors
5G’s transformative potential extends across diverse sectors. In communication, 5G facilitates instant and seamless global connectivity, enabling real-time collaboration and communication. In entertainment, it allows for the smooth streaming of high-quality video content and immersive gaming experiences. In commerce, 5G facilitates faster online transactions, remote payments, and the development of new business models.
Summary Table of Mobile Internet Generations
| Generation | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 2G | Voice calls, basic text messaging. Limited data capacity. | Voice calls, SMS. |
| 3G | Enhanced data speeds, enabling mobile internet access. | Mobile browsing, video streaming (low resolution). |
| 4G | Faster data speeds, improved reliability. Suitable for video streaming and high-bandwidth applications. | High-resolution video streaming, online gaming, video conferencing. |
| 5G | Extremely high speeds, ultra-low latency, and high network capacity. | Virtual reality, augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, IoT applications. |
Internet Evolution and Impact
The internet’s journey from a research network to a ubiquitous force in daily life has been nothing short of transformative. Its evolution has profoundly impacted how we communicate, learn, work, and interact with the world around us. This section explores the increasing integration of the internet into modern society, examining its effects on social interactions, cultural norms, and the various challenges it presents.
Furthermore, it analyzes the role of governance in shaping this digital landscape and the profound influence it has had on numerous industries.
Integration into Daily Life
The internet has become deeply embedded in our daily routines, permeating nearly every aspect of modern life. From online banking and shopping to accessing education and entertainment, the internet has become indispensable. This integration has dramatically altered work patterns, social interactions, and personal pursuits.
Impact on Social Interactions and Cultural Norms
The internet has fostered new forms of social interaction, creating global communities and enabling individuals to connect with people across geographical boundaries. However, it has also presented challenges to traditional social norms and cultural values, including concerns about privacy, misinformation, and cyberbullying. The rise of social media platforms has significantly altered how we interact with each other, impacting interpersonal communication styles and the formation of social groups.
Challenges and Concerns
The rapid expansion of the internet has presented several challenges. Concerns about online safety, privacy, and the spread of misinformation are prominent. The digital divide, with disparities in access and skills, remains a significant issue. The proliferation of misinformation and disinformation poses a threat to informed decision-making and public discourse.
Role of Governments and Organizations
Governments and international organizations play a critical role in shaping the internet’s evolution. They are responsible for establishing regulations, promoting digital literacy, and ensuring internet access for all citizens. Policies and regulations regarding data privacy, content moderation, and cybersecurity are crucial aspects of this responsibility. Different countries have taken varying approaches, reflecting differing cultural values and priorities.
Impact on Various Industries
The internet’s influence extends across numerous industries. E-commerce has revolutionized retail, while online education has broadened access to knowledge. Communication and collaboration tools have dramatically improved business operations and productivity. This impact is particularly visible in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and entertainment.
Impact on Different Demographics
| Demographic | Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Young Adults | Enhanced communication, access to information, and opportunities for career development. Social connections transcend geographical boundaries. | Exposure to cyberbullying, potential for addiction, and the pressure to maintain a perfect online persona. |
| Middle-Aged Adults | Access to updated information and new skillsets for professional development. Convenience in managing finances and personal errands. | Adapting to new technologies, potential for feeling overwhelmed by the constant influx of information, and concerns about job displacement. |
| Senior Citizens | Increased access to healthcare information, socialization opportunities, and reduced isolation. | Difficulties adapting to new technologies, potential for scams and misinformation, and digital literacy gaps. |
The table above provides a comparative analysis of the internet’s impacts on various demographics, highlighting the differing experiences and concerns across age groups. The internet has brought immense benefits to many, but also introduces unique challenges for diverse groups.
The Future of Internet Development: History Of Internet Development From Arpanet To 5g
The internet, a ubiquitous force in modern life, is constantly evolving. Emerging technologies are poised to reshape its infrastructure and applications, offering both exciting possibilities and potential challenges. The future of the internet promises a more interconnected, intelligent, and personalized experience, driven by innovations in areas like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI).
The future internet will be significantly influenced by the rapid advancement of technologies like the IoT and AI. These advancements are set to dramatically alter the way we interact with and utilize the internet. The internet of tomorrow will be characterized by increased automation, personalized experiences, and a seamless integration of digital and physical worlds. This will bring about new challenges, like managing the massive data generated by interconnected devices and ensuring data security in this interconnected ecosystem.
Potential Impact of IoT
The proliferation of interconnected devices, driven by the IoT, will generate unprecedented amounts of data. This data will be crucial for optimizing processes and creating new applications, but it will also demand robust infrastructure to handle the massive influx. Imagine smart cities using real-time data from sensors to optimize traffic flow and resource management, or industrial processes using data from connected machinery to predict maintenance needs and increase efficiency.
Successfully managing and utilizing this data is crucial to the future of the internet.
Potential Impact of AI
Artificial intelligence will play a pivotal role in personalizing user experiences and streamlining tasks. AI-powered search engines will provide more accurate and relevant results, and AI-driven content creation tools will personalize the information we receive. Imagine personalized learning platforms tailored to individual needs, or AI-powered customer service bots handling inquiries efficiently and effectively. These advancements will require careful consideration of ethical implications, such as data privacy and algorithmic bias.
Potential Challenges for Future Internet Development
While the future of the internet holds immense potential, significant challenges remain. Ensuring cybersecurity in a more interconnected world is paramount. Protecting user data and preventing malicious attacks will be critical to maintaining trust and reliability. Moreover, managing the massive influx of data from IoT devices requires sophisticated infrastructure and effective data management strategies.
Potential Directions for Internet Connectivity
Future internet connectivity will likely focus on higher speeds, greater reliability, and improved accessibility. 5G and beyond will pave the way for seamless connectivity, enabling real-time applications and supporting the needs of an increasingly mobile and connected world. The development of new protocols, such as those supporting virtual and augmented reality, will be crucial for immersive experiences.
Potential Future Internet Protocols and Technologies
New internet protocols and technologies will emerge to support the needs of a more complex and interconnected world. Protocols supporting low-latency communication will be vital for real-time applications. Protocols that can dynamically adapt to varying network conditions will be critical for reliable connectivity. Protocols that address data security and privacy will be indispensable for maintaining trust in the internet ecosystem.
Projected Growth and Impact of Internet Technologies
| Technology | Projected Growth | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 5G | Exponential growth in adoption and deployment | Enhanced mobile internet experience, supporting IoT devices, and enabling new applications. |
| IoT | Massive increase in connected devices | Revolutionizing industries, enabling smart cities, and creating new business models. |
| AI | Rapid advancements in capabilities and applications | Personalizing user experiences, streamlining tasks, and driving innovation across various sectors. |
| Quantum Computing | Emerging technology with potential for significant impact | Potentially accelerating the development of advanced algorithms and protocols, potentially leading to faster and more secure communications. |
Outcome Summary
Source: internetpasoapaso.com
In conclusion, the history of internet development, from its humble beginnings in ARPANET to the transformative power of 5G, reveals a remarkable journey of innovation and growth. This evolution has profoundly impacted nearly every aspect of modern life, connecting billions across the globe and revolutionizing how we communicate, access information, and conduct business. As we look towards the future, the potential impact of emerging technologies like IoT and AI promises further advancements, while also presenting challenges and opportunities for navigating the ever-evolving digital landscape.













Post Comment