Difference Between Ddr4 And Ddr5 Ram
Difference between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM is a crucial consideration for any computer enthusiast or upgrader. Understanding the nuances between these two RAM technologies is vital for making informed decisions about system performance and compatibility. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, comparing speed, power consumption, and key technical specifications, enabling readers to confidently choose the right RAM for their needs.
This in-depth exploration will cover the specifications of both DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, highlighting the differences in their technical characteristics. We’ll delve into the specifics of clock speeds, timings, and voltage requirements. The comparison table will visually illustrate the performance disparities, while the subsequent sections will explore their applications, compatibility, and future trends.
Introduction to RAM
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a fundamental component of all modern computer systems. It serves as the computer’s short-term memory, holding the data and instructions currently being used by the processor. Without RAM, a computer would be unable to perform tasks efficiently, as the processor would constantly have to access the slower storage devices like hard drives.RAM is volatile memory, meaning its contents are lost when the power is turned off.
This contrasts with non-volatile storage like hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs), which retain data even without power. Its volatile nature allows for quick access and manipulation of data, but requires the computer to reload data from persistent storage every time it’s turned on.
Different Types of RAM
Various types of RAM have emerged over time, each with improvements in speed, capacity, and power efficiency. DDR4 and DDR5 are two of the most recent and widely used standards.
Basic Functionalities of RAM
RAM’s primary function is to store data that the CPU needs to access quickly. It enables the CPU to execute instructions and perform tasks at a high speed. Data is loaded into RAM when needed, allowing the CPU to retrieve and process it efficiently. This process is crucial for everything from running applications to playing games. When a program or application is closed, the data associated with it is typically removed from RAM.
Comparison of RAM Types
| Characteristic | DDR4 | DDR5 | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Typically operating at speeds ranging from 2133 MHz to 3200 MHz. | Generally operates at speeds from 4800 MHz to 7600 MHz or even higher. | DDR5 offers significantly faster data transfer rates, enabling quicker processing speeds for applications. |
| Power Consumption | Generally consumes more power compared to DDR5, particularly at higher speeds. | Designed with lower power consumption, leading to better battery life in laptops and reduced heat generation. | DDR5’s lower power consumption is a key improvement over DDR4, particularly beneficial for mobile devices and energy-conscious systems. |
| Architecture | Uses a less complex architecture. | Employs a more sophisticated architecture to enable higher speeds and efficiency. | The advanced architecture allows for more complex data transfer and processing operations, boosting overall system performance. |
| Manufacturing Process | Manufactured using more established processes. | Utilizes advanced manufacturing processes to create smaller and more efficient components. | This allows for greater capacity and higher performance while maintaining lower power consumption. |
DDR4 RAM Specifications
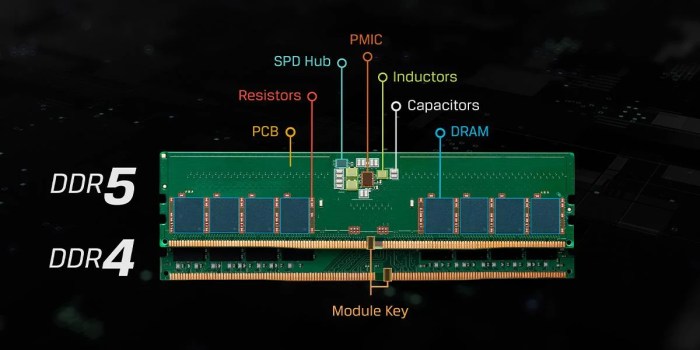
Source: cgdirector.com
DDR4 RAM, a prevalent memory technology, has significantly shaped the modern computing landscape. Its specifications, while superseded by DDR5, remain crucial for understanding the evolution of RAM technology. This section delves into the key technical aspects of DDR4, including its clock speeds, timings, and voltage.
Key Technical Specifications
DDR4 RAM’s performance is defined by several key technical specifications. Clock speed, measured in MHz, dictates the rate at which data is transferred. Timings, expressed in nanoseconds (ns), represent the delay between signals. Lower timings generally equate to faster performance. Voltage, typically 1.2V, dictates the electrical potential used for data transmission.
Understanding these elements is vital for selecting RAM compatible with your system and achieving optimal performance.
