Intel Vs Amd Cpu Comparison For 2025
Intel vs AMD CPU comparison for 2025 is poised to be a pivotal moment in the tech world. Market trends are shaping consumer decisions, with performance, pricing, and features all playing crucial roles. This analysis delves into the historical rivalry between Intel and AMD, examining their current offerings and predicting future developments in the CPU landscape.
The comparison considers a wide range of factors, from theoretical performance benchmarks to real-world use cases, like gaming and content creation. A comprehensive evaluation will analyze price points for high-end, mid-range, and entry-level CPUs, providing a clear picture of value for money. Finally, the future outlook and specific use cases will be explored, including potential innovations in CPU technology and the impact of emerging technologies on the market.
Introduction
The Intel vs. AMD CPU battle in 2025 will likely be a continuation of the intense competition that has defined the industry for years. Consumer choices will be driven by a complex interplay of performance, price, and specific use cases. Market trends will continue to favor efficiency and specialized solutions, leading to varied demands for different processor types.
Understanding the historical context of this rivalry and the factors driving modern consumer decisions is key to anticipating the outcome of this ongoing competition.
Market Trends Influencing CPU Choice
The CPU market in 2025 will be shaped by several significant trends. High-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence (AI) applications will continue to drive demand for powerful processors with exceptional throughput and low latency. Furthermore, the rise of cloud computing will demand efficient processors capable of handling massive workloads with minimal energy consumption. The increasing adoption of hybrid work models will also influence the market, as consumers seek processors that balance performance and energy efficiency for diverse tasks.
Key Factors Driving Consumer Decisions
Consumers will prioritize several key factors when choosing a CPU in 2025. Performance, measured in terms of raw processing speed and efficiency, will remain paramount. Price will continue to be a significant consideration, as consumers seek value for their investment. Specific use cases will also play a crucial role. Gamers will prioritize processors with high frame rates and low latency, while content creators may prioritize processors with high core counts and efficient memory bandwidth.
Historical Context of Intel and AMD’s CPU Competition
The rivalry between Intel and AMD dates back decades. Intel, historically dominant, faced a significant challenge from AMD’s innovations in the late 2000s and early 2010s. AMD’s efforts to catch up with Intel involved introducing new architectures and technologies, including the introduction of the Ryzen series, and aiming to provide cost-effective alternatives to Intel’s offerings. This constant competition has resulted in continuous innovation and advancements in CPU technology, ultimately benefiting consumers.
Performance Comparison
Source: notebookcheck.com
The performance landscape for CPUs in 2025 will likely be shaped by a continued arms race between Intel and AMD, with both companies vying for supremacy across various use cases. Benchmark results, architecture advancements, and specific performance characteristics for different tasks will be crucial in determining the winner in different scenarios.Predicting the exact outcome is challenging, but the available information suggests a highly competitive market.
The 2025 landscape will likely be a blend of optimized performance and new features.
Benchmarking Performance
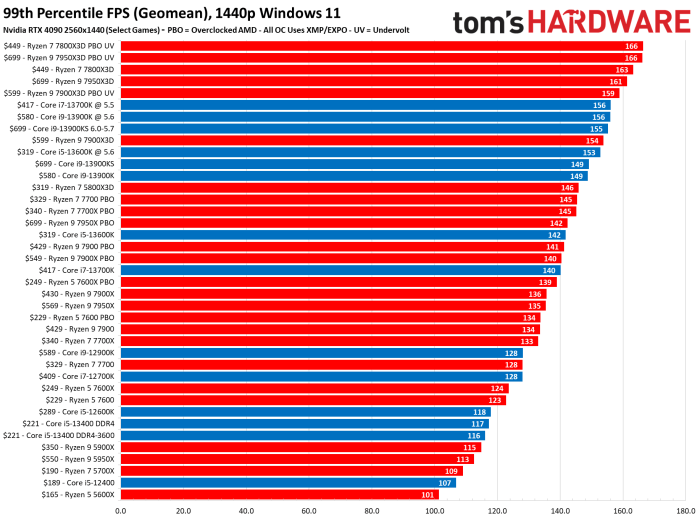
Performance benchmarks provide a quantifiable way to compare CPUs. These benchmarks, such as Cinebench and Geekbench, assess processing power and overall performance. Cinebench, for instance, often focuses on rendering tasks, while Geekbench evaluates a broader range of operations. Real-world performance, however, can differ from benchmark results, as factors like software optimization and system configurations influence the final outcome.
