How To Protect Your Computer From Malware And Cyber Attacks
How to Protect Your Computer from Malware and Cyber Attacks is a critical topic in today’s digital landscape. Malicious software, or malware, and cyberattacks pose significant threats to individuals and organizations alike. Understanding these threats, implementing robust security practices, and developing safe online habits are crucial steps in safeguarding your digital assets.
This comprehensive guide explores various aspects of computer security, from identifying different types of malware and cyberattack methods to implementing strong security measures, practicing safe online behaviors, and developing data backup and recovery strategies. We’ll also cover responding to potential infections and educating yourself and others about online safety.
Understanding Malware and Cyberattacks
Protecting your computer from malicious software and cyberattacks is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Knowing the different types of threats and how they work is the first step toward effective defense. This section will delve into the various forms of malware, the tactics cybercriminals employ, and the potential repercussions of falling victim to these attacks.Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, making a thorough understanding of these attacks vital for safeguarding your systems and data.
Cybercriminals employ sophisticated techniques to infiltrate systems, and awareness of these methods is essential for prevention. The following sections will illuminate the characteristics of different malware types, the methods cybercriminals utilize, and the consequences of such attacks.
Different Types of Malware
Understanding the various types of malware is fundamental to effective protection. Each type operates differently and poses distinct risks. Knowing these distinctions allows for targeted defense strategies.
- Viruses are self-replicating programs that attach themselves to other files. They spread by infecting files and programs, often causing significant disruptions. A classic example is the Melissa virus, which spread through email attachments in the late 1990s.
- Worms are standalone programs that replicate themselves across networks. They don’t need to attach to other files and can spread rapidly, often clogging networks. The Morris worm, released in 1988, is a notorious example of a worm’s destructive potential.
- Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software, tricking users into installing them. Once inside, they can perform malicious actions, such as stealing data or granting unauthorized access. Zeus, a notorious Trojan, was used for financial fraud.
- Ransomware is designed to encrypt a victim’s files, making them inaccessible. Cybercriminals then demand payment (a ransom) to decrypt the data. WannaCry and NotPetya are examples of ransomware attacks that caused significant disruptions and financial losses.
- Spyware is designed to monitor user activity without their knowledge. It can collect sensitive information, such as login credentials, browsing history, and financial data. Spyware is often used to steal personal information for identity theft.
Methods of Cyber Infiltration
Cybercriminals employ various tactics to gain unauthorized access to systems. Understanding these methods is critical for effective prevention.
- Phishing involves tricking users into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details. Phishing attacks often use deceptive emails or websites mimicking legitimate organizations.
- Social Engineering manipulates individuals into performing actions that compromise their security. This can involve exploiting trust, fear, or curiosity to gain access to sensitive information.
- Exploit Kits are tools used to exploit vulnerabilities in software. These kits often target specific software versions and operating systems.
Consequences of Malware Infections and Cyberattacks
The consequences of malware infections and cyberattacks can be severe, affecting individuals, businesses, and even entire organizations.
- Data Loss is a frequent consequence of malware attacks. Data may be encrypted, deleted, or stolen, leading to significant losses for individuals and organizations.
- Financial Damage can result from malware infections, such as ransomware attacks or data breaches. Financial losses can range from minor expenses to significant financial crises.
- Reputational Harm is a serious concern for businesses that suffer cyberattacks. A damaged reputation can lead to loss of customers and decreased trust.
Comparison of Malware Types
The table below summarizes the key characteristics and impacts of different malware types.