Available Modules
DDR4 RAM comes in various modules, each with specific capabilities. Dual In-line Memory Modules (DIMMs) are the most common, differentiated by their capacity and form factor. Unbuffered DIMMs (UDIMMs) are a common type, and Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs) are typically used in server environments for higher reliability and stability. Furthermore, different manufacturers often provide variations on DIMM designs.
Common Module Sizes
DDR4 RAM modules are available in a range of sizes. Common capacities include 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, and 32GB. The selection of the right size depends on the specific needs of the user, ranging from basic applications to demanding tasks.
DDR4 Channels, Difference between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM
DDR4 RAM utilizes memory channels to enhance data transfer rates. The number of channels, typically 2, 4, or more, impacts overall system performance. Each channel supports a specific number of DIMMs, and the combination of channel count and DIMM capacity determines the overall RAM capacity of a system. Utilizing multiple channels for memory allows for parallel data transfer, thereby improving the overall speed and performance.
Compatibility with Motherboards
Compatibility between DDR4 RAM and motherboards is paramount. Different motherboards support varying specifications for DDR4 RAM. It’s essential to ensure that the RAM’s specifications, particularly the frequency and timings, are compatible with the motherboard’s capabilities. Mismatched RAM and motherboard specifications can lead to system instability or boot failures. Consult your motherboard’s documentation for the supported DDR4 RAM specifications.
DDR4 RAM Frequencies
| Frequency (MHz) | Description |
|---|---|
| 2133 | A standard baseline frequency for DDR4. |
| 2400 | A moderately high frequency that provides improved performance over 2133. |
| 2666 | A common frequency for many systems seeking slightly higher speeds. |
| 3000 | A more common higher frequency, often chosen for gaming and other performance-demanding applications. |
| 3200 | A frequently selected frequency, offering a noticeable boost in speed over lower frequencies. |
| 3600 | A higher frequency, ideal for high-performance applications and advanced users. |
| 4000 | A high-end frequency, often sought by enthusiasts seeking the utmost performance. |
This table provides a general overview of common DDR4 RAM frequencies. The optimal frequency depends on individual system requirements and the desired performance level.
DDR5 RAM Specifications: Difference Between DDR4 And DDR5 RAM

Source: rockpapershotgun.com
DDR5 RAM represents a significant advancement in memory technology, offering substantial performance enhancements and power efficiency improvements over its predecessor, DDR4. These enhancements are crucial for modern high-performance computing systems, supporting demanding applications like gaming, content creation, and data analysis.DDR5 RAM’s key specifications, including clock speeds, timings, and voltage, contribute to its superior performance. Its design incorporates several crucial innovations that elevate its capabilities and make it a pivotal component for future computing needs.
Key Technical Specifications
DDR5 RAM boasts enhanced clock speeds, typically ranging from 4800 MHz to 7600 MHz, compared to DDR4’s maximum speeds. These higher clock speeds directly translate to faster data transfer rates, significantly impacting overall system performance. Lower timings, such as 36-38-38-78, further contribute to reduced latency and improved responsiveness. DDR5 employs a lower operating voltage compared to DDR4, typically 1.1V, which contributes to enhanced power efficiency.
This reduced voltage translates to lower heat generation, enabling improved system stability and longer lifespan.
Modules Available for DDR5 RAM
DDR5 RAM modules come in various forms, including Dual In-Line Memory Modules (DIMMs). These DIMMs are designed for various form factors and configurations, providing flexibility for system builders and users. Different manufacturers might offer variations in module design, but the fundamental functionality and specifications remain consistent.
Common DDR5 RAM Module Sizes
DDR5 RAM modules are available in several standard sizes, including 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, and 64GB. These sizes cater to diverse user needs, from basic systems to high-end configurations demanding extensive memory capacity.
DDR5 RAM Channels
DDR5 RAM can be configured in dual-channel, triple-channel, or quad-channel architectures. These channel configurations enable parallel data transfer, leading to enhanced bandwidth and overall system performance. The specific number of channels a system supports depends on the motherboard’s design and capabilities.
