How 5g Impacts Computer Internet Speed And Performance
How 5G Impacts Computer Internet Speed and Performance is a deep dive into the revolutionary effects of 5G technology on our digital experiences. This cutting-edge cellular network promises a paradigm shift in data transmission rates and responsiveness, significantly impacting how we browse the web, game online, and conduct real-time activities. We’ll explore the technical underpinnings of 5G, examining its key differences from previous generations and the resulting performance enhancements.
From the enhanced bandwidth and reduced latency of 5G, to the implications for network infrastructure and equipment, this discussion unravels the intricate connection between 5G and the speed and performance of your computer internet. We’ll also address factors beyond the network itself, including computer hardware and software configurations, to provide a holistic understanding of the 5G impact.
Introduction to 5G Technology
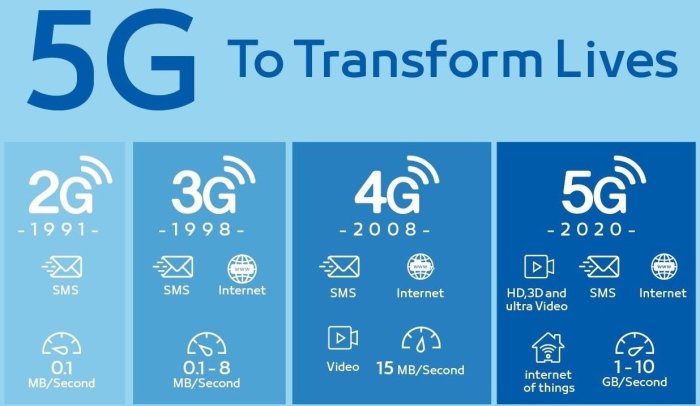
Fifth-generation (5G) cellular technology represents a significant advancement in mobile communications, surpassing previous generations in speed, capacity, and low latency. It offers a more responsive and reliable connection for a wider range of applications, from everyday internet use to sophisticated industrial automation.G technology fundamentally alters how we interact with the digital world by offering significantly enhanced connectivity and performance.
It builds upon the foundations of previous generations, yet incorporates groundbreaking innovations in its architecture and technical specifications. This allows for unprecedented speeds, lower latency, and higher network capacity, which will greatly influence the internet speed and performance of computers.
Key Features and Capabilities of 5G
G boasts several key features that distinguish it from its predecessors. These features enable faster data transmission, lower latency, and a greater number of connected devices. The improved efficiency in data transmission is critical for handling the growing demands of modern applications and services.
Differences Between 5G and Previous Generations
G differs from 4G and earlier generations primarily in its enhanced radio access technology and core network architecture. 4G networks rely on a single frequency band, whereas 5G utilizes multiple frequency bands, enabling much higher data rates and network capacity. The core network architecture of 5G is more adaptable to handle the diverse and demanding requirements of modern applications.
Furthermore, 5G utilizes more sophisticated protocols for handling massive data volumes and many concurrent connections.
Technical Specifications of 5G
G’s technical specifications contribute to its enhanced performance. These specifications include the use of new radio access technologies, such as millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies and massive MIMO antenna arrays. These technologies allow for significantly higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to previous generations. Furthermore, 5G incorporates more efficient signal processing techniques, resulting in improved performance and reduced interference.
Comparison of Key 5G Parameters, How 5G Impacts Computer Internet Speed and Performance
The following table highlights the key performance differences between 5G and its predecessors.
| Parameter | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | Typically 10-20 MHz | Can utilize up to 100 MHz or more, including mmWave bands |
| Latency | Around 20-40 milliseconds | Sub-10 milliseconds, in some cases down to a few milliseconds |
| Data Rates | Up to several hundred megabits per second (Mbps) | Gigabits per second (Gbps) |
| Network Capacity | Limited capacity for handling a large number of devices | High capacity to handle many connected devices simultaneously |
Impact on Data Transmission Rates
G networks represent a significant leap forward in mobile data transmission, offering substantial improvements over previous generations. This enhancement translates directly to faster internet speeds and more responsive online experiences. The key drivers behind these improvements lie in 5G’s increased bandwidth and reduced latency.The enhanced bandwidth capacity of 5G allows for greater amounts of data to be transmitted simultaneously, leading to substantially faster download and upload speeds.
Lower latency, or the delay between sending and receiving data, further improves the responsiveness of online activities. This responsiveness is particularly noticeable in real-time applications, such as online gaming and video conferencing.