| Malware Type | Characteristics | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Viruses | Self-replicating, attaches to files | Disruptions, data corruption |
| Worms | Standalone, replicates across networks | Network congestion, data corruption |
| Trojans | Disguised as legitimate software | Data theft, unauthorized access |
| Ransomware | Encrypts files, demands ransom | Data loss, financial damage |
| Spyware | Monitors user activity | Data theft, privacy violations |
Implementing Strong Security Practices
Source: cloudfront.net
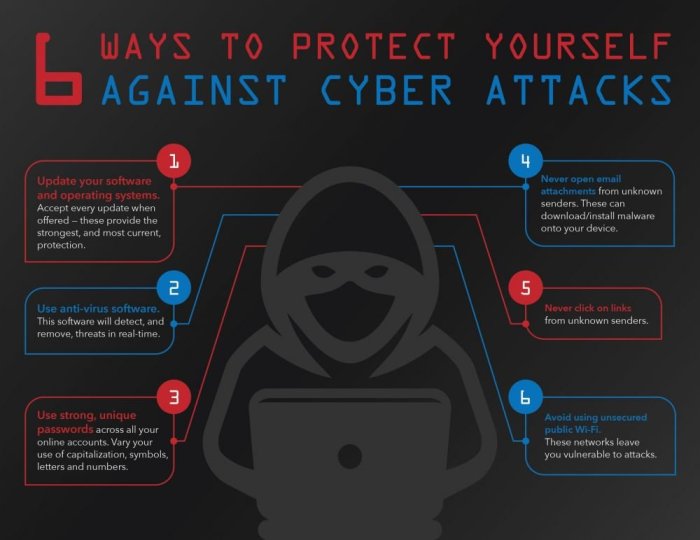
Protecting your computer from malware and cyberattacks requires more than just awareness; it necessitates proactive measures. Robust security practices are crucial in building a strong defense against evolving threats. These practices, when implemented diligently, significantly reduce the risk of compromise and ensure the safety of your digital assets.Implementing strong security measures is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process.
Regularly reviewing and adapting your security posture is essential in keeping pace with emerging threats. This includes staying informed about new vulnerabilities and adapting your strategies to address them.
Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Strong passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Weak passwords are easily cracked by sophisticated tools and techniques. Creating and maintaining strong passwords is vital for safeguarding your accounts. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than just a password to log in.Implementing MFA significantly reduces the risk of account compromise, even if a password is stolen.
It’s a best practice to enable MFA whenever possible for all important accounts. By combining strong passwords with MFA, you significantly enhance the security of your accounts and personal data.
Regular Software Updates
Regularly updating software and operating systems is paramount for maintaining a robust security posture. Updates often include critical security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by cybercriminals. Leaving systems unpatched leaves them susceptible to attacks.Failure to update software exposes systems to known exploits, potentially leading to data breaches or malware infections. Outdated systems are like open doors for malicious actors.
Staying updated is a proactive approach to safeguarding against vulnerabilities.
Reputable Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Using reputable antivirus and anti-malware software is a fundamental security practice. These tools actively scan for and remove malware, protecting your system from various threats. Regular scans are essential to detect and eliminate threats in a timely manner.Choosing reputable vendors is key. Look for software with robust detection capabilities and frequent updates. This will help to ensure that the software stays up-to-date with the latest threats.
Reliable antivirus and anti-malware software is a cornerstone of a strong defense.
Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between your network and the internet, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic. They prevent unauthorized access to your system and network resources. Proper configuration and maintenance of firewalls are crucial.By controlling network traffic, firewalls mitigate the risk of malicious actors gaining access to your system or data. This proactive approach safeguards your network against unauthorized access.
Effective firewalls are an essential part of a comprehensive security strategy.
Creating Strong Passwords
Creating strong passwords requires careful consideration and adherence to specific criteria. Avoid easily guessed passwords such as birthdays, names, or common phrases.
Strong passwords are complex and unique to each account.
A strong password should be at least 12 characters long, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. A random password generator can help create strong, unique passwords.
| Software Type | Update Frequency Recommendation | Potential Risks of Not Updating |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Systems | Monthly or as needed | Exposure to known vulnerabilities, increased risk of malware infections |
| Applications | As needed, often weekly or bi-weekly | Exposure to known vulnerabilities, potentially leading to system compromise |
| Antivirus/Anti-malware | Daily or as needed | Loss of protection against the latest threats, reduced effectiveness against emerging malware |
Safe Browsing and Downloading Habits: How To Protect Your Computer From Malware And Cyber Attacks
Safe online practices are crucial for protecting your computer from malware and cyberattacks. Careful browsing and downloading habits are essential layers of defense against these threats. Avoiding untrusted sources and verifying website legitimacy are vital steps in safeguarding your digital assets.Understanding the risks associated with downloading files from untrusted sources, verifying the legitimacy of websites, recognizing phishing attempts, and practicing safe downloading procedures are all vital aspects of creating a secure online environment.