Improvements in DDR5 over DDR4
DDR5 RAM introduces several key improvements over DDR4. These enhancements include higher bandwidth, lower latency, and increased power efficiency. These attributes make DDR5 RAM a superior choice for applications demanding high performance and responsiveness.
Enhanced Power Efficiency of DDR5 RAM
DDR5 RAM’s reduced voltage requirement significantly improves power efficiency. This feature reduces energy consumption, leading to lower operating costs and potentially extended battery life in mobile devices. The lower voltage also results in lower heat generation, enhancing system stability and longevity.
DDR5 RAM Frequencies
| Frequency (MHz) | Description |
|---|---|
| 4800 | A common starting frequency for DDR5. |
| 5600 | A frequently encountered frequency offering a balanced performance. |
| 6000 | A widely used frequency, often found in high-end systems. |
| 6400 | A frequency that generally delivers a notable performance increase. |
| 7200 | A high-end frequency, usually preferred for intensive tasks. |
| 7600 | The upper limit of commonly available DDR5 frequencies. |
Key Differences between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM
DDR4 and DDR5 represent significant advancements in RAM technology, each offering improved performance characteristics over its predecessor. Understanding these differences is crucial for discerning the optimal RAM choice for various computing needs.
Clock Speeds
DDR5 RAM boasts significantly higher clock speeds compared to DDR4. This translates to faster data transfer rates, enabling quicker processing speeds and overall system responsiveness. For example, DDR5 modules are frequently seen operating at 5200 MT/s or higher, whereas DDR4 modules are generally capped at 3200 MT/s.
Power Consumption
DDR5 RAM generally consumes less power than DDR4 RAM, a key advantage for laptops and other portable devices. This reduced power consumption contributes to improved battery life and reduced heat generation within the system. The lower power requirements are due to the optimized architecture and advanced power management techniques incorporated in DDR5.
Data Transfer Rates
DDR5 RAM demonstrates substantial improvements in data transfer rates. The enhanced bandwidth enables faster data movement between RAM and the CPU, leading to smoother multitasking and quicker application loading times. The increased data transfer rates directly contribute to the overall speed and efficiency of the computer system.
Voltage Requirements
DDR5 RAM operates at lower voltage levels compared to DDR4 RAM. This lower voltage is achieved through advanced circuit designs and manufacturing processes, reducing energy consumption and potentially extending the lifespan of the components. The lower voltage is also a factor in reducing heat generation and improving reliability.
Summary of Performance Differences
| Feature | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
| Speed (MT/s) | Up to 3200 | Up to 6400+ |
| Power Consumption (Watts) | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Data Transfer Rates (GB/s) | Lower | Higher |
| Voltage (V) | 1.2V | 1.1V |
Compatibility and Upgrades
Upgrading your computer’s RAM can significantly boost performance, but it’s crucial to understand the compatibility aspects between different RAM types. Choosing the right RAM for your motherboard is essential to avoid issues and ensure a smooth upgrade process. DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, while both serving the same purpose, are not interchangeable due to architectural differences.Compatibility between RAM and motherboards is a critical factor.
Motherboards are designed to support specific RAM types, and attempting to install incompatible RAM can lead to system instability, boot failures, or even damage to components. Therefore, carefully examining your motherboard’s specifications is paramount before making any upgrades.
Compatibility Requirements
DDR4 and DDR5 RAM are not compatible with each other. A motherboard designed for DDR4 RAM will not support DDR5 RAM, and vice versa. This incompatibility stems from the different electrical and data transfer protocols employed by each generation. Checking the motherboard’s documentation is essential to ascertain the supported RAM type. Incorrect RAM installation will not result in the motherboard recognizing the RAM, or the system may boot but experience performance issues.
Upgrading from DDR4 to DDR5
Upgrading from DDR4 to DDR5 RAM necessitates a complete replacement of the existing RAM modules with DDR5 modules. The process involves removing the DDR4 modules and installing the new DDR5 modules. The motherboard’s compatibility with DDR5 RAM is crucial; otherwise, the system won’t recognize the new RAM.
Installing DDR5 RAM
The process of installing DDR5 RAM is generally similar to installing DDR4 RAM. However, careful attention to detail is critical to prevent potential damage.
- Power Down and Disconnect: Before starting any RAM installation, ensure that the computer is powered off and disconnected from the power source. Disconnect any peripherals and cables.