Methods for Measuring Data Transfer Rate Increases
Accurate measurement of 5G’s impact on data transfer rates is crucial for assessing its effectiveness. Several methods are employed to quantify the increase in data transfer rates with 5G, including specialized network testing tools and real-world user trials. These tools measure the speed at which data is transmitted over the network, including download and upload speeds. A variety of metrics are used, such as bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (kbps), megabits per second (mbps), and gigabits per second (gbps).
Sophisticated protocols are used to precisely measure the throughput and latency under different network conditions.
Average Download Speeds on Different Networks
Significant improvements in download speeds are anticipated with 5G, compared to 4G and 3G networks. The following table provides a general comparison of average download speeds across these generations of mobile networks in various regions. It’s important to note that actual speeds can vary significantly based on factors like location, network congestion, and device capabilities.
| Network Generation | Average Download Speed (Mbps)
|
Average Download Speed (Mbps)
|
Average Download Speed (Mbps)
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 5G | 150-300 | 100-250 | 120-280 |
| 4G | 30-80 | 20-70 | 25-75 |
| 3G | 3-10 | 2-8 | 3-9 |
Note: These are estimated averages and actual speeds may differ. Factors such as network congestion, device capabilities, and location influence the observed download speeds.
Influence on Latency and Response Time: How 5G Impacts Computer Internet Speed And Performance

Source: techrayzer.com
G’s impact extends beyond simply increasing data transmission rates. A crucial aspect of the technology is its ability to drastically reduce latency, the time delay between an action and its response. This characteristic significantly enhances user experiences in various applications, particularly those requiring immediate feedback. Lower latency translates to faster responses, smoother interactions, and ultimately, a more satisfying digital experience.
Impact on Real-Time Applications
G’s low latency is a game-changer for real-time applications. This characteristic allows for near-instantaneous responses, making applications feel more responsive and interactive. The reduction in delay is especially noticeable in online gaming, video conferencing, and other applications that demand a quick turnaround time.
Influence on Online Gaming
Online gaming experiences are greatly enhanced by 5G’s reduced latency. Players experience smoother gameplay, with reduced lag and quicker responses to actions. This results in a more immersive and engaging gaming experience, allowing for more fluid movement and reactions. The minimized delay in data transmission enables more precise control over in-game actions.
Enhancement of User Experience in Online Video Conferencing
Reduced latency is pivotal for high-quality video conferencing. With 5G, participants experience significantly improved video and audio quality, minimizing delays and interruptions during calls. This results in a more seamless and natural communication experience, as if participants were in the same room. The near-instantaneous transmission of data allows for real-time interactions, including immediate feedback during discussions.
Impact on Applications Requiring Immediate Responses
Applications requiring rapid responses, such as online shopping or stock trading, benefit greatly from 5G’s low latency. The faster response times translate to quicker order confirmations, faster transaction processing, and minimized delays in receiving market data. This is crucial in high-stakes environments, where even a few milliseconds of delay can have significant consequences. Real-time information updates contribute to better decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
Comparison of Latency Measurements Across Cellular Generations
| Cellular Generation | Typical Latency (ms) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2G | >100 ms | Significant delays were common in 2G networks, making real-time applications impractical. |
| 3G | >100 ms | 3G networks offered some improvement, but real-time applications still experienced considerable delays. |
| 4G | >20 ms | 4G networks represented a notable step forward, enabling smoother video streaming and some real-time interactions. |
| 5G | <10 ms | 5G significantly reduces latency, making real-time applications and interactions far more responsive. |
The table above illustrates the substantial reduction in latency achieved by 5G compared to previous generations. This improvement is directly attributable to advancements in network infrastructure and technologies, such as more efficient signal processing and optimized network architecture. The lower latency offered by 5G paves the way for a more interactive and responsive digital landscape.
Impact on Network Infrastructure and Equipment
The transition to 5G necessitates significant upgrades to existing network infrastructure and equipment. This involves not only replacing components but also reconfiguring the overall network architecture to accommodate the higher data rates, lower latency, and increased capacity demanded by 5G. This transformation ensures a seamless integration of 5G services into the existing telecommunications landscape.Existing 4G networks, while functional, often struggle to handle the massive data volumes and stringent latency requirements of 5G.
The new network infrastructure must be robust enough to handle the increased demands. This includes improved signal coverage and capacity, optimized network management, and a reliable system for managing the complex interactions between different network elements.
Changes Needed in Existing Network Infrastructure
To effectively support 5G, the existing network infrastructure needs substantial modifications. This includes the deployment of new radio access network (RAN) components, upgrades to core network infrastructure, and enhancements in backhaul capacity. The implementation of small cells, strategically positioned to improve signal strength and coverage, is also critical. These small cells, often deployed in densely populated areas, address the limitations of traditional cell towers.