This section details these practices, highlighting their importance in preventing malware infections and cyberattacks.
Risks of Downloading from Untrusted Sources
Downloading files from untrusted sources significantly increases the risk of malware infection. These sources often host malicious software disguised as legitimate files. This software can infiltrate your system, potentially leading to data breaches, identity theft, or financial losses. Furthermore, untrusted sources may contain viruses, spyware, or ransomware, all of which can severely compromise your computer’s security.
Verifying Website Legitimacy
Before entering sensitive information on a website, verify its legitimacy. Look for the padlock icon in the address bar, which indicates a secure connection. Examine the website’s URL carefully; a legitimate site will typically have a recognizable and trustworthy domain name. Check for misspellings or unusual characters, as these can be red flags. Ensure the website uses HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) to encrypt communications.
Recognizing Phishing Attempts
Phishing attempts are deceptive attempts to steal sensitive information. These attacks often involve fraudulent emails, messages, or websites designed to mimic legitimate entities. Pay close attention to suspicious links and emails; they often contain urgent requests for personal information or use alarming language.
Common Phishing Techniques
| Phishing Technique | How to Identify |
|---|---|
| Fake Emails/Messages | Look for poor grammar, urgent tones, and requests for personal information. Verify the sender’s email address carefully. |
| Spoofed Websites | Examine the website’s URL carefully for misspellings or unusual characters. Look for subtle inconsistencies in the design or layout of the site, which might differ from the legitimate site. |
| Malicious Links | Hover over links before clicking to see the actual destination. Shortened URLs (bit.ly, tinyurl) often hide malicious destinations. |
| Fake Pop-up Windows | Be cautious of pop-up windows claiming to be from a bank or other legitimate institutions. They often appear suddenly and demand immediate action. |
Safe Online Browsing Tips
- Use a reputable antivirus program. Antivirus software can detect and remove malicious software, protecting your system from potential threats.
- Keep your software updated. Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities, safeguarding your system from known threats.
- Be cautious about clicking on unknown links or attachments. Exercise caution and verify the source of any links or attachments before opening them.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA). This extra layer of security adds an extra verification step, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access your accounts.
Safe Downloading and Installation
Downloading and installing software from trusted sources is crucial. Verify the legitimacy of the software vendor and download the software from official websites or reputable app stores. Read reviews and user comments to ensure the software’s safety and reliability. Carefully follow the installation instructions provided by the vendor to avoid potential issues.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies

Source: titanfile.com
Regular data backups are crucial for safeguarding your computer’s valuable information. Without them, a malware attack, hardware failure, or accidental deletion could result in irreversible data loss. A well-implemented backup strategy significantly mitigates these risks.Data loss can be devastating, impacting personal files, business records, and crucial documents. A proactive approach to data backup ensures the continuity of operations and minimizes the potential for significant disruptions.
Importance of Regular Data Backups
Regular data backups are essential for preventing data loss. They provide a safety net, allowing you to recover lost or corrupted data quickly and efficiently. This is vital for both personal and professional users. A well-defined backup strategy protects against accidental deletion, hardware failure, natural disasters, and, critically, malicious cyberattacks. Without backups, restoring data from scratch can be time-consuming, costly, and often impossible.
Different Backup Methods
Various methods exist for backing up your data. Cloud storage services, external hard drives, and network-attached storage (NAS) devices are popular choices.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud-based backup solutions offer convenience and accessibility. Data is stored remotely, allowing for access from multiple devices. Examples include services from providers like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive. Cloud storage typically offers automatic backups, but security and privacy concerns should be considered. Cloud storage is particularly beneficial for users who need to access their data from multiple locations.
- External Hard Drives: External hard drives provide a physical storage solution. They offer significant storage capacity and are relatively inexpensive. However, they require physical storage space and are vulnerable to physical damage or theft. Regular backups to external drives are vital for safeguarding data against various threats.