- Open the Computer Case: Carefully open the computer case. Consult the motherboard manual for specific instructions.
- Locate the RAM Slots: Identify the RAM slots on the motherboard. Note that not all slots are necessarily active.
- Remove Existing Modules: Carefully remove the existing DDR4 RAM modules. Consult the motherboard manual to identify the correct procedure for releasing the modules from their slots.
- Insert the New Modules: Align the DDR5 RAM modules with the RAM slots and gently press down until they click into place. Pay attention to the orientation of the modules. Incorrect installation can cause damage.
- Close the Computer Case: Carefully close the computer case and reconnect all cables and peripherals.
- Power On and Test: Turn on the computer and verify that the system boots properly. Monitor the system for any instability or errors.
Potential Issues During Upgrades
Several potential issues can arise during the upgrade process. Mismatched RAM speeds or timings can cause instability. Incorrectly seated RAM modules can lead to system failures or damage to the motherboard. Incorrect voltage settings can also damage the components.
Safe RAM Upgrade Steps
A safe RAM upgrade involves meticulous planning and execution.
- Verify Compatibility: Before purchasing any RAM, confirm that it is compatible with your motherboard model.
- Consult the Motherboard Manual: Review the motherboard manual for specific installation instructions and recommended RAM specifications.
- Select Compatible RAM: Choose RAM modules with matching specifications, including speed, voltage, and timings.
- Proper Handling: Handle RAM modules with care to prevent static electricity damage.
- Thorough Testing: After the upgrade, thoroughly test the system for stability and performance.
Applications and Use Cases
DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, differing significantly in speed and capabilities, cater to various computing needs. Understanding their suitability for specific tasks is crucial for optimal performance and investment. This section delves into the applications and use cases for each RAM type, highlighting their respective strengths.The choice between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM depends heavily on the specific demands of the application.
While DDR5 offers substantial performance gains, its higher cost may not justify its use in all scenarios. Conversely, DDR4 remains a viable option for tasks where its performance is sufficient.
DDR4 RAM Applications
DDR4 RAM remains a prevalent choice for a wide range of applications due to its affordability and compatibility with existing systems.
- Desktop PCs: DDR4 is a dominant choice for standard desktop PCs. Its availability and affordability make it an attractive option for consumers seeking a balance between cost and performance for general computing tasks like web browsing, document editing, and casual gaming.
- Workstations: Many workstations still utilize DDR4 RAM. Its speed is often adequate for tasks like video editing, 3D modeling, and data analysis. The cost-effectiveness is a significant advantage in these professional environments.
- Servers (entry-level and mid-range): DDR4 RAM is commonly found in entry-level and mid-range servers. The reliability and established ecosystem of DDR4 make it a practical choice for basic server operations, such as handling web traffic and running standard applications.
- Laptops and Ultrabooks: DDR4 RAM remains a common choice for laptops and ultrabooks due to its cost-effectiveness. While DDR5 is starting to gain traction, DDR4 is still a good choice for everyday tasks in these portable devices.
DDR5 RAM Applications
DDR5 RAM’s enhanced speed and features are ideally suited for demanding applications.
- High-end PCs and Workstations: DDR5 is a superior choice for users requiring the utmost performance. Its higher bandwidth and lower latency make it ideal for tasks like high-resolution 3D modeling, intensive video editing, and professional gaming. These demanding workloads benefit greatly from the speed and efficiency of DDR5.
- High-performance Servers: Modern data centers and servers often utilize DDR5 RAM. The higher speed and bandwidth support complex computations and data processing, essential for applications in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analysis.
- Future-proof Systems: Choosing DDR5 RAM allows for future upgrades. Its architecture and specifications are designed to accommodate evolving hardware requirements, ensuring long-term system performance.
