History Of Social Media Platforms
History of social media platforms chronicles the fascinating evolution of online communication. From the earliest bulletin board systems to the mobile-first apps we use today, social media has fundamentally reshaped how we connect and share information. This journey explores the key milestones, technological advancements, and societal impacts that have defined the development of these platforms.
This overview will examine the early stages of social media, highlighting the rise of social networking sites and the impact of mobile technology. It will delve into the role of social media in information sharing, business practices, and societal norms. Finally, it will consider the potential future of social media and the challenges and opportunities it presents.
Early Stages of Social Media
The genesis of social media platforms marks a pivotal moment in human communication, fundamentally altering how individuals connect and share information. These early iterations laid the groundwork for the sophisticated networks we use today, showcasing the evolving nature of online interaction.These nascent platforms, while seemingly simple compared to modern iterations, revolutionized interpersonal communication. They offered a new avenue for users to express themselves, build communities, and participate in public discourse.
This evolution was directly influenced by technological advancements that enabled the growth and accessibility of these online spaces.
Timeline of Early Social Media Platforms
The early stages of social media development were characterized by a rapid evolution. This timeline highlights key milestones and innovations, demonstrating the transformative power of these emerging technologies.
- 1970s-1980s: Bulletin Board Systems (BBS) emerged as early forms of online communities. Users could access shared information, engage in discussions, and exchange files. BBSs demonstrated the potential for online interaction and facilitated the groundwork for later social media platforms.
- 1990s: The rise of the internet and web browsers fueled the development of online forums and discussion boards. These platforms allowed for organized conversations around specific interests, signifying a shift towards targeted online communities.
- Late 1990s: SixDegrees.com, launched in 1997, is considered a pioneering social networking site. It enabled users to create profiles, connect with friends, and view their connections. This represented a more structured approach to online social interaction, establishing a foundation for future platforms.
- Early 2000s: Friendster, MySpace, and LinkedIn emerged as significant players in the social networking landscape. These platforms offered more sophisticated features, such as profiles with personal information, photos, and friend lists. MySpace, in particular, was influential in its use of user-generated content, setting the stage for the personalized online experiences we see today.
- 2004: Facebook’s launch marked a watershed moment. Its user-friendly interface and focus on connecting with friends and family resonated with a large user base. The platform’s growth and evolution demonstrated the potential for large-scale social networking.
Technological Advancements
Key technological advancements underpinned the growth of early social media platforms.
- Increased internet access and affordability: The widening availability of affordable and accessible internet connections, coupled with the proliferation of personal computers, enabled a larger portion of the population to participate in online communities.
- Web browser development: Improvements in web browsers facilitated easier navigation and interaction on online platforms, making them more user-friendly and accessible to a broader audience.
- Database and server technologies: Advancements in database and server technologies enabled platforms to handle increasing user loads and data volumes. This crucial infrastructure allowed for the expansion and growth of these networks.
Comparison of Early Social Media Platforms
A comparative analysis of the earliest social media platforms reveals key differences in their functionalities and features.
| Platform | Key Features | Social/Cultural Context |
|---|---|---|
| SixDegrees.com | User profiles, connections, friend lists | Emerged during the early days of the internet, reflecting a nascent interest in online networking. |
| Friendster | Profiles, photos, friend lists, groups | Emerged during a period of growing online interaction, offering more elaborate features than earlier platforms. |
| MySpace | Profiles, music sharing, blogs, user-generated content | Aligned with the rise of user-generated content and music culture, showcasing a more personalized online experience. |
| Profiles, connections, news feeds, groups | Developed in response to the desire for more targeted and personalized connections, appealing to a broad range of users. |
Challenges Faced by Early Social Media Platforms
Early social media platforms faced a variety of challenges in their initial stages.
- Scalability issues: Early platforms struggled to handle the increasing number of users and data volumes, requiring significant investments in infrastructure and technological advancements to maintain performance.
- Security concerns: The vulnerability of early platforms to security breaches and misuse raised concerns about user privacy and data protection, prompting the development of enhanced security protocols and measures.
- Defining user experience: Early social media platforms had to experiment with design and functionality to create a compelling user experience that fostered engagement and participation. Iterative development and user feedback were crucial.
Rise of Social Networking Sites
The shift from early online communities to dedicated social networking sites marked a significant evolution in online interaction. This transition was fueled by a confluence of technological advancements and societal shifts, leading to the rapid growth and pervasive influence of these platforms. The rise of social networking sites fundamentally altered how people communicated and interacted, fostering new forms of social connections and shaping the contemporary digital landscape.The rapid growth of social networking sites stemmed from several key factors.