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS): NAS devices offer a dedicated storage solution within your network. They provide robust data protection and are suitable for large-scale backups. NAS solutions are often more secure and efficient than other methods for backing up large volumes of data, particularly in business settings.
Restoring Data from Backups
The process of restoring data from backups should be straightforward and well-documented. A clear recovery plan is crucial for minimizing downtime in the event of an attack or data loss.
- Identify the Backup Location: Locate the backup files or folders you require. Ensure you have the correct backup and the location is accessible.
- Choose the Recovery Method: Select the appropriate method for retrieving your data from the chosen backup location.
- Restore Data: Follow the recovery instructions provided by the backup software or the backup provider.
- Verify Data Integrity: Once the data is restored, verify that it is complete and accurate. Check files, folders, and applications to ensure everything is functional.
Setting Up a Comprehensive Data Backup Strategy
A comprehensive data backup strategy includes multiple layers of protection. This minimizes the risk of data loss from various sources.
- Regular Backups: Schedule regular backups at defined intervals, whether daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on the data’s criticality. Regular backups are essential to protect against data loss from any cause.
- Version Control: Implement version control to maintain previous versions of your data. This is vital for reverting to earlier states if necessary. This allows for the restoration of previous versions in the event of data corruption or accidental deletion.
- Off-Site Backup: Store backups in a location separate from your primary computer or network. This safeguards your data against localized disasters. Maintaining off-site backups ensures data security and reduces the impact of local failures.
Data Recovery Options
Several data recovery options exist for restoring lost or damaged data.
- Data Recovery Software: Specialized software can attempt to recover data from damaged or inaccessible drives. This is a crucial tool for handling data loss issues. However, recovery success is not guaranteed.
- Professional Data Recovery Services: In complex situations, professional data recovery services can be employed. This is often the best option when dealing with significant data loss or complex hardware issues. Professional data recovery services can be expensive but may be necessary for crucial data recovery.
Backup Solution Comparison
The following table compares different backup solutions based on their storage capacity, cost, and security features.
| Backup Solution | Storage Capacity | Cost | Security Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Storage | Variable | Monthly/annual subscription | Encryption, access controls |
| External Hard Drives | High | One-time purchase | Limited encryption, physical security |
| NAS | High | One-time purchase + ongoing maintenance | Strong encryption, access controls |
Responding to Malware Infections and Cyberattacks
Taking proactive steps to safeguard your digital environment is crucial. However, despite the best precautions, encountering malware or cyberattacks is a possibility. Knowing how to respond effectively is vital to minimizing damage and restoring functionality. This section details the actions to take when you suspect a threat.Responding to a suspected malware infection or cyberattack requires a swift and methodical approach.
Immediate action can significantly reduce the impact of the incident. The following steps Artikel the process for dealing with such situations.
Identifying Suspicious Activity
Recognizing the signs of a potential malware infection or cyberattack is the first step in the response process. Symptoms can vary widely, but common indicators include unusual system behavior, unexpected pop-ups, or slow performance. Monitoring your system’s behavior and looking for deviations from the norm is key.
Disconnecting Infected Devices
Immediately disconnecting infected devices from the network is paramount. This prevents the malware from spreading to other connected devices and systems. Disconnecting the device from the network stops the malware from further communication and potentially transmitting to other connected computers.
Running a Full System Scan
Executing a full system scan with reputable antivirus software is essential for identifying and removing malware. Antivirus software employs various scanning methods to identify and eliminate malicious code from the system. Comprehensive scanning protocols are crucial to detect all malware components.
Seeking Professional Help, How to Protect Your Computer from Malware and Cyber Attacks
In complex or severe cyberattacks, seeking professional help from cybersecurity experts is recommended. These experts possess the expertise to investigate and resolve complex situations. Specialized cybersecurity firms or law enforcement agencies are appropriate avenues for expert assistance.
- Cybersecurity firms: Provide specialized expertise and advanced tools to identify and remediate complex threats.
- Law enforcement agencies: Offer support and guidance, especially in cases involving criminal activity or data breaches.
- Incident response teams: Specialized teams with dedicated expertise in handling cyberattacks.
