What Is A Keylogger And How To Detect It
What is a keylogger and how to detect it? This guide delves into the insidious world of keyloggers, exploring their various forms, functions, and methods of installation. We’ll examine how these tools capture keystrokes, collect sensitive data, and ultimately compromise systems. Understanding keyloggers is crucial for protecting your digital assets.
From defining keyloggers and their different types, to the methods they use to infiltrate systems, we’ll cover everything from identifying signs of infection to preventing future attacks. This comprehensive approach equips readers with the knowledge and tools needed to combat this digital threat.
Defining Keyloggers

Source: niraiya.com
A keylogger is a type of surveillance software or hardware device designed to record every keystroke made on a targeted computer or device. This data capture can encompass typed characters, passwords, and other sensitive information. Understanding keyloggers is crucial for maintaining online security and protecting personal data.Keyloggers operate by intercepting and recording keystrokes as they are inputted. This data can be stored locally on the compromised system or transmitted to a remote location, potentially endangering the user’s privacy and security.
Various methods exist for capturing keystrokes, ranging from simple software monitoring to more sophisticated hardware-based interception.
Types of Keyloggers
Keyloggers can be broadly categorized into software and hardware types. Each approach employs different methods to achieve their objective.
Software Keyloggers
Software keyloggers are programs installed on a computer system. They function by intercepting the input from the keyboard and recording the keystrokes. These programs often operate in the background, making them stealthy and difficult to detect. They are frequently disguised as legitimate applications or utilities. The level of sophistication varies significantly, with some being basic and others offering advanced features, such as logging specific application actions or even screenshots.
Hardware Keyloggers
Hardware keyloggers are physical devices that are typically installed between the keyboard and the computer’s motherboard. These devices intercept the keystrokes physically before they reach the computer. Hardware keyloggers are often more challenging to detect compared to software keyloggers as they are often hidden from view. Their implementation can sometimes require specialized technical knowledge to install and use effectively.
Methods of Keystroke Capture
Keyloggers employ various methods to capture keystrokes. These methods range from intercepting the data directly at the keyboard level to using the system’s operating system to monitor and record keystrokes. Sophisticated keyloggers might employ techniques like hooking into the operating system’s input processing, allowing them to record keystrokes even from specific applications. The choice of method often depends on the type of keylogger and its intended functionality.
Comparison of Software and Hardware Keyloggers
| Type | Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software | Installed as a program; intercepts keystrokes through software-level access. | Relatively easier to deploy; often less expensive; adaptable to specific needs. | Potentially detectable; user awareness and security tools can often identify their presence; susceptible to removal or detection by security software. |
| Hardware | A physical device placed between the keyboard and computer; intercepts keystrokes physically. | Generally more difficult to detect; often bypassed security software. | More complex to install; can be expensive; often requires specialized technical knowledge. |
Keylogger Functionality
Keyloggers, as insidious surveillance tools, operate by recording keystrokes. Their capabilities extend far beyond simply logging typed characters, encompassing a range of data collection methods. Understanding their functionality is crucial for effective detection and prevention.Keyloggers meticulously capture a wide array of data beyond just typed characters. This includes timestamps associated with each keystroke, allowing for precise tracking of activity.
Moreover, they can log website addresses visited, providing insight into online behavior. This detailed information, when combined, paints a comprehensive picture of a user’s online and offline activities.
Keystroke Recording Methods
Keyloggers employ diverse techniques to record keystrokes. These methods often involve subtle manipulation of the operating system or applications, making detection challenging. Their stealthy nature is a key component of their effectiveness.
Data Collection Beyond Keystrokes
Keyloggers gather more than just the literal characters typed. They record the time and date of each keystroke, allowing for a timeline of activity. Furthermore, they can capture the websites visited during browsing sessions. This expanded data collection is a critical aspect of the keylogger’s function.
Keylogger Implementation Techniques
Keyloggers are implemented in various ways. They can be embedded within seemingly legitimate software, masking their true purpose. This is often done through sophisticated code injection techniques, which can evade traditional security measures. This concealed nature significantly increases the difficulty of detection.
