The Future Of High-Speed Internet And Its Effect On Computers
The Future of High-Speed Internet and Its Effect on Computers sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of how rapidly evolving internet technologies are reshaping the digital landscape. From groundbreaking advancements in fiber optics and 5G to the transformative potential of quantum computing, this discussion delves into the intricate interplay between internet speed and computing capabilities.
This exploration covers the broad spectrum of impacts, from the changing architecture of software to the evolving demands on data storage and security. The discussion also examines the anticipated shifts in user experience, including advancements in online gaming and streaming, and the potential for revolutionizing remote work and education.
Technological Advancements in High-Speed Internet

Source: boredpanda.com
High-speed internet has revolutionized communication and access to information, dramatically altering daily life. This evolution is driven by continuous technological advancements, pushing the boundaries of data transmission speed and capacity. From the early days of dial-up to the cutting-edge technologies of today, the journey has been marked by significant leaps forward.
Key Technological Advancements
The development of high-speed internet is a testament to human ingenuity. Several key technological breakthroughs have propelled its growth. These advancements span various fields, from fiber optic cable technology to sophisticated wireless protocols. The quest for ever-increasing bandwidth and reliability continues to fuel innovation.
Different Types of High-Speed Internet Technologies
Various technologies underpin modern high-speed internet access. Each technology offers unique characteristics in terms of speed, range, and application.
- Fiber Optics:
- 5G Wireless Technology:
- Satellite Internet:
Fiber optic cables transmit data as light pulses through thin strands of glass or plastic. This method boasts significantly higher bandwidth compared to traditional copper cables, enabling incredibly fast speeds. Fiber optic networks are the backbone of many modern high-speed internet deployments, particularly in urban areas.
5G wireless technology represents a significant leap forward in mobile internet access. It provides substantial improvements in speed and capacity over its predecessors, like 4G LTE. 5G is crucial for applications requiring high data rates, such as streaming high-definition video and online gaming. Its widespread deployment is expected to further enhance internet connectivity in diverse settings.
Satellite internet access provides connectivity in areas with limited or no terrestrial infrastructure. While generally slower than fiber optic or 5G, it offers a vital solution for remote locations. Advances in satellite technology are steadily improving speeds and reliability.
Innovative Technologies Expected to Enhance Internet Speed, The Future of High-Speed Internet and Its Effect on Computers
Emerging technologies promise to further enhance internet speed and accessibility.
- Lightwave Communications:
- Next-Generation Wireless Standards:
- Quantum Computing and Internet Infrastructure:
Research into lightwave communication systems is exploring novel ways to transmit data at even faster rates. These advancements aim to leverage the full potential of light for data transmission, potentially exceeding current fiber optic capabilities.
The development of 6G and beyond promises even greater speeds and capacity, addressing the demands of future applications and technologies. These innovations are expected to facilitate advancements in areas like augmented reality and virtual reality.
Quantum computing, though still in its nascent stages, has the potential to dramatically transform internet infrastructure. Quantum algorithms could enhance encryption, routing, and data processing, leading to significantly faster and more secure networks.
Comparative Speeds of High-Speed Internet Technologies
The table below provides a comparison of current and projected speeds for various high-speed internet technologies. Note that these are estimates and actual speeds may vary depending on factors like location and service provider.
| Technology | Current Speeds (Mbps) | Projected Speeds (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Optics | 100-1000+ | 1000+ – 10000+ |
| 5G | 100-1000+ | 1000+ – 10000+ |
| Satellite Internet | 10-100 | 100-1000+ (with advanced technology) |
Impact on Computing Devices
High-speed internet is rapidly reshaping the landscape of computing, driving significant transformations in personal computers and other devices. This evolution extends beyond mere speed improvements, impacting the very architecture and functionality of how we interact with technology. The increased bandwidth empowers new applications and functionalities, fundamentally altering the role of computing devices in our lives.The transformative effect of high-speed internet extends beyond simple speed enhancements.
It fosters a new paradigm in how we approach computing, influencing everything from the way we interact with software to the very design of hardware. This profound impact underscores the crucial role of high-speed internet in shaping the future of computing.
Transformation of Personal Computers
Personal computers, once the cornerstone of individual computing, are undergoing a multifaceted transformation. The enhanced capabilities of high-speed internet enable more demanding applications, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible on desktop and laptop systems. This includes the seamless integration of cloud services, the utilization of advanced graphical processing units (GPUs) for demanding tasks, and the increased reliance on high-performance storage solutions.
Modern PCs are increasingly being used as hubs for managing and interacting with data stored in the cloud.