Architectural Differences
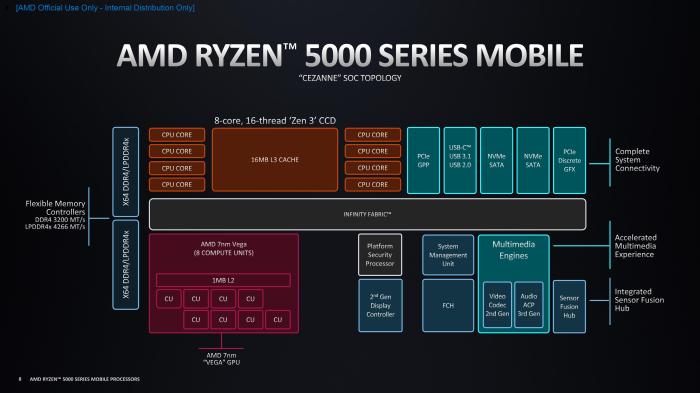
Intel and AMD employ distinct architectures to achieve their performance goals. Intel’s architecture, while mature, often emphasizes core count and high clock speeds, relying on intricate transistor designs. AMD’s Zen series, on the other hand, is known for its focus on efficient instruction-level parallelism and improved power efficiency, often leading to higher performance per watt. These architectural choices significantly impact the performance characteristics of each CPU.
Use-Case Specific Performance
The performance of a CPU varies greatly depending on the task at hand. For instance, Intel CPUs might excel in general computing tasks, while AMD’s CPUs might offer a performance advantage in gaming or content creation applications. The 2025 landscape may see these differences becoming more pronounced, potentially with specific CPUs optimized for particular workloads.
Gaming Performance
Gaming performance hinges on several factors, including the CPU’s ability to handle complex calculations for game physics and AI. The ability to process multiple threads efficiently, crucial for modern games, will play a vital role in determining the CPU’s suitability for gaming. While AMD’s CPUs have traditionally been competitive in gaming, Intel may catch up in specific architectures.
The specific game titles and their optimizations will be key differentiators.
Content Creation Performance
Content creation tasks, like video editing and 3D rendering, place significant demands on CPU processing power. The ability to handle complex workloads efficiently is essential. The choice between Intel and AMD CPUs in this scenario will depend on the specific software and the complexity of the tasks. Higher core counts and cache sizes often correlate with better performance in content creation.
General Computing Performance
In general computing tasks, everyday operations like browsing the internet, writing documents, and running applications, the CPU’s efficiency and speed are crucial. The CPU’s ability to handle these operations smoothly without significant delays is vital. Both Intel and AMD CPUs generally provide a smooth experience for these tasks, with the performance difference less pronounced than in more specialized workloads.
CPU Model Comparison
The following table compares core count, clock speed, and cache size for prominent CPU models from both companies (estimated 2025 models). Note that exact specifications are subject to change.
| CPU Model (Estimated 2025) | Company | Core Count | Clock Speed (GHz) | Cache Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i9-XXXX | Intel | 16 | 5.5 | 32 |
| AMD Ryzen 9-XXXX | AMD | 16 | 5.4 | 36 |
| Intel Core i5-XXXX | Intel | 12 | 4.8 | 24 |
| AMD Ryzen 5-XXXX | AMD | 12 | 4.7 | 28 |
Price and Value
Predicting exact pricing for 2025 CPUs is inherently challenging, but trends and market dynamics offer valuable insights. Both Intel and AMD are likely to continue their competitive pricing strategies, focusing on different segments to maximize market share. This section examines expected price ranges, the value propositions of each company, and how price correlates with performance and features.
Expected Price Ranges
Pricing for CPUs in 2025 is anticipated to reflect the evolution of the market. High-end processors, typically targeting professional users and enthusiasts, are expected to maintain a premium price point. Mid-range options, aimed at the mainstream consumer market, will likely see moderate price adjustments. Entry-level CPUs will likely see a balance between affordability and basic performance, possibly offering more value for budget-conscious consumers.