Table of Keystroke Logging Methods
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software-based keyloggers | These keyloggers are embedded within applications. They intercept keystrokes as they are entered, and log them to a file or database. | Often disguised as legitimate software, making detection difficult. | Can be detected by antivirus software if the keylogger is poorly disguised. Requires installing the keylogger application, which is not always done discreetly. |
| Hardware-based keyloggers | These keyloggers are physical devices that are installed between the keyboard and the computer. | Can capture keystrokes directly from the keyboard, without relying on software. | Relatively easy to detect if the device is physically observed. Requires physical access to the computer. |
| Browser extensions | These keyloggers are disguised as browser extensions, providing the illusion of enhanced functionality. | Can collect keystrokes within a web browser, which can include sensitive data. | Usually detected by users if the extension is poorly designed. Modern browsers have security features to prevent installation of malicious extensions. |
| Rootkit-based keyloggers | These keyloggers exploit system vulnerabilities to gain root-level access, allowing them to intercept keystrokes at a deeper level. | Can bypass many security measures and persist undetected for a longer time. | High risk of system instability or damage. Usually require significant technical expertise to implement and deploy. |
Keylogger Installation and Propagation
Keyloggers, insidious in their operation, require sophisticated methods of installation and propagation to evade detection. Understanding these techniques is crucial for effective protection against these malicious programs. This section details the common methods used to deploy keyloggers, highlighting the potential for disguise and the various vectors for infection.Keyloggers are often deployed using various methods, ranging from the exploitation of vulnerabilities in software to more subtle approaches like social engineering.
Understanding the different methods of installation and propagation provides crucial insight into how to mitigate the risk of infection. This knowledge empowers users and administrators to develop robust security measures.
Common Installation Methods
Keyloggers can be stealthily introduced into systems through various channels, including malicious software and social engineering tactics. Understanding these avenues of infiltration is essential for effective security measures.
- Malware Distribution: Keyloggers are frequently bundled with other software, often disguised as legitimate applications. This allows attackers to gain access to a user’s system without their knowledge or consent. The keylogger is activated once the host program is installed. The victim is typically unaware that they are downloading and installing the keylogger alongside the seemingly legitimate program.
- Social Engineering: Social engineering exploits human psychology to trick users into installing keyloggers. This often involves deceptive emails or messages that appear to come from trusted sources, prompting the user to download and install malicious files disguised as legitimate documents or software updates. Phishing emails, for example, may contain malicious attachments or links that, when clicked, download and install a keylogger onto the victim’s system.
Disguising Keyloggers as Legitimate Software
Attackers employ various techniques to mask keyloggers as legitimate applications, making detection difficult. The keylogger’s presence is concealed to prevent suspicion.
- Bundling with legitimate software: A common technique involves bundling keyloggers with legitimate software downloads. The keylogger is hidden within the installer or setup files, often in inconspicuous locations. Users may download a seemingly harmless program, unaware of the malicious component embedded within. This is a significant threat as victims may not be aware of the additional software being installed.
Keylogger Bundling Examples
Keyloggers can be integrated into a wide variety of programs. Some examples include:
- Fake antivirus programs: These programs often contain keyloggers and may pose as legitimate security software. They promise to protect the user’s system but, in reality, collect sensitive information.
- Torrent clients: Keyloggers may be bundled with torrent clients or other file-sharing programs. Users may download and install a torrent client unknowingly installing a keylogger as well.
Keylogger Infection via Email Attachment
Malicious emails are a prevalent method for spreading keyloggers. The emails often mimic legitimate communications, making them difficult to detect.
- Email Attachment Infection: A user might receive an email containing a seemingly innocuous file, such as a document (.doc, .docx), an image (.jpg, .png), or even a compressed archive (.zip, .rar). This attachment may contain the keylogger. Opening the attachment executes the malicious code, infecting the system. The email may appear to be from a trusted contact or institution, increasing the likelihood of the user opening it.
The attachment could also contain a malicious link that redirects the user to a compromised website to download the keylogger. This method is often highly effective due to its subtlety and apparent legitimacy.
Detection Methods
Identifying a keylogger’s presence on a system is crucial for mitigating potential harm. Careful observation of system behavior and the use of appropriate detection tools can significantly increase the chances of uncovering malicious software. Early detection allows for swift remediation, preventing further data compromise.A keylogger, by its nature, aims to record keystrokes. Therefore, understanding the typical symptoms of a keylogger infection is vital.
These symptoms may range from subtle performance issues to overt indications of malicious activity. Recognizing these indicators is a critical step in proactive security management.
Signs Suggesting Keylogger Presence
Several indicators suggest a keylogger is active on a system. These signs can vary in their severity, ranging from minor performance glitches to more obvious red flags. Careful monitoring and analysis are essential in assessing the potential threat.
- Slow System Performance: A keylogger, especially resource-intensive ones, can cause noticeable slowdowns in system performance. This may manifest as sluggish response times, prolonged loading times for applications, or general sluggishness during typical operations.
- Unusual Pop-ups or Alerts: Unexpected pop-up windows, error messages, or security alerts can be a sign of a keylogger. These alerts can be disguised as legitimate system notifications, making them harder to spot.