Evolving Role of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is experiencing a surge in importance due to high-speed internet. The accessibility and scalability of cloud resources are crucial for facilitating collaborative projects, supporting complex data analysis, and providing readily available computing power. Cloud services, now integrated into virtually every facet of modern computing, are no longer an optional add-on but a fundamental part of the computing experience.
This integration streamlines workflow and facilitates data access from virtually any location.
Increased Processing Power in Devices
High-speed internet facilitates the transfer of data and instructions required for complex computations, leading to increased processing power in connected devices. This capability allows for more sophisticated software and applications, enabling real-time processing and sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) models to be implemented directly on devices. Modern smartphones and laptops are demonstrating this increased processing power with the execution of tasks that were previously only possible on more powerful servers.
Software Architecture Changes
High-speed internet necessitates adjustments to software architecture. Applications are increasingly designed with cloud-based components, enabling seamless data sharing and processing. This necessitates a shift in focus from locally-stored data to cloud-based repositories, requiring software to be more efficient in managing remote resources and handling high-volume data transfers. Modern software is designed with a greater emphasis on cloud connectivity and data synchronization.
Impact on Different Computer Types
| Computer Type | Impact of High-Speed Internet |
|---|---|
| Desktops | Enhanced ability to handle demanding tasks, seamless cloud integration for data storage and processing, and more powerful graphics processing. |
| Laptops | Improved responsiveness and efficiency for tasks requiring frequent data transfer and cloud-based processing, greater mobility with seamless access to cloud-based applications. |
| Mobile Devices | Greater access to cloud-based applications and services, faster data transfer speeds for seamless communication and entertainment, more efficient use of mobile computing resources, supporting complex applications through cloud computing. |
Data Handling and Storage: The Future Of High-Speed Internet And Its Effect On Computers

Source: ctvforme.com
High-speed internet has dramatically increased the volume and velocity of data generated, processed, and transmitted. This necessitates a significant evolution in data storage solutions to accommodate the ever-growing digital footprint. The demand for faster access to this data, coupled with the need for reliable and secure storage, drives innovation in the field. This section will delve into the challenges and opportunities presented by these advancements.Current data storage technologies face limitations in scalability and speed to keep pace with the escalating data deluge.
The capacity and accessibility of storage systems need to be dramatically improved to accommodate the exponentially growing data volume generated by high-speed internet services. This includes everything from user-generated content to machine-learning models and massive datasets in scientific research.
Increasing Demands on Data Storage Solutions
The exponential growth of data, fueled by high-speed internet, places unprecedented demands on storage solutions. This includes the need for higher capacity, faster access times, and enhanced reliability. Consider the sheer volume of online video streaming, social media posts, and the constant generation of data by various IoT devices. This flood of information necessitates robust storage infrastructure capable of handling terabytes, petabytes, and even exabytes of data.
Comparison of Current and Future Data Storage Technologies
Current data storage technologies encompass a range of solutions, including hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and cloud storage. HDDs offer relatively high capacity but slower access speeds, while SSDs provide faster access but lower capacity. Cloud storage offers scalability and accessibility but often depends on network bandwidth and latency. Future technologies, such as non-volatile memory express (NVMe) storage, offer even faster access speeds and lower latency.
Further innovations, such as holographic storage and quantum computing-assisted storage, hold the promise of significantly higher capacities and faster access. The shift towards cloud-based storage solutions will continue, driven by the need for scalability and the flexibility they provide.
Potential Security Concerns
The increased flow of data necessitates robust security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. Data breaches can have devastating consequences for individuals and organizations, resulting in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. The rise of sophisticated cyberattacks necessitates the development of advanced encryption methods, secure data transmission protocols, and improved intrusion detection systems.
Data encryption and access controls are paramount in safeguarding the growing volume of sensitive data.
Impact on Data Center Design
High-speed internet significantly affects the design of data centers. The need for high bandwidth connectivity, redundancy, and cooling solutions is paramount. Modern data centers are designed with advanced cooling systems, redundant power supplies, and highly efficient network infrastructure to handle the enormous volume of data traffic. This requires substantial investment in infrastructure and expertise in managing complex systems.
Evolution of Data Storage Methods
| Storage Method | Capacity (approx.) | Access Speed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Tape | Terabytes | Slow | Historically high capacity, but slow access |
| Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) | Terabytes | Moderate | Common storage for large volumes of data |
| Solid State Drives (SSDs) | Terabytes to Petabytes | Fast | Faster access than HDDs, higher cost per gigabyte |
| Cloud Storage | Petabytes to Exabytes | Variable | Scalable, accessible, but dependent on network |
| NVMe Storage | Petabytes | Very Fast | High-performance storage for demanding applications |
The table above provides a glimpse into the evolution of data storage technologies. The increasing capacities and speeds are directly linked to the demands of high-speed internet.