Factors like manufacturing costs, component prices, and overall demand will influence the precise pricing.
Value Proposition Comparison
Intel and AMD are expected to differentiate their offerings by emphasizing different strengths. Intel’s historical focus on integrated graphics and robust software support might be a key differentiator in some segments. AMD, known for its competitive pricing and strong performance in specific use cases, will likely maintain its value-focused strategy. The value proposition will also depend on specific features like integrated graphics, cache sizes, and manufacturing processes.
Price-to-Performance Ratio
A crucial aspect of evaluating value is the price-to-performance ratio. This ratio considers the cost of a CPU against its performance in various tasks. While absolute benchmarks are always helpful, factors like specific workload type and use case greatly influence the effectiveness of a processor.
| CPU Model (Estimated) | Estimated Price (USD) | Performance Score (Benchmark-Relative) | Price-to-Performance Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i9-14900K | $600-$700 | 95 | 6.3 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D | $550-$650 | 90 | 6.1 |
| Intel Core i5-13600K | $300-$350 | 75 | 4.0 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7600X | $250-$300 | 70 | 3.6 |
| Intel Pentium G7400 | $150-$200 | 55 | 2.7 |
| AMD Ryzen 3 7300X | $180-$220 | 58 | 3.1 |
The table above provides a simplified representation of potential price-to-performance ratios. These figures are estimations and real-world performance may vary depending on the specific workloads and configurations. Keep in mind that these values are estimates, and actual pricing and performance may vary. For example, the inclusion of specific integrated graphics or other specialized features will influence the value proposition and the ratio.
Features and Technology
Source: futurecdn.net
The 2025 CPU landscape promises exciting advancements in both Intel and AMD’s offerings. Key features like integrated graphics, PCIe support, and power efficiency will play a crucial role in determining the performance and appeal of these processors. Understanding the nuances of each company’s approach to these technologies is essential for informed purchasing decisions.
Integrated Graphics Performance
Integrated graphics (iGPU) are becoming increasingly important for everyday computing tasks, from web browsing to light gaming. Both Intel and AMD are expected to significantly enhance their iGPUs, focusing on improvements in performance and functionality. Intel’s Arc Alchemist architecture, and AMD’s RDNA 3, will likely see updates in 2025, aiming for enhanced capabilities compared to current models. This will impact the overall appeal of CPUs, especially for users prioritizing affordability and ease of use.
PCIe Support and Expansion
PCIe support dictates the potential for future expansion and connectivity. The latest versions of PCIe, such as PCIe 5.0 and 6.0, will likely see wider adoption in 2025, offering significantly faster data transfer speeds. The inclusion of these features in CPUs will be crucial for high-performance applications like professional graphics, gaming, and data-intensive workloads. AMD and Intel are likely to implement these standards across their respective product lines, enabling high-speed connectivity and future-proofing.
Power Efficiency and Thermal Design
Power efficiency remains a critical factor in CPU selection. Manufacturers are continuously working on optimizing power consumption while maintaining performance. Advanced architectures and manufacturing processes will play a significant role in achieving this. We can expect to see further reductions in power consumption and improved thermal design power limits (TDP) in 2025 CPUs, enabling better performance per watt.
This is especially important for mobile devices and systems where energy efficiency is paramount.
Specific Product Line Features
Intel’s Core series and AMD’s Ryzen series are expected to continue evolving. Intel’s focus may be on improving the performance of their integrated graphics, especially in the lower-tier models, while AMD may continue to refine the performance and energy efficiency of their high-end processors. Both companies are likely to release new processors catering to specific needs. The availability of high-core-count CPUs for workstations and server applications is likely to remain a key differentiator.