Increased internet accessibility, coupled with the proliferation of affordable and powerful computing devices, provided the necessary infrastructure for widespread participation. The development of user-friendly interfaces, designed for intuitive navigation and interaction, significantly lowered the barrier to entry for new users. Furthermore, the burgeoning concept of online communities and the desire for social connection played a pivotal role in driving adoption.
The promise of connecting with friends, family, and like-minded individuals across geographical boundaries resonated with a broad demographic.
Key Factors Contributing to Growth
Several crucial elements fostered the explosive growth of social networking sites. Improved internet infrastructure and decreasing costs made online access more attainable, allowing a broader segment of the population to participate. Intuitive interfaces, designed for easy navigation and interaction, played a vital role in attracting and retaining users. The inherent appeal of online communities and the desire for social connections across geographical boundaries also drove user adoption.
These interconnected factors created a fertile ground for the development and proliferation of social networking sites.
Impact on Interpersonal Communication
Social networking sites fundamentally reshaped interpersonal communication. They enabled instant communication and fostered connections across vast distances. However, concerns arose regarding the potential for superficial interactions and the erosion of face-to-face communication. While these sites offered new avenues for interaction, the impact on established forms of communication remained a subject of ongoing debate.
Comparison of User Engagement Approaches
Different social networking sites employed varied approaches to user engagement. Some platforms focused on connecting users based on shared interests, while others prioritized maintaining connections with existing social circles. The varying strategies reflected the diverse needs and motivations of users, ultimately contributing to the diverse landscape of social networking sites. Examples include sites prioritizing professional connections versus those emphasizing casual friendships.
Prominent Platform Features
Key features that made these platforms popular included user profiles, friend lists, status updates, and the ability to share media. The ease of creating profiles, adding friends, and posting updates fostered a sense of community and encouraged ongoing interaction. The ability to share images, videos, and other media content further enhanced user engagement and fostered a more dynamic online experience.
Evolution of User Interfaces and Functionalities
The user interfaces and functionalities of social networking sites have evolved significantly over time. Early platforms were characterized by simple profiles and basic communication tools. As the platforms matured, they incorporated more complex features, such as sophisticated search algorithms, advanced privacy controls, and a wider range of content sharing options. These changes reflect the continuous evolution of user needs and technological advancements.
The evolution has moved from static profiles to dynamic content streams, from simple updates to sophisticated tools for engagement.
Mobile-First Era
The rise of smartphones and readily available mobile internet access fundamentally reshaped the social media landscape. This “mobile-first” era saw a dramatic shift in how people interacted, communicated, and consumed content, leading to a new generation of social media apps tailored to the specific capabilities and limitations of mobile devices. This period dramatically altered the dynamics of online interaction, influencing not only the functionality but also the very nature of social media platforms.The mobile-first era saw a significant shift in social media interactions.
Previously, desktop computers were the dominant platform for social media engagement. However, the increasing accessibility and affordability of smartphones, coupled with rapid advancements in mobile internet connectivity, created a mobile-centric environment. This shift had a profound impact on how users consumed information, shared content, and built relationships online.
Impact of Mobile Devices on Social Media
Mobile devices facilitated a greater degree of spontaneity and immediacy in social interactions. Users could respond to updates, share photos and videos, and engage in conversations more readily than ever before. This constant connectivity fostered a sense of immediacy and accessibility, blurring the lines between online and offline interactions. The portability of smartphones also enabled social media engagement in diverse locations and situations, unlike the constraints of a fixed desktop computer.
Examples of Mobile Platform Alterations
Several key examples illustrate the impact of mobile platforms on social media interactions. The rise of location-based services like check-ins on platforms like Foursquare and Instagram Stories showcased how mobile devices could integrate real-time location data into social media experiences. The widespread adoption of messaging apps, such as WhatsApp and WeChat, further demonstrated how mobile devices could facilitate instant communication and group interactions.
Moreover, the proliferation of social media apps specifically designed for mobile devices, like Snapchat and TikTok, demonstrated the potential of mobile-first platforms to introduce unique features and formats for content creation and consumption.
Emergence of Mobile-Specific Social Media Apps, History of social media platforms
Mobile-specific social media apps emerged as a direct response to the changing landscape. These apps often focused on visual content, user-generated content, and features that catered to mobile-first interactions. Snapchat, for example, popularized ephemeral content and direct messaging features tailored for mobile devices. Similarly, TikTok’s focus on short-form video content and interactive features reflected the preferences of a mobile-first generation.
The unique capabilities of mobile devices, such as cameras and touchscreens, were directly incorporated into the design and functionality of these platforms.