- High Disk Activity: Keyloggers often generate log files, leading to increased disk activity. Observing unusually high disk activity, especially during periods of inactivity, can suggest a keylogger is operating.
- Suspicious Process Activity: Monitoring running processes can reveal hidden processes associated with keyloggers. Unfamiliar or unauthorized processes running in the background can indicate a potential infection.
- Increased Network Traffic: Certain keyloggers might transmit captured data over a network. Elevated network traffic, particularly during periods of normal inactivity, could suggest the presence of a keylogger.
Common Symptoms of Keylogger Infection
Recognizing common symptoms of keylogger infection is a vital aspect of proactive security. Identifying these patterns helps in recognizing and addressing potential threats.
- Unintentional Data Leakage: One of the most significant symptoms is unintentional data leakage. Users may notice sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details, being exposed or recorded without their knowledge.
- Compromised Confidentiality: A keylogger compromises the confidentiality of personal data. This includes sensitive information like financial details, personal identification numbers, and login credentials.
- Unauthorized Access: Keyloggers enable unauthorized access to sensitive information, potentially leading to identity theft or financial fraud.
Techniques to Detect Keyloggers
Various methods can help detect keyloggers on a system. These methods range from simple system monitoring to utilizing specialized anti-virus software. Employing a multi-faceted approach is often recommended for comprehensive protection.
- System Monitoring Tools: Dedicated system monitoring tools offer detailed insights into system activity. These tools can track process behavior, resource usage, and network traffic, providing valuable clues about potential keylogger activity.
- Anti-Virus Software: Anti-virus software plays a critical role in detecting and removing keyloggers. Regular scans and updates are essential to maintain effective protection against evolving threats.
- Security Audits: Performing periodic security audits can identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could allow keyloggers to infiltrate the system.
Comparison of Detection Tools
A comparative analysis of detection tools can highlight their strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific needs and resources of the user.
| Tool | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task Manager | Displays running processes | Simple, readily available | Limited detection capabilities, may not identify hidden processes |
| Process Explorer | Detailed process information | More comprehensive view of processes | Requires some technical knowledge to interpret |
| Anti-virus Software | Scan for known malware | Wide range of malware signatures | May miss zero-day or newly developed threats |
| Specialized Keylogger Detection Tools | Dedicated to identifying keyloggers | High accuracy in detecting keyloggers | May be more expensive, require expertise |
Indicators of Keylogger Infection
Recognizing indicators of keylogger infection is crucial for prompt remediation. A thorough understanding of these indicators can help mitigate potential risks.
- Unusually high disk space usage.
- Unusual network activity.
- Sudden performance slowdowns.
- Unexplained pop-ups or error messages.
- Hidden or unauthorized processes running in the background.
- Suspicious log files.
- Unexplained changes to system settings.
Prevention Measures: What Is A Keylogger And How To Detect It
Protecting yourself from keyloggers requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing cautious online behavior and robust security practices. A proactive stance against malicious software is crucial in mitigating the risk of keylogger infiltration. Implementing these preventative measures significantly reduces the likelihood of compromising your sensitive information.
Avoiding Malicious Software Downloads, What is a keylogger and how to detect it
A fundamental preventative measure against keyloggers is meticulous scrutiny of software downloads. Unverified sources are a significant risk factor. Carefully consider the origin and reputation of any software before installation. Always download from trusted and reputable websites. Verify the software’s authenticity and look for reputable reviews from verified sources.
Downloads from untrusted websites or file-sharing platforms can lead to the inadvertent installation of malicious software, including keyloggers. Exercise caution and vigilance when engaging in downloads.
Security Practices Against Keylogger Installation
Employing robust security practices is vital in safeguarding against keylogger installation. Employ strong passwords and avoid using easily guessable combinations. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection, requiring more than just a password for login. Regularly update your operating system and applications. Outdated software can contain vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit to install keyloggers.
Maintain up-to-date anti-virus and anti-malware software to detect and neutralize threats in real-time.
Importance of Strong Passwords and Regular Software Updates
Strong passwords are a cornerstone of online security. Avoid using easily guessable combinations, like birthdays or names. Use a combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols. Employ a password manager to create and store complex passwords securely. Regularly update software, including operating systems, applications, and security software.
Patches often address vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit to install keyloggers. This proactive approach significantly strengthens your digital defenses.
Best Practices for Safe Internet Browsing
Safe internet browsing involves vigilance and caution. Avoid suspicious websites or links, especially those that seem too good to be true. Be wary of unsolicited emails or messages containing attachments or links. Be skeptical of any requests for personal information or financial details. Use a virtual private network (VPN) when accessing public Wi-Fi networks to encrypt your connection and protect your data.