The improved coverage significantly enhances the user experience by minimizing signal degradation.
Upgrades to Existing Equipment
Upgrading existing equipment, such as routers and modems, is another crucial aspect of the 5G transition. Modern 5G-compatible equipment is designed to handle the unique characteristics of 5G signals. These advancements facilitate the seamless integration of 5G into the existing network architecture. Furthermore, these devices incorporate advanced signal processing capabilities to handle the complex communication protocols of 5G.
Technical Requirements for 5G Network Deployment
The successful deployment of a 5G network hinges on several key technical requirements. Firstly, high-bandwidth backhaul connections are essential to facilitate the rapid transfer of data between network components. Secondly, efficient spectrum allocation is crucial to ensure optimal use of available radio frequencies. The deployment of new antennas and the optimization of existing infrastructure are crucial aspects to ensure robust and reliable coverage.
Types of 5G Antennas and Their Applications
| Antenna Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Panel Antennas | These antennas are characterized by their flat, rectangular design. | Wide-area coverage, especially in urban environments. |
| Sectorial Antennas | Sectorial antennas are designed to focus signal transmission in a specific direction. | Targeted coverage in particular areas, such as highways or stadiums. |
| Patch Antennas | Patch antennas are known for their compact size and low profile. | Small cell deployments, especially in densely populated areas. |
| Phased Array Antennas | Phased array antennas utilize multiple antenna elements to steer the signal beam dynamically. | Enhanced beamforming, resulting in improved signal quality and reduced interference. |
Different antenna types are suited to diverse applications, ranging from providing comprehensive coverage to focusing signals on specific locations. The choice of antenna depends on the specific needs of the deployment.
Factors Affecting Computer Internet Performance
Beyond the advancements in 5G technology, numerous factors influence a computer’s internet speed and performance. These factors extend beyond the network itself, encompassing the computer’s internal capabilities, software configurations, and even external network conditions. Understanding these elements is crucial for optimizing internet usage and troubleshooting connectivity issues.
Computer Hardware Influence
Computer hardware plays a significant role in internet performance. A faster processor, for example, can handle more data efficiently, leading to quicker loading times for web pages and applications. Likewise, the amount of Random Access Memory (RAM) available directly impacts how smoothly a computer can manage multiple tasks, including internet browsing, streaming, and downloading. Insufficient RAM can cause sluggish performance and slow internet speeds.
The type of hard drive, whether solid-state drive (SSD) or traditional hard disk drive (HDD), also affects data transfer speeds. SSDs generally offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs, resulting in quicker loading times for files and applications, which in turn can enhance internet performance.
Software Configuration Impact
Software configurations, including browser settings and network drivers, can significantly affect internet speed. Outdated or improperly configured network drivers can lead to connectivity problems and slowdowns. Similarly, browser settings, such as cache size and cookie management, can impact performance. Over time, browser caches can become bloated, hindering loading times. Moreover, improperly configured security software can sometimes interfere with network communication, reducing overall internet speed.
Network Congestion Effects
Network congestion, often caused by high user traffic or faulty network infrastructure, can dramatically reduce internet speed. When too many users try to access the same network resources simultaneously, the network’s capacity becomes overwhelmed. This can result in slower loading times, dropped connections, and overall reduced internet performance. Factors such as the time of day, geographic location, and even the popularity of a website can contribute to network congestion.
For instance, during peak hours, the internet traffic on a shared network may become congested, resulting in slower speeds for all users. Network congestion is a significant challenge, particularly in areas with limited network infrastructure or during periods of high internet usage.
Real-World Scenarios and Case Studies
Real-world demonstrations of 5G’s impact on internet speed and performance are becoming increasingly common. These examples often highlight the significant leap forward in data transmission rates and reduced latency compared to previous generations. The improvements are particularly noticeable in applications demanding rapid data exchange.
Impact on Gaming Performance
G’s lower latency is demonstrably beneficial for online gaming. Players experience reduced lag, leading to smoother gameplay and more responsive controls. This is particularly noticeable in real-time multiplayer games where milliseconds can determine the outcome of a match. A noticeable example is the reduced lag time in online multiplayer gaming experiences. Users are experiencing faster loading times for game content and a more fluid, responsive experience.
Enhanced Video Streaming Experience
The high bandwidth capabilities of 5G enable seamless high-definition video streaming. Users can enjoy uninterrupted video playback without buffering or lag, even in congested network environments. This is a substantial improvement over 4G, where buffering was a common occurrence. A notable example is the capability to stream 8K video content without interruptions. The smooth playback of high-definition video content demonstrates the superior performance characteristics of 5G networks.