Comparison of Mobile-First and Desktop-Based Platforms
Traditional desktop-based platforms often struggled to adapt to the limitations and capabilities of mobile devices. Mobile-first platforms, conversely, were built from the ground up to optimize user experience on smaller screens and touch interfaces. This difference led to distinct features and functionalities, impacting everything from content consumption to user interaction. Desktop platforms often prioritized features like extensive text-based conversations and detailed profiles, while mobile platforms focused on ease of use, visual appeal, and quick sharing.
Key Features and Advantages of Different Mobile Social Media Platforms
| Platform | Key Features | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Visual-centric sharing, Stories, Reels | Excellent for visual communication, fosters creativity, highly engaging | |
| TikTok | Short-form video, trends, challenges | High virality potential, engaging for younger audiences, innovative content formats |
| Snapchat | Ephemeral content, filters, lenses | Unique experience, fosters creativity, encourages spontaneity |
| Messaging, group chats, voice calls | Excellent for instant communication, effective for group coordination, cost-effective communication |
Social Media and Information Sharing
Social media platforms have fundamentally altered how information is disseminated and consumed globally. Their rapid growth has facilitated unprecedented levels of connectivity and information exchange, yet this accessibility has also presented unique challenges, particularly regarding the spread of misinformation and disinformation. This section examines the role of social media in shaping public discourse, the challenges associated with the spread of false information, and how platforms are adapting to mitigate these risks.The influence of social media on information sharing is undeniable.
Platforms like Twitter and Facebook enable individuals and organizations to disseminate information at a scale previously unimaginable. This rapid dissemination can be a powerful tool for education, awareness campaigns, and the mobilization of support for various causes. However, the very characteristics that enable rapid information sharing also make social media susceptible to the spread of inaccurate or misleading content.
Role of Social Media in Information Dissemination
Social media has become a primary channel for disseminating information, enabling instant global reach. News, updates, and diverse perspectives are shared in real-time, fostering a sense of collective awareness. However, this immediacy can also lead to the rapid spread of unsubstantiated claims and narratives.
Challenges Related to Misinformation and Disinformation
The ease with which false or misleading information can proliferate on social media poses a significant challenge. Algorithms designed to maximize user engagement can inadvertently amplify contentious or sensational content, regardless of its accuracy. The anonymity offered by some platforms can embolden the spread of malicious intent, including the creation and propagation of fabricated narratives. Misinformation can undermine trust in established institutions, influence public opinion, and even incite violence.
Examples include the spread of false narratives about vaccines or the manipulation of election outcomes.
Influence of Social Media on Public Opinion and Political Discourse
Social media platforms have profoundly impacted public opinion and political discourse. The ability to connect with like-minded individuals and share perspectives has fostered the development of online communities and echo chambers. This phenomenon can reinforce existing beliefs and limit exposure to diverse viewpoints, potentially leading to polarization and a lack of constructive dialogue. The accessibility of platforms has also allowed political candidates and campaigns to engage directly with voters, circumventing traditional media outlets.
Evolution of Content Moderation and User Safety
In response to the challenges of misinformation and harmful content, social media platforms have increasingly invested in content moderation strategies. These efforts involve the development of automated tools to detect and flag potentially problematic content, as well as the deployment of human moderators to review flagged posts. However, the challenge of maintaining balance between freedom of expression and user safety remains complex.
Determining what constitutes harmful content, especially in sensitive contexts, can be difficult and often requires careful consideration of local laws and cultural norms. Examples include the use of artificial intelligence to identify hate speech or the development of community guidelines to address harassment.
Examples of Social Media Use for Social Movements and Activism
Social media has become an essential tool for social movements and activism. The ability to organize events, mobilize support, and raise awareness about critical issues has empowered marginalized groups and fostered collective action. From the Arab Spring to the #MeToo movement, social media has facilitated the dissemination of information, organization of protests, and mobilization of resources. The rapid dissemination of information allows for real-time updates and mobilization efforts during crises or social unrest.
Examples include the use of hashtags to organize protests, the sharing of stories to raise awareness about social injustices, and the use of live streaming to document events.
Social Media and Business: History Of Social Media Platforms
Social media has fundamentally reshaped the landscape of modern business. From marketing strategies to customer interactions, it has become an indispensable tool for companies of all sizes. Businesses now leverage social media platforms to connect with their target audiences, build brand recognition, and foster a loyal customer base. This transformation is driven by the ability to reach vast audiences quickly and affordably, enabling real-time engagement and feedback.The integration of social media into business practices has gone far beyond simple advertising.