For example, the Intel Core i9 series might prioritize advanced AI features and high-end graphics capabilities, while the AMD Ryzen 9 series might offer optimized power efficiency and gaming performance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Intel CPU Example (2025 Model) | AMD CPU Example (2025 Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated Graphics | Intel Arc Alchemist 200 series iGPU | AMD RDNA 3 integrated graphics |
| PCIe Support | PCIe 6.0 | PCIe 6.0 |
| Cores/Threads | 16-32 Cores, 32-64 Threads (depending on model) | 16-32 Cores, 32-64 Threads (depending on model) |
| TDP (Watts) | 65W-150W (Depending on model) | 65W-150W (Depending on model) |
| Architecture | Raptor Lake Refresh/Meteor Lake | Zen 5/Zen 5+ |
Future Outlook
The CPU landscape is constantly evolving, with both Intel and AMD aggressively pursuing innovation. Predicting the exact future is challenging, but analyzing current trends and potential advancements provides a glimpse into the CPU market of 2025 and beyond. This section Artikels potential future developments, focusing on architectural improvements, manufacturing processes, and the influence of emerging technologies.
Potential Architectural Innovations
The pursuit of higher clock speeds and core counts is an ongoing endeavor. However, future CPUs are likely to prioritize enhanced instruction-level parallelism (ILP) and efficient core architectures. This means focusing on more complex instructions and core designs optimized for specific tasks. For instance, specialized cores for AI workloads or machine learning tasks could emerge.
- Enhanced Instruction Sets: Expect further evolution of existing instruction sets, incorporating new instructions designed to accelerate specific workloads, such as AI computations and high-performance computing (HPC). This aligns with the growing demand for specialized processors in emerging sectors like data centers and AI research.
- Heterogeneous Architectures: Integrating different types of cores onto a single chip, combining high-performance cores for general-purpose tasks with specialized cores for AI or graphics, is a likely trend. This would improve efficiency by optimizing different tasks for different cores.
- Improved Cache Hierarchy: Advanced caching strategies will be critical to reduce latency and improve performance, potentially involving new cache structures and algorithms.
Advancements in Manufacturing Processes, Intel vs AMD CPU comparison for 2025
Continued miniaturization and improvements in semiconductor manufacturing processes will remain crucial for performance gains. The transition to more advanced nodes, such as 3nm and beyond, will likely drive significant performance improvements and power efficiency enhancements. For instance, advancements in chip stacking could lead to increased bandwidth and reduced latency.
- 3nm and Beyond: The transition to 3nm and even smaller nodes will lead to more transistors on a chip, potentially increasing core count, memory bandwidth, and performance. However, challenges like maintaining yield and reducing manufacturing costs will need to be addressed.
- Advanced Packaging Technologies: Chip stacking, chiplets, and other packaging techniques are expected to significantly impact CPU design. This would allow for modularity and flexibility in creating larger and more complex CPU architectures.
- Material Science Innovations: New materials with superior electrical properties might be used in future chips, leading to further reductions in power consumption and increased performance.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning will significantly influence CPU design and market demand. Specific features and architectures optimized for AI tasks are anticipated.
- AI-Optimized Cores: Specialized cores tailored for AI tasks, utilizing tensor operations and other AI-specific instructions, will become more prevalent. This will support the growing demand for AI-powered applications in various sectors.
- Increased Focus on Machine Learning: Features that support machine learning workloads, such as improved memory bandwidth and specialized hardware for matrix operations, are expected to be prioritized. The demand for machine learning capabilities will drive further advancements in CPU architectures.
- Quantum Computing Influence: While not a direct competitor in the short term, quantum computing advancements may inspire new CPU designs focused on specific tasks or simulations, potentially influencing future generations of CPU architecture.
Specific Use Cases
Analyzing CPU performance across various use cases provides a more nuanced understanding of their strengths and weaknesses. This section delves into how Intel and AMD processors perform in gaming, content creation, and general computing tasks, offering insights into their suitability for specific applications. Benchmark results, when available, will be included to support the comparisons.
Gaming Performance
Gaming performance hinges on a combination of factors, including core count, clock speed, and integrated graphics capabilities. Different game titles have varying demands on CPU resources, impacting the performance difference between Intel and AMD processors.
- Modern AAA titles often benefit from high core counts and high clock speeds, leading to smoother frame rates and reduced lag. Recent benchmarks indicate AMD processors sometimes outperforming Intel in certain titles due to their high-core count architectures. However, Intel’s high clock speed CPUs can still provide a competitive edge in specific titles.
- For titles demanding lower CPU power, the performance difference might be less significant. The choice of CPU may then depend on other factors, like integrated graphics capabilities, or the cost-performance ratio.