Effects on User Experience
High-speed internet fundamentally reshapes the user experience across various online activities. The improved bandwidth and reduced latency enable more seamless and engaging interactions, transforming how we consume content and interact with digital services. This enhanced experience is particularly noticeable in applications demanding high data throughput, such as online gaming and streaming.The evolution of high-speed internet significantly alters the user experience, offering a level of responsiveness and fluidity previously unimaginable.
This increased responsiveness translates to a more immersive and engaging online environment, impacting everything from simple web browsing to complex online interactions.
Changes in User Experience
High-speed internet facilitates a remarkable shift in user experience, characterized by faster loading times, reduced buffering, and smoother transitions between online content. This enhanced responsiveness is a crucial factor in elevating the overall user experience, making online interactions more intuitive and enjoyable.
Influence on Online Gaming and Streaming Services
High-speed internet dramatically enhances online gaming and streaming experiences. Lower latency allows for more precise controls and real-time interactions in online games, improving the overall gameplay experience. Similarly, streaming services benefit from the reduced buffering, enabling seamless video playback, reducing interruptions and enhancing the overall viewing experience. Examples include the ability to stream high-definition content without noticeable lag or interruptions.
Impact on Different User Groups
The impact of high-speed internet varies among user groups. Students benefit from faster access to educational resources and online learning platforms, accelerating their learning process. Professionals gain access to sophisticated collaborative tools and communication platforms, enhancing productivity and efficiency in their work. The benefits extend to everyday users, who experience more seamless browsing, faster downloads, and improved access to entertainment and information.
Improvements in Communication and Collaboration
High-speed internet significantly improves communication and collaboration. Video conferencing platforms become more effective with lower latency, enabling more natural and engaging interactions. Cloud-based document sharing and collaboration tools operate more efficiently, promoting real-time feedback and seamless teamwork. Instant messaging and social media interactions are enhanced with reduced delays and faster responses.
Table Illustrating Improvements in Online Experiences
| Online Experience | Improvement with High-Speed Internet |
|---|---|
| Web browsing | Faster loading times, smoother transitions, and enhanced responsiveness. |
| Online gaming | Lower latency, improved precision in controls, and more immersive gameplay. |
| Streaming services | Seamless video playback, reduced buffering, and improved viewing experience. |
| Video conferencing | More natural and engaging interactions due to lower latency. |
| Document sharing | More efficient real-time collaboration and feedback. |
Future Applications and Possibilities
High-speed internet, with its increasing bandwidth and lower latency, is poised to revolutionize numerous sectors. This transformative power extends far beyond simple browsing and downloading; it’s poised to fundamentally reshape the landscape of artificial intelligence, virtual reality, remote work, education, entertainment, and social interaction. The potential for innovation and progress is vast and exciting.
Impact on Artificial Intelligence
The demands of AI algorithms are immense, requiring significant computational power and data transfer. High-speed internet enables quicker training of complex AI models by facilitating rapid data exchange between servers and processing units. This allows for more sophisticated machine learning, leading to advancements in areas like image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics. The increased speed allows for the development of more powerful and efficient AI systems, enabling them to perform tasks previously considered impossible or impractical.
Enhanced Virtual and Augmented Reality Experiences
High-speed internet is critical for the seamless delivery of immersive VR and AR experiences. The transmission of high-resolution visuals, complex 3D models, and real-time interactions requires extremely low latency connections. This translates to smoother, more responsive experiences, allowing users to interact with virtual environments and augmented realities in a more intuitive and engaging way. Users will be able to experience richer, more detailed, and more responsive virtual worlds.
Revolutionizing Remote Work and Education
High-speed internet significantly improves the efficacy of remote work and learning. Remote collaboration tools, video conferencing platforms, and cloud-based applications all rely on fast, reliable internet connections. The improved connectivity allows for more fluid and effective communication between geographically dispersed teams and enables high-quality virtual classrooms. The quality of remote work and learning will improve with seamless access to resources and interactions.
Impact on Entertainment and Social Interaction
High-speed internet fosters a richer entertainment landscape. Streaming services can offer more high-definition content and lower latency, allowing for smoother gameplay and real-time interaction in online games. Social interaction will also benefit, as faster internet connections enable more immersive and interactive experiences. For instance, virtual concerts and social events can become more realistic and engaging. These improvements in speed and connectivity will enable more immersive and realistic entertainment and social experiences.