It now encompasses diverse aspects of operations, including customer service, product development, and market research. The dynamic nature of social media allows businesses to adapt rapidly to changing trends and customer preferences, fostering a more agile and responsive approach to the marketplace.
Transforming Business Practices
Social media has revolutionized business practices across various sectors. Companies now use it for market research, allowing them to gauge consumer sentiment, gather feedback on products and services, and identify emerging trends. This data-driven approach enables businesses to refine their strategies and products, tailoring them to meet the specific needs and desires of their target audiences. Furthermore, social media has facilitated enhanced customer service by enabling quick and efficient responses to queries and complaints.
This direct engagement builds trust and fosters loyalty, leading to improved customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Social Media for Marketing and Advertising
Businesses utilize social media platforms for targeted advertising campaigns. These platforms offer sophisticated targeting options, allowing companies to reach specific demographics, interests, and behaviors. This precision marketing significantly increases the effectiveness of advertising budgets, enabling a more efficient return on investment. Moreover, social media advertising often integrates engaging content, including videos, images, and interactive elements, which can effectively capture audience attention and drive conversions.
Businesses can run contests and giveaways on social media, generating excitement and brand awareness.
Impact on Customer Engagement and Brand Building
Social media plays a pivotal role in customer engagement and brand building. Direct interaction with customers through comments, messages, and posts fosters a sense of community and personal connection. This direct interaction creates a more personal brand image, enhancing customer trust and loyalty. Businesses can showcase their brand personality through tailored content and interactive experiences, thus strengthening their brand image.
Transparency and authenticity in social media interactions are vital to establishing a trustworthy and relatable brand.
Role of Social Media in Creating Online Communities
Social media platforms provide businesses with a unique opportunity to build and foster online communities. These communities facilitate direct engagement between businesses and customers, enabling two-way communication and fostering loyalty. Businesses can create interactive spaces for customers to share experiences, opinions, and feedback. By responding to customer concerns and celebrating successes, businesses can cultivate a sense of belonging and engagement, strengthening the bond between the brand and its community.
Strategies for Leveraging Social Media
| Business Goal | Social Media Strategy | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Brand Awareness | Consistent posting schedule with high-quality content, influencer marketing, and targeted advertising. | A fashion brand consistently posts stylish images and videos on Instagram, collaborates with fashion influencers, and runs targeted ads to reach potential customers. |
| Lead Generation | Running contests, quizzes, and polls; using lead magnets (e.g., ebooks, webinars) in exchange for contact information; implementing chatbots for quick responses. | A software company runs a giveaway on Twitter for a free trial of their software, offering an ebook on productivity tips in exchange for email addresses, and uses a chatbot to answer frequently asked questions. |
| Customer Support | Actively monitoring comments and messages; providing quick and helpful responses; creating FAQs and tutorials. | An online retailer responds to customer inquiries promptly on Twitter and Facebook, creates a comprehensive FAQ section on their website, and provides helpful video tutorials on product usage. |
| Sales Promotion | Running promotions and discounts; using social media ads to drive traffic to product pages; hosting live Q&A sessions with product experts. | A restaurant uses Instagram to offer daily specials and discounts, promotes its online ordering system through targeted ads, and hosts live cooking demonstrations with chefs. |
Social Media and Society
Social media has profoundly reshaped societal interactions, norms, and values. Its pervasive influence extends to individual well-being, public discourse, and even the way we perceive and address social issues. This section delves into the multifaceted relationship between social media and contemporary society.Social media platforms have become powerful tools for social change, facilitating communication and collaboration on a global scale.
However, their impact on society is complex and multifaceted, encompassing both positive and negative consequences. This section examines the effects of social media on societal norms and values, mental health, and public discourse. It also considers the evolving relationship between social media and privacy.
Influence on Societal Norms and Values
Social media platforms often shape perceptions of societal norms and values by influencing how information is disseminated and consumed. Trends, behaviors, and even opinions are often amplified and disseminated through these platforms, leading to the potential for both positive and negative influences on social values. The rapid spread of information can create challenges in discerning credible sources from misinformation, and this can contribute to the formation of biased or inaccurate perceptions.
Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Social media has been linked to a range of mental health concerns, including anxiety, depression, and body image issues. The constant exposure to curated and often idealized portrayals of others’ lives can foster feelings of inadequacy and social comparison. Cyberbullying and online harassment are also significant concerns, impacting mental health and well-being negatively. Conversely, social media can also provide support networks and resources for individuals facing mental health challenges.