Exercise caution and awareness when interacting with online content.
Preventative Measures Table
| Category | Action | Rationale | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Download | Download software only from trusted and reputable websites. | Reduces the risk of downloading malicious software that may contain keyloggers. | Downloading software from the official website of the developer, not a third-party site. |
| Security Practices | Use strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication. | Makes it harder for attackers to gain access to your accounts and install keyloggers. | Using a unique, complex password for each online account and enabling two-factor authentication wherever possible. |
| Software Updates | Regularly update your operating system and applications. | Addresses vulnerabilities that could be exploited to install keyloggers. | Installing security patches and updates as soon as they are released. |
| Internet Browsing | Be cautious of suspicious websites and links, and avoid clicking on unsolicited emails. | Reduces the risk of visiting malicious websites that may attempt to install keyloggers. | Not clicking on links in spam emails or from unknown senders. |
Removal Strategies
Removing a keylogger from a compromised system requires a methodical approach. Failure to thoroughly address the infection can lead to persistent data breaches and potential security vulnerabilities. A proper removal strategy encompasses a complete system scan, targeted removal of malicious components, and, crucially, system restoration to ensure a clean slate.
System Scan and Removal Process
A comprehensive system scan is the first step in eliminating a keylogger. This involves utilizing various security tools to identify and isolate the malicious software. A thorough scan should cover all system files, registry entries, and potentially hidden processes. This multi-faceted approach is essential for locating all components of the keylogger, not just the primary executable.
Keylogger Removal Tools
Several tools can assist in removing keyloggers. These tools often employ advanced algorithms to detect and remove malicious code. Examples include:
- Malwarebytes Anti-Malware: A popular anti-malware tool known for its comprehensive scanning capabilities and ability to detect various threats, including keyloggers.
- Kaspersky Anti-Virus: Another widely used security suite that provides comprehensive scanning and removal of malware, including keyloggers. It offers real-time protection and regular updates to maintain efficacy.
- Microsoft Defender: A built-in security tool available on Windows systems, providing basic but effective malware detection and removal. While not as comprehensive as dedicated third-party tools, it offers a crucial first line of defense.
Step-by-Step Removal Guide
The following steps provide a structured approach to removing a keylogger:
- Isolate the System: Disconnect the infected system from the network to prevent further data breaches or potential spread of the keylogger. This crucial step isolates the compromised system from other devices, reducing the risk of additional infection.
- Boot into Safe Mode: Boot the computer into Safe Mode. This mode minimizes startup processes, making it less likely for the keylogger to interfere with the removal process.
- Run a Full System Scan: Employ a reputable anti-malware program to conduct a complete system scan, identifying and isolating malicious files and processes associated with the keylogger.
- Quarantine or Delete Malicious Files: Quarantine or delete the identified malicious files and folders, ensuring they are removed completely from the system. Carefully review any prompts or warnings during this step.
- Run a Registry Scan: Scan the Windows registry for any malicious entries or modifications related to the keylogger. Cleaning the registry can address keylogger functionality that might be hidden or persistent.
- Check for Associated Processes: Check for any processes related to the keylogger and terminate them. This step ensures the complete removal of any remaining components or hidden processes of the malware.
- Restart the System: Restart the system to ensure the changes take effect and to eliminate any lingering malicious components.
- Verify Removal: Conduct another scan with the anti-malware program to confirm the keylogger has been completely removed. A second scan will provide confirmation that no traces of the keylogger remain.
System Restoration Procedure
In cases of severe keylogger infection, restoring the system from a known good backup is highly recommended. This process reinstalls a previous, uninfected state of the system. The specific steps depend on the backup method used.
Legal Implications

Source: antivirusinsider.com
Keyloggers, while seemingly innocuous tools for monitoring computer activity, can have significant legal and ethical ramifications. Their use must be approached with careful consideration of the potential consequences, especially when employed without proper authorization. Understanding these implications is crucial for both users and developers to avoid legal trouble and maintain ethical standards.
Legal Ramifications of Keylogger Use
The use of keyloggers is governed by a complex web of laws, primarily focused on privacy, data protection, and unauthorized access. These laws vary across jurisdictions, but the underlying principles generally revolve around respecting individuals’ rights to privacy and controlling the collection and use of personal data.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Keylogger Use
Ethical considerations regarding keylogger use are equally crucial. The act of monitoring someone’s keystrokes without their explicit knowledge and consent is fundamentally a breach of trust and can lead to serious consequences, both personally and professionally. The inherent violation of privacy is a key ethical concern. The potential for misuse, ranging from simple snooping to more malicious actions like theft of confidential information, underscores the need for caution.