Potential Uses in Various Sectors
| Sector | Potential Uses |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, telemedicine, faster drug discovery |
| Manufacturing | Real-time data analysis for production optimization, remote maintenance and control of machinery, improved supply chain management |
| Finance | Faster transaction processing, improved fraud detection, real-time market analysis, enhanced customer service |
| Education | Interactive online learning platforms, virtual classrooms, access to global resources, personalized learning experiences |
| Entertainment | High-definition streaming, immersive virtual reality experiences, interactive games, live virtual events |
Societal and Economic Implications
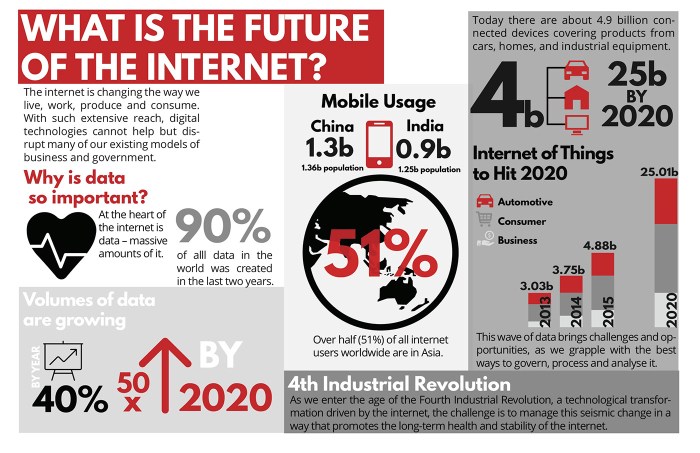
Source: behance.net
High-speed internet is no longer a luxury but a necessity in the modern world. Its widespread adoption has profound effects on various aspects of society and the economy, presenting both opportunities and challenges. This section will explore the potential economic benefits, social implications for different demographics, challenges in ensuring equitable access, effects on global connectivity, and the potential impact on various industries.
Economic Benefits of High-Speed Internet Infrastructure
The rollout of high-speed internet infrastructure can stimulate economic growth across numerous sectors. Improved communication and collaboration enhance productivity in businesses, fostering innovation and expansion. Remote work opportunities become more viable, leading to a wider talent pool and reduced commuting costs. E-commerce flourishes, creating new markets and employment opportunities. Furthermore, increased efficiency in various industries, such as healthcare and manufacturing, can contribute to cost savings and improved service delivery.
Social Implications of High-Speed Internet Access for Different Demographics
High-speed internet access profoundly impacts different demographics. For example, it empowers individuals in underserved communities by providing access to educational resources, job opportunities, and social networks. It can bridge the digital divide, enabling greater participation in the global economy and society. However, it’s important to acknowledge the potential for widening existing inequalities if access isn’t equitably distributed.
The elderly and individuals with disabilities may require tailored support to leverage the benefits of high-speed internet effectively.
Challenges in Ensuring Equitable Access to High-Speed Internet
Ensuring equitable access to high-speed internet remains a significant challenge. Geographic limitations, economic disparities, and digital literacy gaps create barriers for certain communities and individuals. Infrastructure development in rural areas, affordability of devices and services, and training programs are crucial for bridging the digital divide. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving public-private partnerships and government initiatives.
Effects on Global Connectivity
High-speed internet facilitates seamless global communication and collaboration. Businesses can operate across borders more efficiently, facilitating international trade and investment. Individuals can connect with others worldwide, fostering cultural exchange and understanding. This enhanced connectivity can potentially lead to greater global awareness and cooperation in addressing shared challenges. However, concerns about data security, privacy, and the potential for misinformation also need to be addressed.
Potential Impact on Different Industries and Sectors
The following table illustrates the potential impact of high-speed internet on various industries and sectors. It highlights the opportunities and challenges presented by this transformative technology.
| Industry/Sector | Potential Benefits | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Improved access to online learning resources, personalized education, and virtual classrooms, fostering greater learning opportunities. | Digital divide disparities, teacher training needs, and ensuring equitable access to technology and resources. |
| Healthcare | Remote consultations, telemedicine, access to medical data, and improved patient care, leading to more efficient and accessible healthcare systems. | Data security and privacy concerns, digital literacy of healthcare professionals, and the need for robust online security protocols. |
| Retail | E-commerce growth, personalized shopping experiences, global market access, and increased efficiency in supply chains. | Competition, security breaches, and maintaining trust in online transactions. |
| Finance | Online banking, investment opportunities, global financial transactions, and improved efficiency in financial services. | Cybersecurity risks, data breaches, and ensuring financial inclusion. |
| Manufacturing | Remote monitoring, automation, improved supply chain management, and increased productivity through connected devices. | Cybersecurity vulnerabilities, skills gaps, and maintaining data integrity. |
Last Word
In conclusion, the future of high-speed internet promises a profound transformation in how we interact with computers and the world around us. The convergence of technological advancements, evolving computing needs, and ever-increasing data demands will shape a future with unparalleled connectivity and accessibility. The implications extend across industries and sectors, impacting everything from entertainment to education and work.













Post Comment