Comparison of Suitability
The table below summarizes the suitability of DDR4 and DDR5 RAM for various tasks.
| Task | DDR4 RAM | DDR5 RAM |
|---|---|---|
| General Computing (Web browsing, document editing) | Excellent | Excellent |
| High-end Gaming | Adequate for some games | Superior performance, especially with high-end graphics cards |
| Video Editing (basic tasks) | Adequate for simple edits | Better performance for complex edits, especially 4K and 8K |
| 3D Modeling (moderate complexity) | Suitable | Improved performance and reduced rendering times |
| Machine Learning/AI Tasks | Limited | Superior performance due to higher bandwidth |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Future Trends
Source: 10scopes.com
The rapid evolution of RAM technology continues, with DDR5 currently dominating the market. However, the pursuit of faster speeds, greater capacity, and lower power consumption fuels ongoing research and development. Understanding the future trends in RAM is crucial for anticipating the next generation of computing capabilities.The next generation of RAM technology is likely to address the limitations of DDR5, such as its power consumption and manufacturing complexity.
This necessitates the exploration of innovative architectures and materials.
Emerging Technologies
Several promising technologies are poised to reshape the RAM landscape beyond DDR5. These technologies aim to achieve higher bandwidth, lower latency, and more efficient power consumption.
- High Bandwidth Memory (HBM): HBM technology, currently used in high-end GPUs, is gradually finding applications in CPUs. This technology employs multiple stacked memory chips, allowing for significantly higher bandwidth compared to traditional RAM. The potential for HBM integration into mainstream systems is significant, offering unprecedented data transfer rates. For example, high-end gaming PCs and servers often utilize HBM to enhance performance for demanding tasks, such as real-time rendering and data processing.
- 3D XPoint Memory: Developed by Intel and Micron, 3D XPoint memory promises exceptionally fast read and write speeds. It offers a blend of RAM and flash memory characteristics, combining the speed of RAM with the durability and non-volatility of flash memory. This technology is currently being investigated for applications requiring both high speed and data persistence, such as enterprise-level data storage and high-performance computing.
Early demonstrations showcase its potential in improving data retrieval and processing speed for specific applications.
- Memristors: Memristors are a type of electronic component that exhibit memory-like properties. These components could potentially lead to revolutionary changes in memory architectures, enabling extremely low-power consumption and high-density storage. Though still in the research and development phase, memristors show promise for the future of RAM, potentially allowing for even smaller and more energy-efficient systems.
Potential Impact
The integration of these emerging technologies will significantly impact various sectors. Higher bandwidth and lower latency RAM will improve the performance of high-performance computing (HPC), data centers, and artificial intelligence (AI) applications.
- High-Performance Computing: The enhanced speed and capacity of next-generation RAM will enable scientists and engineers to tackle more complex simulations and analyses, potentially accelerating advancements in fields like medicine, materials science, and aerospace engineering.
- Data Centers: More efficient and higher-bandwidth RAM will drive the scalability and efficiency of data centers, enabling them to handle ever-increasing amounts of data and support growing demands for cloud computing and data storage services. This leads to more responsive and efficient cloud services.
- Artificial Intelligence: The advancements in RAM technology will facilitate the development and deployment of more sophisticated AI models and algorithms. Faster data processing and storage will be crucial for training and running these models, enabling more accurate predictions and faster responses.
Predictions for RAM Advancements
While precise timelines are difficult to predict, certain advancements in RAM technology appear highly probable in the coming years. The transition from DDR5 to the next generation is anticipated to be gradual, with iterative improvements in speed and efficiency.
- Continued Evolution of DDR Technologies: DDR6, or its successor, is expected to build upon the foundation laid by DDR5, introducing enhancements in bandwidth and power efficiency. Real-world examples suggest the industry often follows this iterative pattern, gradually increasing performance with each new generation.
- Hybrid Approaches: We might see hybrid memory architectures combining the strengths of different technologies, such as HBM and 3D XPoint, to create a system with high bandwidth and persistent storage capabilities.
- Focus on Energy Efficiency: As power consumption becomes a more critical factor in computing systems, RAM manufacturers will likely prioritize technologies that consume significantly less energy to support the sustainability of these systems.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, DDR5 RAM represents a significant leap forward in RAM technology, offering superior speed and power efficiency compared to DDR4. However, the decision to upgrade hinges on the specific needs of the user and the budget constraints. The compatibility aspects between the RAM and the motherboard must be thoroughly considered before any upgrade. The choice between DDR4 and DDR5 ultimately depends on the balance of performance, cost, and compatibility with existing hardware.













Post Comment