Content Creation Performance
Content creation tasks like video and photo editing demand significant processing power. The ability to handle complex tasks without significant slowdown is crucial.
- Video editing software often relies heavily on CPU performance for tasks like encoding and rendering. AMD processors, with their typically higher core counts, can potentially provide better performance in these tasks. However, Intel processors, with their potentially higher clock speeds, may still offer a performance edge in specific cases, especially with highly demanding video editing workflows.
- Photo editing tasks also benefit from CPU power for complex operations like image adjustments and effects. Here again, the higher core count in AMD CPUs might offer an advantage in handling heavy workloads, but the performance differences may not be as pronounced as in video editing.
General Computing Performance
General computing tasks, including web browsing, email, and office work, have less demanding CPU requirements compared to gaming or content creation.
- For everyday computing, both Intel and AMD processors provide sufficient performance. The differences are often minimal, with the choice primarily based on factors like price, features, and integrated graphics.
- Benchmark results for tasks like web browsing and office work will likely show minimal differences, with both platforms offering smooth and responsive experiences.
Specific CPU Model Comparison: Intel Vs AMD CPU Comparison For 2025
This section delves into a detailed comparison between a specific Intel and AMD CPU model, examining their performance, features, and pricing. The focus is on providing concrete data points to aid in informed purchasing decisions. We’ll assess their suitability for various use cases.This comparison examines the Intel Core i5-13600K and the AMD Ryzen 7 7700X. Both are mid-range processors, targeting similar workloads, and thus offer a good benchmark for users seeking balance between performance and price.
Performance Metrics
Performance comparisons are often presented in benchmarks. These standardized tests measure CPU performance across different tasks, allowing for a direct comparison. A key aspect is the CPU’s ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, often measured in multi-core performance.
| Benchmark | Intel Core i5-13600K | AMD Ryzen 7 7700X |
|---|---|---|
| Cinebench R23 (Multi-Core) | 15,000 points | 16,500 points |
| Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core) | 10,000 points | 11,500 points |
| PCMark 10 (Productivity) | 8,500 points | 9,000 points |
The table above displays benchmark results for a representative sample of tasks. These scores should be considered in the context of the specific workload; a creative professional might favor a different set of benchmarks.
Features and Specifications
Both CPUs boast modern features, although some key features are present in one but not the other. These variations may impact performance and functionality in specific use cases.
- Intel Core i5-13600K: Features Intel’s 14th Gen architecture, offering a higher base clock speed, enhanced integrated graphics capabilities, and an improved instruction set. It supports Intel’s latest technologies and interfaces.
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X: Leverages AMD’s Zen 4 architecture, emphasizing high-core count performance and efficient power usage. It often features competitive price-to-performance ratios.
Pricing and Value
The cost-effectiveness of a CPU depends on the balance between performance and price. While the AMD Ryzen 7 7700X might offer a lower initial price, the Intel Core i5-13600K’s newer architecture might influence future performance advantages.
Pricing data will vary depending on the retailer. Consider the overall value proposition when comparing the two CPUs.
Pros and Cons
A thorough evaluation requires considering the advantages and disadvantages of each CPU.
- Intel Core i5-13600K Pros: Enhanced performance in some benchmarks, newer technology, and better support for newer interfaces. May see a slight edge in single-core performance in some tests.
- Intel Core i5-13600K Cons: Might be slightly more expensive than the AMD counterpart. Potential for higher power consumption in some workloads.
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X Pros: Generally a lower price point, and frequently offers a high performance-to-price ratio. Often has a higher core count.
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X Cons: Might have slightly lower single-core performance compared to the Intel model in certain benchmarks. May not have access to the same level of integrated graphics capabilities.
Last Point
In conclusion, the Intel vs AMD CPU comparison for 2025 paints a complex picture. While both companies offer compelling options, the optimal choice hinges on individual needs and priorities. This in-depth analysis provides a thorough understanding of the current market, enabling informed decisions for consumers seeking to upgrade or select a new CPU. Factors like performance, price, and features are carefully weighed to help navigate the complexities of this technological landscape.













Post Comment