Laws Concerning Unauthorized Access and Data Collection
Privacy laws are designed to safeguard personal information and prevent unauthorized access. These laws, which vary across jurisdictions, typically prohibit the collection and use of personal data without the informed consent of the individual. Examples of such laws include the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
These regulations Artikel specific requirements for data collection, storage, and processing, which keylogger use must adhere to.
Potential Penalties for Keylogger Misuse
Misuse of keyloggers can lead to severe penalties, ranging from civil fines to criminal charges. The severity of the penalties depends on factors such as the nature of the data collected, the intent behind the use, and the applicable laws. Violation of privacy laws, unauthorized access, and potential harm to individuals can result in substantial legal repercussions. Examples include imprisonment, substantial fines, and reputational damage.
A company found to have misused keyloggers could face substantial financial penalties and damage to its reputation.
Keylogger Examples
Keyloggers, while often associated with malicious intent, can also have legitimate applications. These tools, when used appropriately, can aid in security audits or tracking user behavior for diagnostic purposes. However, their use without proper authorization and safeguards often crosses ethical boundaries and can lead to serious privacy violations. Understanding the diverse ways keyloggers are employed, both legitimate and malicious, is crucial for assessing their impact and potential risks.
Real-World Keylogger Examples
Various keyloggers exist, varying in sophistication and capabilities. Some are simple programs designed to record keystrokes on a specific machine, while others are sophisticated tools capable of stealing data across networks. Examples include:
- Commercial Keyloggers: Some companies provide legitimate keylogging tools for monitoring employee activity, ensuring compliance with regulations, and detecting potential security breaches. These often come with robust reporting features and user-friendly interfaces.
- Malware Keyloggers: These keyloggers are often bundled with other malware or downloaded through malicious websites. Their purpose is often to steal sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, and other confidential data. These keyloggers may be part of larger botnet operations, capable of affecting numerous systems simultaneously.
- Spyware Keyloggers: Designed to gather information without the user’s knowledge, spyware keyloggers are often installed surreptitiously. These can be used to monitor personal or corporate activity without consent, raising serious ethical and legal concerns.
Keylogger Targets and Motivations
Keyloggers can target a wide range of individuals and organizations, each with their own motivations. The potential damage caused by these tools varies greatly depending on the target and the malicious intent behind their use.
| Target | Motivation | Potential Use Case | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corporations | Intellectual property theft, competitive analysis, internal security breaches, or monitoring employee activities without consent | Stealing confidential documents, monitoring employee logins to discover leaks, or gaining insights into competitor strategies | Robust security measures, including strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, secure network protocols, and regular security audits. Employee training on cybersecurity best practices is crucial. |
| Individuals | Financial gain, identity theft, harassment, or extortion | Stealing login credentials for online banking, credit card details, or personal information for identity theft; tracking online activities to harass or blackmail. | Strong passwords, use of reputable websites, regular software updates, awareness of phishing scams, and cautious handling of personal information. |
| Government Agencies | Surveillance, monitoring political opponents, or gaining access to sensitive information | Monitoring communication, collecting data for intelligence gathering, or gaining access to classified information. | Robust data encryption, secure communication protocols, and strict adherence to legal and ethical guidelines. |
Last Recap
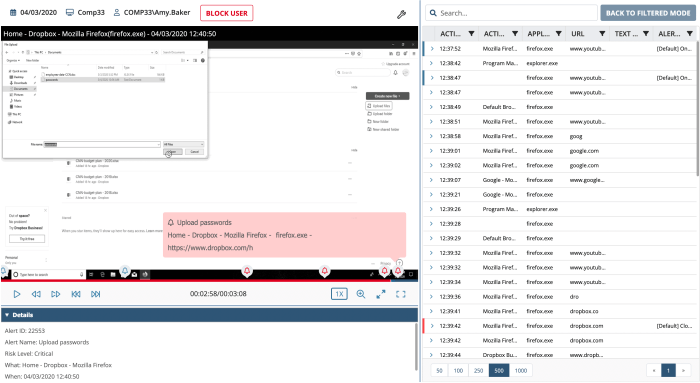
Source: ekransystem.com
In conclusion, keyloggers pose a significant security risk, but understanding their nature and employing effective detection and prevention strategies are essential. This guide has provided a thorough overview of keyloggers, from their definition and functionality to methods of installation, detection, and removal. By applying the insights shared, individuals and organizations can better safeguard their systems and data.













Post Comment