Improved Mobile Data Speeds for File Transfers
G significantly speeds up file transfers, a key factor for individuals and businesses alike. The high data rates allow for quick downloads and uploads of large files, such as videos, software, or documents. The faster download and upload speeds for large files exemplify the advantages of 5G technology.
5G vs. Previous Generations in Specific Applications
| Application | 5G Performance Improvement | 4G Performance ||——————–|—————————|—————–|| Online Gaming | Reduced lag, smoother gameplay | Lag, less responsive controls || Video Streaming | Uninterrupted HD playback | Buffering, lag, lower resolution options || File Transfers | Significantly faster downloads/uploads | Slow downloads/uploads || Mobile Data Usage | Increased capacity and speed | Limited capacity and speed |
Future Trends and Potential Developments
The evolution of 5G technology is poised to significantly reshape internet speed and performance. Anticipated advancements promise substantial improvements in data transmission rates, reduced latency, and enhanced network infrastructure, ultimately impacting internet usage across diverse applications. This section explores the potential future trends and developments in 5G, along with their implications for internet performance.
Anticipated Advancements in 5G Technology
Future iterations of 5G are expected to leverage innovative technologies to further enhance data transmission capabilities. These advancements are crucial to satisfying the ever-increasing demands for high-speed internet access and low-latency applications.
- Enhanced Spectrum Utilization: 5G networks will likely explore new frequency bands and utilize existing ones more efficiently. This enhanced spectrum utilization can significantly increase the available bandwidth for data transmission, resulting in faster speeds and lower latency. For instance, the utilization of millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum has the potential to drastically improve peak data rates.
- Improved Network Infrastructure: The development of more sophisticated and distributed network infrastructure, including small cells and edge computing, will play a vital role in supporting future 5G applications. This distributed architecture will improve coverage, reduce latency, and enable seamless connectivity in densely populated areas.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Future 5G networks are likely to integrate with other emerging technologies like satellite communication, enhancing coverage and extending the reach of 5G services to remote areas. This integration will be instrumental in providing reliable and consistent internet access in areas previously underserved by terrestrial networks.
Theoretical Advancements and Their Impacts
Several theoretical advancements in 5G technology hold significant promise for further enhancing internet performance. These innovations could lead to even faster data transmission and improved network efficiency.
- Massive MIMO: This technology, which employs multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver, enables a significant increase in the capacity and throughput of 5G networks. Massive MIMO allows for simultaneous data transmission to multiple users, enhancing network efficiency and enabling high-speed internet access for more users.
- Network Slicing: Network slicing allows for the creation of dedicated virtual networks with tailored performance characteristics for specific applications. This approach enables tailored configurations for different services, from gaming to video streaming, leading to improved quality of service (QoS) and more responsive internet experiences. This feature is particularly useful for time-sensitive applications.
- Advanced Coding Techniques: The development and implementation of advanced coding schemes will likely enhance the reliability and efficiency of data transmission in 5G networks. These advancements can significantly reduce data errors and improve data integrity, contributing to a more stable and reliable internet experience.
Future Impact on Internet Usage and Applications
The potential improvements in 5G technology will likely reshape internet usage patterns and accelerate the adoption of various applications.
- Enhanced Mobile Gaming: Lower latency and higher speeds in 5G networks will enable more immersive and responsive mobile gaming experiences, reducing lag and improving overall gameplay. The ability to stream high-quality graphics and sound at high speeds will be critical to this advancement.
- Advancements in Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR applications will benefit from the low latency and high bandwidth offered by 5G. This will create more realistic and engaging experiences, enabling users to interact with virtual environments and augmented realities in a more responsive and seamless manner.
- Expansion of IoT Applications: The high reliability and low latency of 5G will unlock the potential of Internet of Things (IoT) applications, allowing for more complex and demanding IoT deployments. This includes applications in smart cities, industrial automation, and healthcare.
Last Point
Source: digitbin.com
In conclusion, 5G’s impact on computer internet speed and performance is profound and multifaceted. While the technology presents significant advantages in data transfer rates and responsiveness, it also necessitates upgrades to existing infrastructure. Ultimately, 5G is poised to reshape the digital landscape, transforming how we interact with the internet and opening doors to a future of seamless, high-speed connectivity.
The future of internet performance is intrinsically linked to 5G’s development and implementation.













Post Comment