Reporting Cyber Incidents
Reporting cyber incidents to the appropriate authorities is a critical step in managing and resolving the issue. This can range from notifying your IT department to contacting law enforcement agencies, depending on the nature and severity of the incident. Reporting helps track the incident, prevent similar attacks, and potentially recover lost data.
Incident Response Procedures
| Type of Cyberattack | Initial Response Steps | Further Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing Attack | Identify the source, quarantine emails, educate users about phishing tactics. | Implement security awareness training, update security protocols. |
| Malware Infection | Disconnect infected device, run a full system scan, isolate affected systems. | Restore from backups, update software, run further scans. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack | Identify the source, block malicious traffic, reroute traffic. | Enhance security infrastructure, implement DDoS protection. |
| Ransomware Attack | Isolate affected systems, secure data, contact law enforcement. | Consult with cybersecurity experts, consider negotiation with attackers. |
Educating Yourself and Others

Source: spaceload.in
Equipping yourself and others with the knowledge and skills to navigate the digital world safely is crucial in mitigating cyber risks. A proactive approach to online safety fosters a culture of vigilance and reduces vulnerability to malicious actors. This section delves into comprehensive strategies for empowering individuals to recognize and respond to online threats effectively.
Building a Strong Security Mindset
A strong security mindset is cultivated through consistent learning and application of best practices. This includes understanding the nature of threats, recognizing potential vulnerabilities, and practicing responsible online behavior. It is not a one-time effort but a continuous process of adaptation to the ever-evolving cyber landscape.
Regular Security Awareness Training
Regular security awareness training programs are essential for equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to identify and mitigate cyber threats. These programs should cover various aspects of online safety, from phishing scams to social engineering tactics. Training should be interactive and engaging to ensure comprehension and retention of the information.
Staying Informed About Emerging Threats
Staying informed about emerging threats is vital for maintaining a robust security posture. Cybercriminals constantly develop new methods to exploit vulnerabilities, and awareness of these trends allows individuals to adapt their security practices accordingly. Following reputable cybersecurity news sources and participating in online security communities can help in staying updated on the latest threats.
Identifying and Reporting Suspicious Activities
Recognizing and reporting suspicious activities is a crucial part of online safety. Users should be trained to identify phishing emails, suspicious websites, and other potentially malicious activities. Reporting suspicious behavior promptly helps security teams identify and address emerging threats effectively. A well-defined reporting process, communicated clearly, encourages users to report suspicious activities.
User Protection Checklist
This checklist provides a framework for users to follow to protect themselves online.
- Regularly update software and operating systems to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all online accounts and enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Be cautious about clicking links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Avoid downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Be wary of suspicious emails or messages, and verify information before acting on it.
- Maintain regular data backups to prevent data loss in case of malware infection or system failure.
- Report any suspicious activity to the appropriate authorities.
Security Awareness Training Topics
Security awareness training should cover a wide range of topics. The following table Artikels some key areas and their associated learning objectives.
| Topic | Learning Objectives |
|---|---|
| Phishing and Social Engineering | Recognize common phishing techniques, identify suspicious emails and messages, and understand social engineering tactics used by cybercriminals. |
| Malware Threats | Understand various types of malware, identify indicators of infection, and know how to respond to potential malware threats. |
| Password Management | Develop strong and unique passwords, understand the importance of multi-factor authentication, and manage passwords securely. |
| Safe Browsing Practices | Identify potentially malicious websites, understand the risks associated with unsafe browsing, and practice safe browsing habits. |
| Data Protection and Privacy | Understand data privacy regulations, protect personal information online, and recognize the importance of data security. |
| Reporting Procedures | Know the proper channels for reporting security incidents, understand the importance of timely reporting, and follow established reporting procedures. |
Final Review
In conclusion, protecting your computer from malware and cyberattacks requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the threats, implementing strong security practices, and developing safe online habits, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability. Regular updates, strong passwords, and vigilant online behavior are essential components of a robust defense strategy. Remember, staying informed and proactive is key to safeguarding your digital world.













Post Comment