Social Media Use to Address Social Issues
Social media platforms have emerged as powerful tools for raising awareness and mobilizing action around social issues. From advocacy campaigns to fundraising initiatives, social media has enabled communities to connect, organize, and support one another in addressing pressing societal problems. However, the rapid spread of information can also lead to the spread of misinformation, which can hinder effective responses to social issues.
Role in Shaping Public Discourse
Social media has significantly altered the landscape of public discourse. It provides a platform for diverse voices and perspectives to be heard, enabling individuals to engage in conversations about important societal issues. However, the nature of online interactions can lead to echo chambers and filter bubbles, where individuals primarily encounter information confirming their existing viewpoints. This can result in polarized opinions and hinder constructive dialogue.
Evolving Relationship Between Social Media and Privacy
The relationship between social media and privacy is constantly evolving. As social media platforms collect and utilize vast amounts of personal data, concerns about data security and the potential for misuse arise. Individuals are increasingly aware of the need to balance the benefits of social media with the importance of safeguarding their personal information. There is a growing demand for greater transparency and control over personal data within the social media ecosystem.
The Future of Social Media
The evolution of social media has been remarkable, transforming how we connect, share information, and conduct business. As technology continues to advance, the future of social media promises even more significant changes, driven by emerging trends and innovations. The landscape will likely be shaped by a blend of user expectations, technological advancements, and societal shifts.
Potential Future Trends and Innovations
Social media platforms are poised to adapt to changing user needs and preferences. We can expect to see a greater emphasis on personalized experiences, augmented reality integration, and the development of more immersive and interactive content formats. The trend toward user-generated content will likely continue, with platforms providing more tools and opportunities for creators to express themselves.
Emerging Technologies Influencing Social Media
Several emerging technologies are poised to significantly impact social media. Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies are likely to become more integrated into social platforms, offering immersive experiences for users. The increasing adoption of the metaverse, a persistent virtual world, might lead to social media experiences within these environments. Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are already reshaping how we interact with social media, impacting everything from content recommendations to user support.
Evolving Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is already playing a crucial role in social media, particularly in areas such as content moderation, personalized recommendations, and user experience optimization. In the future, AI will likely become even more sophisticated, allowing for more nuanced understanding of user needs and preferences, leading to more targeted and relevant content feeds. This increased sophistication will also enable AI to play a more active role in detecting and mitigating harmful content.
Future Challenges and Opportunities for Social Media Companies
Social media companies face both significant challenges and opportunities in the future. Maintaining user trust and addressing issues of misinformation and online harassment will remain paramount. Adapting to new technologies and user expectations while fostering innovation and creativity will be critical to staying competitive. Companies will need to focus on building robust systems for content moderation, user safety, and privacy protection.
On the other hand, opportunities abound in exploring new business models, leveraging emerging technologies, and expanding into new markets.
Possible Future Social Media Platforms and Features
| Potential Platform | Potential Features |
|---|---|
| Immersive Social Hub | VR/AR integration, interactive 3D environments, personalized avatars, social events in virtual spaces. |
| AI-Powered Community Forums | AI-driven content filtering, personalized discussion recommendations, automated moderation, advanced sentiment analysis for discussions. |
| Personalized Content Network | Hyper-personalized content recommendations based on individual preferences, dynamic content feeds adapting to user context, seamless integration with other apps and devices. |
| Decentralized Social Media Platform | Blockchain-based identity management, community-driven content moderation, transparent data sharing policies, user-controlled data ownership. |
Conclusion
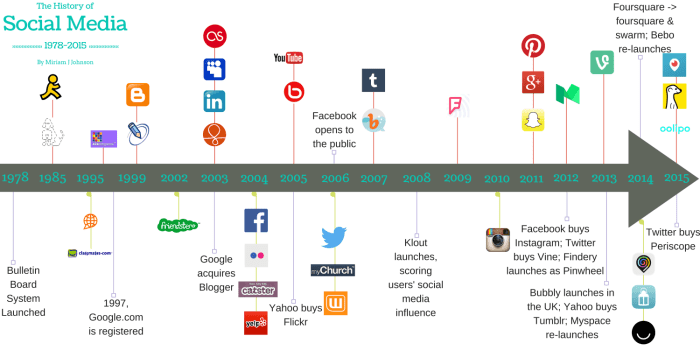
Source: co.uk
In conclusion, the history of social media platforms is a dynamic narrative of technological innovation, cultural shifts, and societal change. From humble beginnings to the ubiquitous tools we use today, social media has dramatically transformed communication and interaction. Understanding this history provides valuable insights into the present and future of this powerful force in our lives.













Post Comment